Abstract
Background
Older adults are at an increased risk of drug-related problems, especially following discharge from hospital. Drug-related readmissions place a large burden on the patient and the healthcare system. However, previous studies report inconsistent results on the prevalence and associated risk factors for drug-related hospital readmissions in older adults.
Objectives
We aimed to assess the prevalence of drug-related readmissions in older adults aged 65 years and older and investigate the drug classes, preventability and risk factors most associated with these readmissions.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were undertaken to answer our objectives. A search of four databases (MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL and Scopus) was conducted. Three authors independently performed title and abstract screening, full-text screening and data extraction of all included studies. A meta-analysis was conducted to calculate the pooled prevalence of drug-related readmissions across all studies, and a subgroup analysis was performed to explore heterogeneity among studies reporting on adverse drug reaction-related readmissions.
Results
A total of 1978 studies were identified in the initial search, of which four studies were included in the final synthesis. Three studies focused on readmissions due to adverse drug reactions and one study focused on readmissions due to drug-related problems. A pooled prevalence of 9% (95% confidence interval 2–18) was found for drug-related readmissions across all studies, and a pooled prevalence of 6% (95% confidence interval 4–10) was found for adverse drug reaction-related readmissions. Three studies explored the preventability of readmissions and 15.4–22.2% of cases were deemed preventable. The drug classes most associated with adverse drug reaction readmissions included anticoagulants, antibiotics, psychotropics and chemotherapy agents. Polypharmacy (the use of five or more medications) and several comorbidities such as cancer, liver disease, ischaemic heart disease and peptic ulcer disease were identified as risk factors for drug-related readmissions.
Conclusions
Almost one in ten older adults discharged from hospital experienced a drug-related hospital readmission, with one fifth of these deemed preventable. Several comorbidities and the use of polypharmacy and high-risk drugs were identified as prominent risk factors for readmission. Further research is needed to explore possible causes of drug-related readmissions in older adults for a more guided approach to the development of effective medication management interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
This review found 9% of older adults discharged from hospital experience a drug-related readmission with up to 22% of these being preventable. |
Polypharmacy and several high-risk drug classes including anticoagulants, antibiotics, psychotropic and chemotherapy agents were associated with an increased risk of readmission. |
Further research into targeted interventions to reduce potentially preventable drug-related problems in at-risk older adults is needed. |
1 Introduction
Older adults are at an increased risk of experiencing drug-related problems (DRPs), owing to a high prevalence of multimorbidity and subsequent polypharmacy [1,2,3,4,5]. Up to 45% of community-dwelling older adults live with polypharmacy [6], with several studies highlighting the high prevalence of DRPs in this population [7, 8]. Drug-related problems include adverse drug events (ADEs), adverse drug reactions (ADRs), medication errors (MEs), potentially inappropriate prescribing and drug interactions, which are associated with adverse health outcomes [9, 10].
Drug-related readmissions are a significant adverse outcome for patients discharged from hospital, where newly initiated medications and changes in medication regimes are common. Past reviews suggest that the rate of MEs occurring after discharge is up to 53% and almost 20% of patients are affected by ADEs [11]. Reoccurring admissions due to DRPs can impact patient safety and place a large financial burden on both the patient and healthcare system, highlighting the need to understand the prevalence and nature of drug-related readmissions. Although the prevalence of drug-related admissions has been studied previously [12,13,14], few studies have focused on drug-related readmissions, with existing studies reporting largely variable results. Past reviews have found that the prevalence of drug-related readmissions in the general adult population has ranged from 0.09 to 64% [15, 16]. Further, the characteristics and risk factors associated with drug-related readmissions are understudied [15, 16]. An understanding of these factors is necessary to inform the implementation of effective policy and clinical interventions to improve patient care, decrease medication-associated harms and reduce healthcare costs [17, 18].
The inconsistency in results from prior research highlights the need for an updated review on the prevalence of drug-related readmissions, with a particular focus on older adults. Thus, this systematic review and meta-analysis primarily aim to assess the prevalence of drug-related readmissions in older adults. Secondary objectives that will be investigated include the preventability, implicated drug classes and potential risk factors associated with drug-related hospital readmissions in older adults.
