Abstract
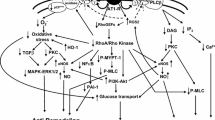
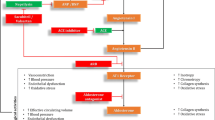
Insights into the Angiotensin II (Ang II) signalling pathways have been provided by extensive studies using Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes patients. These syndromes are characterized by activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system but do not develop hypertension and cardiovascular remodelling, therefore represent a mirror image of hypertension and clinically manifest themselves as the opposite of hypertension. The short and the long-term signalling of Ang II remain an important matter of investigation to shed light on mechanisms responsible for the pathophysiology of hypertension and its long-term complications, such as cardiovascular remodelling and atherogenesis. In particular the long-term signalling of Ang II is involved in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular-renal remodelling, inflammatory and hypertrophic responses in which the relationship between RhoA/Rho kinase pathway and NO system plays a crucial role. This review reports the results of our studies in Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes to get better insight these processes and the role of Ang II signaling. The information obtained from the studies in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s patients can, in fact, clarify, confirm or be used to gather more general data on the biochemical mechanisms responsible for the pathophysiology of hypertension and its long-term complications and could contribute to identify additional potential significant targets of therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehta PK, Griendling KK. Angiotensin II cell signaling. Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;92:C82–97.
Nguyen Dinh Cat A, Touyz RM. Cell signaling of angiotensin II on vascular tone: novel mechanisms. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011;13:122–8.
Dzau VJ, Lopez-Ilasaca M. Searching for transcriptional regulators of Ang II induced vascular pathology. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2319–22.
Benigni A, Corna D, Zoja C, Sonzogni A, Latini R, Salio M, Conti S, Rottoli D, Longaretti L, Cassis P, Morigi M, Coffman TM, Remuzzi G. Disruption of the Ang II type 1 receptor promotes longevity in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:524–30.
Calò L, D’Angelo A, Cantaro S, Rizzolo M, Favaro S, Antonello A, Borsatti A. Intracellular calcium signalling and vascular reactivity in Bartter’s syndrome. Nephron. 1996;72:570–3.
Calò LA, Schiavo S, Davis PA, Pagnin E, Mormino P, D’Angelo A, Pessina AC. Angiotensin II signaling via type 2 receptors in a human model of vascular hyporeactivity: implications for hypertension. J Hypertens. 2010;28:111–8.
Calò LA, Davis PA, Rossi GP. Understanding the mechanisms of angiotensin II signaling involved in hypertension and its long-term sequelae: insights from Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes, human models of endogenous angiotensin II signaling antagonism. J Hypertens. 2014;32:2109–19.
Bartter FC, Pronove P, Gill JR, Maccardle RC. Hyperplasia of the juxtaglomerular complex with hyperaldosteronism and hypokalemic alkalosis. Am J Med. 1962;33:811–28.
Naesens M, Steels P, Verberckmoes R, Vanrenterghem Y, Kuypers D. Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes: From gene to clinic. Nephron Physiol. 2004;96:65–78.
Simon DB, Karet FE, Hamdan JM, DiPietro A, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP. Bartter’s syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nat Genet. 1996;13:183–8.
Simon DB, Karet FE, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Hamdan JH, DiPietro A, Trachtman H, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP. Genetic heterogeneity of Bartter’s syndrome revealed by mutations in the K+ channel, ROMK. Nat Genet. 1996;14:152–6.
Simon DB, Bindra RS, Mansfield TA, Nelson-Williams C, Mendonca E, Stone R, Schurman S, Nayir A, Alpay H, Bakkaloglu A, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Morales JM, Sanjad SA, Taylor CM, Pilz D, Brem A, Trachtman H, Griswold W, Richard GA, John E, Lifton RP. Mutation in the chloride channel gene CLCNKB cause Bartter’s syndrome type III. Nat Genet. 1997;17:171–9.
Gitelman HJ, Graham JB, Welt LG. A new familial disorder characterized by hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Trans Assoc Am Phys. 1966;79:221–35.
Bettinelli A, Tosetto C, Colussi G, Tommasini G, Edefonti A, Bianchetti MG. Electrocardiogram with prolonged QT interval in Gitelman disease. Kidney Int. 2002;62:580–4.
Scognamiglio R, Calò LA, Negut C, Coccato M, Mormino P, Pessina AC. Myocardial perfusion defects in Bartter and Gitelman syndromes. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008;38:888–95.
Favero M, Calò LA, Schiavon F, Punzi L. Bartter’s and Gitelman’s diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:637–48.