2 Method
A systematic review was conducted on the prevalence of and risk factors for drug-related readmissions in older adults in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) guidelines. “Drug-related” is a broad term that encompasses ADRs, ADEs and MEs (Table 1). For this review, any study that reported on a drug-related problem that resulted in a hospital readmission was included in the screening process. This systematic review was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023409005).
2.1 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Studies were included in this review if they were published peer-reviewed articles from January 2013 to April 2023 (to ensure recency and relevancy of included studies); that examined drug-related readmissions in participants aged 65 years and over; and contained data that could allow for the calculation of prevalence such as the number of participants, all-cause readmissions and drug-related readmissions. Studies were excluded if they focused on drug-related issues such as drug abuse, intentional overdose or any illicit drug use; were case reports, case series or qualitative studies where calculating prevalence was difficult; or were studies not available in the English language.
2.2 Search Strategy
To identify relevant studies for the review, a search of MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, and Scopus was conducted. A search strategy was developed based on three key searchable concepts including ‘DRPs’, ‘readmissions’ and ‘older adults’ (see Tables 1–4 of the Electronic Supplementary Material [ESM]). The studies were collated in Endnote (EndNote 20; Clarivate, Philadelphia, PA, USA) and uploaded to Covidence (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, VIC, Australia), where title and abstract screening was conducted by three independent reviewers (NP, EL, IW) as per the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any conflicts regarding inclusion and exclusion were resolved by discussion among all reviewers. Three independent reviewers (NP, EL, IW) conducted full-text screening of the remaining studies to determine the final eligible studies for the review. Conflict regarding inclusion of studies was resolved by discussion between all authors.
2.3 Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
Data extraction was done independently by three reviewers (NP, EL, IW). Extracted data included the author, country, study design, setting, sample size, mean age, definition of DRP, type of DRP that resulted in readmission, number of drug-related readmissions, total number of readmissions, drug classes, clinical presentations, preventability, reported risk factors and method of causality assessment. Risk factors associated with drug-related readmissions were extracted and presented adjusted odds ratios or hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals, as reported by the study. Quality assessment of included studies was conducted independently by two authors (NP, EL) based on the checklist for prevalence studies developed by The Joanna Briggs Institute. Any discrepancies were resolved by discussion with all authors.
2.4 Statistical Analysis
The prevalence of drug-related readmissions was calculated by the number of drug-related readmissions divided by the total number of participants in the study. Only statistically significant findings were included where a 95% confidence interval that did not include the null value of 1 was considered statistically significant. Preventability was calculated as the number of drug-related readmissions deemed preventable divided by the number of drug-related readmissions. A meta-analysis was conducted using Meta-XL 5.3 (http://www.epigear.com) to calculate the pooled prevalence of drug-related readmissions across all studies, and \(I^{2}\) statistics were used to assess degree of heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses were performed to examine heterogeneity between studies involving ADR-related readmissions in terms of study design, sample size, study objective, setting, causality assessment, identification method and time to readmission.
3 Results
3.1 Study Selection
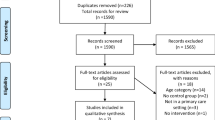
The initial screening process identified 1978 studies that was narrowed down to 1668 studies after de-duplication as shown in Fig. 1. Following title and abstract screening, 58 studies were eligible for full-text review and six studies were selected to be included in the paper. The authors of two papers were contacted for further details to allow for the calculation of drug-related readmissions specifically in the older population; however, they did not respond, leaving four studies that were included in the final review.