Vargas-Poussou R, Dahan K, Kahila D, Venisse A, Riveira-Munoz E, Debaix H, Grisart B, Bridoux F, Unwin R, Moulin B, Haymann JP, Vantyghem MC, Rigothier C, Dussol B, Godin M, Nivet H, Dubourg L, Tack I, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Houillier P, Blanchard A, Devuyst O, Jeunemaitre X. Spectrum of mutation in Gitelman syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:693–703.
Nguyen Dinh Cat A, Touyz RM. A new look at the renin-angiotensin system—focusing on the vascular system. Peptides. 2011;31:2141–50.
Crowley SD, Coffman TM. Recent advances involving the renin-angiotensin system. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318:1049–56.
Clementi E. Role of nitric oxide and its intracellular signalling pathways in the control of Ca2+ homeostasis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55:713–8.
Dzau VJ. Tissue angiotensin and pathobiology of vascular disease. A unifying hypothesis. Hypertension. 2001;37:1047–52.
Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL. Signal transduction Mechanisms Mediating the physiological and pathophysiological actions of angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:639–72.
Calò LA, Ceolotto G, Milani M, Pagnin E, van den Heuvel LP, Sartori M, Davis PA, Costa R, Semplicini A. Abnormalities of Gq-mediated cell signaling in Bartter and Gitelman syndromes. Kidney Int. 2001;60:882–9.
Calò LA, Davis PA, Semplicini A. Reduced content of alpha subunit of Gq-protein in monocytes of Bartter and Gitelman syndromes: relationship with vascular hyporeactivity. Kidney Int. 2002;61:353–4.
Calò LA. Vascular tone control in humans: insights from studies in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes. Kidney Int. 2006;69:963–6.
Calò L, Davis PA, Milani M, Cantaro S, Antonello A, Favaro S, D’Angelo A. Increased endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA level in Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndrome. Relationship to vascular reactivity. Clin Nephrol. 1999;51:12–7.
Calò L, Cantaro S, Calabrò A, Piarulli F, Rizzolo M, Favaro S, Antonello A, Crepaldi G, Borsatti A. Endothelium-derived vasoactive substances in Bartter’s syndrome. Angiology. 1995;46:905–13.
Calò L, D’Angelo A, Cantaro S, Bordin MC, Favaro S, Antonello A, Borsatti A. Increased urinary NO2-/NO3- and cyclic GMP levels in patients with Bartter’s syndrome: relationship to vascular reactivity. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;27:874–9.
Calò LA, Puato M, Schiavo S, Zanardo M, Tirrito C, Pagnin E, Balbi G, Davis PA, Palatini P, Pauletto P. Absence of vascular remodelling in a high angiotensin-II state (Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes): implications for angiotensin II signalling pathways. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:2804–9.
Calò LA, Pagnin E, Davis PA, Sartori M, Semplicini A. Oxidative stress related factors in Bartter’s and Gitelman’s sindrome: relevance for angiotensin II signaling. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:1518–25.
Calò LA, Sartore G, Bassi A, Basso C, Bertocco S, Marin R, Zambon S, Cantaro S, D’Angelo A, Davis PA, Manzato E, Crepaldi G. Reduced susceptibility of low density lipoprotein to oxidation in patients with overproduction of nitric oxide (Bartter’s and Gitelman’s sindrome). J Hypertens. 1998;16:1001–8.
Heximer SP, Blumer KJ. RGS proteins: Swiss army knives in seven-transmembrane domain receptor signaling networks. Sci STKE. 2007;370:pe2.
Zhong H, Neubig RR. Regulator of G protein signalling proteins; novel multifunctional drug targets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:837–45.
Tang M, Wang G, Lu P, Karas RH, Karas RH, Aronovitz M, Heximer SP, Kaltenbronn KM, Blumer KJ, Siderovski DP, Zhu Y, Mendelsohn ME. Regulator of G-protein signaling-2 mediates vascular smooth muscle relaxation and blood pressure. Nat Med. 2003;9:1506–12.
Calò LA, Pagnin E, Davis PA, Sartori M, Ceolotto G, Pessina AC, Semplicini A. Increased expression of regulator of G protein signaling-2 (RGS-2) in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndrome. A role in the control of vascular tone and implication for hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:4153–7.
Semplicini A, Lenzini L, Sartori M, Papparella I, Calò LA, Pagnin E, Strapazzon G, Benna C, Costa R, Avogaro A, Ceolotto G, Pessina AC. Reduced expression of regulator of G protein signaling-2 in hypertensive patients increases calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by angiotensin II. J Hypertens. 2006;24:1115–24.