3.2 Characteristics of Studies
A total of four studies [23,24,25,26] were included in the review including two prospective cohort studies [25, 26], one retrospective cohort study [23] and one post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial [24]. The studies were conducted across Sweden [24, 25], France [23] and the UK [26], and were based in general (n = 2) or teaching hospitals (n = 2). The cohort sizes ranged from 390 to 2637 participants and the mean age ranged from 77 to 86 years. The time between index admission and readmission varied between 30 days and 1 year. Three studies focused on ADR-related readmissions [23, 25, 26] and one study focused on DRP-related readmissions [24]. No studies were found that focused on MEs or ADEs. Two studies identified drug-related readmissions using clinical judgement including the assessment of individual cases by senior clinicians [25] as well as senior geriatricians, senior pharmacists and senior researchers [26]. Two studies identified drug-related readmissions using International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes to identify the initial hospital admissions. Hospital readmissions were identified using either ICD-10 codes related to ADRs [23] or a review of all cases by an expert panel [24] (Table 2).
3.3 Prevalence
Data extracted from all four studies [23,24,25,26] were used to calculate prevalence rates. Three studies [23, 25, 26] focused on ADRs while one study [24] focused on DRPs. The study design also differed in each subgroup where the studies focusing on ADRs were cohort studies and the study focusing on DRPs was a post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial. The total calculated pooled prevalence across the four studies was 9% (95% CI 2–18) with an \({I}^{2}\) value of 99% suggesting considerable heterogeneity (Fig. 2). The calculated pooled prevalence of the ADR subgroup was 6% (95% CI 4–10) with an \({I}^{2}\) value of 87% highlighting considerable heterogeneity between the studies.
3.4 Subgroup Analysis
A subgroup analysis was performed on the ADR subgroup [23, 25, 26] to identify possible sources of heterogeneity, as shown in Table 3. Prospective studies presented a lower readmission rate compared with retrospective studies, and non-teaching hospitals had a lower readmission rate compared with teaching hospitals. The use of a published method of assessing causality (Naranjo) and identifying cases (ICD codes) also resulted in a lower readmission rate.
3.5 Risk Factors
Two studies [23, 24] explored risk factors associated with DRP-related readmissions using multivariate logistic regression as shown in Table 4. Neoplasm (odds ratio 7.69, 95% CI 4.59–12.88) was identified as the only statistically significant risk factor for ADR-related readmissions [23]. One study [24] found several comorbidities that increased the risk of DRP-related readmissions. Liver disease (HR 2.46, 95% CI 1.15–5.24), peptic ulcer disease (HR 1.86, 95% CI 1.10–3.14) and ischaemic heart disease (HR 2.06, 95% CI 1.32–3.21) were the conditions with the highest risk of DRP-related readmissions. Patients taking five or more medications were also found to be more likely to be readmitted than those taking fewer than five medications (HR 1.45, 95% CI 1.06–1.98), and the risk increased for patients taking ten or more medications (HR 1.69, 95% CI 1.22–2.32). Dementia (HR 0.55, 95% CI 0.39–0.78), urinary tract infections (HR 0.60, 95% CI 0.39–0.92) and injuries, intoxications and certain other complications or external factors (HR 0.50, 95% CI 0.31–0.83) were identified as protective factors for DRP-related readmissions.
3.6 Drug Classes
Two studies [23, 25] identified drug classes and specific medications that were associated with drug-related readmissions as shown in Table 5. The most implicated drug classes identified include anticoagulants (13.8% and 15.6%), psychotropics (6.9% and 23.1%) and antibiotics (4.6% and 7.7%). One study [23] noted a large representation of chemotherapy agents that caused drug-related readmissions. Specific agents were not mentioned; however, common clinical presentations included aplasia, agranulocytosis, polyneuropathy and osteoporosis. Both studies identified anticoagulants, antibiotics and antipsychotics as prominent causes of drug-related readmissions. Anticoagulants were associated with clinical presentations such as gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal pain, haematoma, anaemia and epistaxis. Implicated drugs included warfarin, fluindione, standard heparin and enoxaparin. The presentations associated with antibiotics were predominantly fever, diarrhoea and dyspnoea and the implicated medications varied including clindamycin, cotrimoxazole, norfloxacin, ceftazidime and linezolid. The implicated psychotropics were antidepressants, antiepileptic agents and antiparkinson medications. Some clinical presentations identified were constipation and falls, and the implicated medications varied across all classes.