Calò LA, Pagnin E, Ceolotto G, Davis PA, Schiavo S, Papparella I, Semplicini A, Pessina AC. Silencing regulator of G protein signaling-2 (RGS-2) increases angiotensin II signaling: insights into hypertension from findings in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes. J Hypertens. 2008;26:938–45.
Heximer SP, Knutsen RH, Sun X, Kaltenbronn KM, Rhee MH, Peng N, Oliveira-dos-Santos A, Penninger JM, Muslin AJ, Steinberg TH, Wyss JM, Mecham RP, Blumer KJ. Hypertension and prolonged vasoconstrictor signalling in RGS2-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:445–52.
Touyz RM. Role of Angiotensin II in regulating vascular structural and functional changes in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2003;5:155–64.
Griendling KK, FitzGerald GA. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular injury. Part II. Animal and human studies. Circulation. 2003;108:2034–40.
Griendling KK, Soresen D, Ushio-Fukai M. NAD(P)H oxidase. Role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ Res. 2000;86:494–501.
Pagnin E, Davis PA, Sartori M, Semplicini A, Pessina AC, Calò LA. Rho kinase and PAI-1 in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes: relationship to angiotensin II signaling. J Hypertens. 2004;22:1963–9.
Calò LA, Pessina AC. RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway: much more than just a modulation of vascular tone. Evidence from studies in humans. J Hypertens. 2007;25:259–64.
Loirand G, Guerin P, Pacaud P. Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Circ Res. 2006;98:322–34.
Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. Rho-kinase is an important therapeutic target in cardiovascular medicine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1767–75.
Budzyn K, Marley PD, Sobey CG. Targeting Rho and Rho-kinase in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:97–104.
Takemoto M, Sun J, Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Liao JK. Rho-kinase mediates hypoxia-induced downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 2002;106:57–62.
Sauzeau V, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Marionneau C, Loirand G, Pacaud P. RhoA expression is controlled by nitric oxide through cGMP-dependent protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:9472–80.
Jin HG, Yamashita H, Nagano Y, Fukuba H, Hiji M, Ohtsuki T, Takahashi T, Kohriyama T, Kaibuchi K, Matsumoto M. Hypoxia-induced upregulation of endothelial small G protein RhoA and Rho-kinase/ROCK2 inhibits eNOS expression. Neurosci Lett. 2006;408:62–7.
Chitaley K, Weber D, Webb RC. RhoA/Rho-kinase, vascular changes and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2001;3:139–44.
Higashi M, Shimokawa H, Hattori T, Hiroki J, Mukai Y, Morikawa K, Ichiki T, Takahashi S, Takeshita A. Long-term inhibition of Rho-Kinase suppresses angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular hypertrophy in rats in vivo. Effect on endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase system. Circ Res. 2003;93:767–75.
Yamakawa T, Tanaka S, Numaguchi K, Yamakawa Y, Motley ED, Ichihara S, Inagami T. Involvement of Rho-kinase in angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy of rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 2000;35:313–8.
Kataoka C, Egashira K, Inoue S, Takemoto M, Ni W, Koyanagi M, Kitamoto S, Usui M, Kaibuchi K, Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. Important role of Rho-kinase in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular inflammation and remodeling induced by long-term blockade of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. Hypertension. 2002;39:245–50.
Pagnin E, Davis PA, Semplicini A, Calò LA. The search for a link between inflammation and hypertension—contribution from Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2340–2.
Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H1597–602.
Takeda K, Ichiki T, Tokunou T, Takemoto M, Ni W, Koyanagi M, Kitamoto S, Usui M, Kaibuchi K, Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. Critical role of Rhokinase and MEK-ERK pathways for angiotensin II-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:868–73.
Eto Y, Shimokawa H, Hiroki J, Morishige K, Kandabashi T, Matsumoto Y, Amano M, Hoshijima M, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A. Gene transfer of dominant negative Rho kinase suppresses neointimal formation after balloon injury in pigs. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:H1744–50.
Nakakuki T, Ito M, Iwasaki H, Kureishi Y, Okamoto R, Moriki N, Kongo M, Kato S, Yamada N, Isaka N, Nakano T. Rho/Rho-kinase pathway contributes to C-reactive protein-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2088–93.
Wolfrum S, Dendorfer A, Rikitake Y, Stalker TJ, Gong Y, Scalia R, Dominiak P, Liao JK. Inhibition of Rhokinase leads to rapid activation of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/protein kinase Akt and cardiovascular protection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:1842–7.
Wennerberg K, Der CJ. Rho-family GTPases: it’s not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1301–12.
Siderovski DP, Willard FS. The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits. Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1:51–66.
Ying Z, Jin L, Dorrance AM, Webb RC. Increased expression of mRNA for regulator of G protein signaling domain-containing Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors in aorta from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:981–5.
Wuertz MC, Lorincz A, Vettel C, Thomas MA, Wieland T, Lutz S. p63RhoGEF—a key mediator of angiotensin II dependent signaling and processes in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 2010;24:4865–76.
Momotani K, Artamonov MV, Utepbergenov D, Derewenda U, Derewenda ZS, Somlyo AV. p63RhoGEF couples Gaq/11-mediated signaling to Ca2+ sensitization of vascular smooth muscle contractility. Circ Res. 2011;109:993–1002.
Guilluy C, Brégeon J, Toumaniantz G, et al. The Rho exchange factor Arhgef1 mediates the effects of angiotensin II on vascular tone and blood pressure. Nat Med. 2010;16:183–90.
Calò LA, Pagnin E, Davis PA, Sartori M, Semplicini A, Pessina AC. Rho kinase inhibition and vascular protection: support from studies in Bartter and Gitelman syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:34–5.
Calò LA, Pagnin E, Sartori M, Semplicini A, Pessina AC. Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes: a confirm in humans of the utility of Rho kinase inhibition for cardiovascular protection. J Hypertens. 2005;23:1273–5.
Datla SR, Dusting GJ, Mori TA, Taylor CJ, Croft KD, Jiang F. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 in vivo suppresses NADPH oxidase derived oxidative stress. Hypertension. 2007;50:636–42.
Martin D, Rojo AI, Salinas M, Diaz R, Gallardo G, Alam J, De Galarreta CM, Cuadrado A. Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf2 transcription factor in response to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:8919–29.
Pagnin E, Semplicini A, Sartori M, Pessina AC, Calò LA. Reduced mRNA and protein content of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RhoGEF) in Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes: relevance for the pathophysiology of hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:1200–5.
Calò LA, Davis PA, Pagnin E, Dal Maso L, Maiolino G, Seccia TM, Pessina AC, Rossi GP. Increased level of p63RhoGEF and RhoA/Rho kinase activity in hypertensive patients. Implications for vascular tone regulation and cardiovascular remodeling. J Hypertens. 2014;32:331–8.
Wirth A. Rho kinase and hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:1276–84.
Savoia C, Tabet F, Yao G, Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM. Negative regulation of RhoA/Rho kinase by angiotensin II type 2 receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells: role in angiotensin II-induced vasodilation in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2005;23:1037–45.
Calò LA, Montisci R, Scognamiglio R, Davis PA, Pagnin E, Schiavo S, Mormino P, Semplicini A, Palatini P, D’Angelo A, Pessina AC. High angiotensin II state without cardiac remodeling (Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes). Are angiotensin II type 2 receptors involved? J Endocrinol Invest. 2009;32:832–6.
Carey RM. Cardiovascular and renal regulation by the angiotensin type 2 receptor: the AT2 receptor comes of age. Hypertension. 2005;45:840–4.
Siragy HM. Evidence for benefits of angiotensin receptor blockade beyond blood pressure control. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2008;10:261–7.
Davis PA, Mussap M, Pagnin E, Bertipaglia L, Savica V, Semplicini A, Calò LA. Early markers of inflammation in a high angiotensin II state. Results of studies in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:1697–701.
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ruperez M, Lorenzo O, Esteban V, Blanco J, Mezzano S, Egido J. Angiotensin II regulates the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the kidney. Kidney Int. 2002;62(Suppl. 82):12–22.
Cheng ZJ, Vapaatalo H, Mervaala E. Angiotensin II and vascular inflammation. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:RA194–205.
Das UN. Is angiotensin II an endogenous pro-inflammatory molecule? Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:155–62.
Perona R, Montaner S, Saniger L, Sanchez-Perez I, Bravo R, Lacal JC. Activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB by Rho, CDC42, and Rac-1 proteins. Genes Dev. 1997;11:463–75.
Segain JP, Raingeard de la Bletiere D, Sauzeau V, Bourreille A, Hilaret G, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Pacaud P, Galmiche JP, Loirand G. Rho kinase blockade prevents inflammation via nuclear factor kappa B inhibition: evidence in Crohn’s disease and experimental colitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1180–7.
Calò LA, Davis PA, Pagnin E, Schiavo S, Semplicini A, Pessina AC. Linking inflammation and hypertension in humans: studies in Bartter’s/Gitelman’s syndromes. J Hum Hypertens. 2008;22:223–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravarotto, V., Pagnin, E., Fragasso, A. et al. Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular-Renal Remodelling in Hypertension: Insights from a Human Model Opposite to Hypertension. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 22, 215–223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0082-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0082-7