3.7 Preventability
The preventability of drug-related readmissions was explored by three studies [23,24,25] and ranged from 15.4 to 22.2%. Two studies [24, 25] used the Hallas criteria [27] to determine the preventability of readmissions where cases classified as ‘definitely avoidable’ by the scale were considered preventable. Along with the Hallas criteria, one study [24] used the Helper criteria proposed by Howard et al. [28] to determine preventability. One study [23] used Olivier’s scale [29] as the method of determining preventability. Further analysis by the definition of readmission shows that 22.2% and 15.4% of cases were considered preventable for ADR-related readmission, respectively [23, 25], and 21.3% of DRP-related readmissions were considered preventable. One study [24] identified the cause of potentially preventable readmissions in the study as inadequate treatment (undertreatment, low dose or lack of treatment, wrong or inappropriate treatment), lack of monitoring or follow-up, and lack of investigations or diagnostics.
3.8 Quality Assessment
The quality assessment conducted using the Joanna Briggs Institute checklist for prevalence studies presented a mean score of 8.75/9. All studies scored full marks, except one study where a low response rate was not explained by the authors [25]. See Table 5 of the ESM for more detail.
4 Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis found the pooled prevalence of drug-related readmissions in older people was 9%, with a range from 3.3 to 22.2%, while the prevalence of ADR-related readmissions in older people was 6%, with a range from 3.3 to 8.7%. Overall, 15–22% of drug-related readmissions were deemed to be preventable. Several risk factors associated with an increased risk of readmission were identified including comorbidities such as cancer, liver disease, peptic ulcer disease and ischaemic heart disease, polypharmacy and specific drug classes including antibiotics, anticoagulants, psychotropics and chemotherapy agents.
A total pooled prevalence of almost one in ten was found for drug-related readmissions, and importantly, a significant proportion of cases were deemed preventable. Importantly, 15–22% of cases were deemed preventable. Past reviews focusing on the entire adult population reveal a large variation in the prevalence of drug-related readmissions, with ranges from 3 to 64% and from 0.09 to 64%, respectively [15, 16]. One systematic review found a median prevalence of 21% (interquartile range 14–23) for drug-related readmissions, which is higher that the prevalence determined by this study. Although the preventability of drug-related readmissions has not been extensively studied, a systematic review [15] found a preventability rate of 69% in DRP-related readmissions, which is higher than the prevalence rate found in this study. Because of significant heterogeneity between studies including variations in target populations and methods of calculating prevalence, it is difficult to compare the prevalence found in this review to past studies. However, it must be noted that a large variation in study designs does not allow for an accurate prevalence rate to be calculated. Despite these differences, it is evident that a significant proportion of older adults experience preventable drug-related hospital readmissions. Exploring risk factors associated with drug-related readmissions can provide insight into certain populations groups at a greater risk of readmissions than others to allow for targeted interventions to be implemented.
Several comorbidities were found to be associated with an increased risk of drug-related readmissions. Cancer was found to increase the risk of readmission for ADR-related cases [23]. Chemotherapy agents are known to be associated with a high level of toxicity and ADRs. Age-related physiological changes, multiple comorbidities and drug–drug interactions may further increase the risk of experiencing an ADR, thus the increased risk of readmission is not an unexpected finding [30]. However, multiple comorbidities were linked to DRP-related readmissions with liver disease presenting the highest risk [24, 31]. Older adults suffer from a poorer prognosis of liver conditions because of age-related changes in liver cells [32]. An increased risk of hepatotoxicity from the use of drugs predominantly metabolised by the liver can explain the increased risk of DRPs. Furthermore, changes in pharmacotherapy to account for decreased metabolic ability of the liver can increase the risk of ADEs. Interestingly dementia, urinary tract infections and injuries, intoxications and certain other complications or external factors were identified as protective factors. However, this may be because of dementia being classified as “caused by the progression of the disease” rather than as a DRP. Other protective factors identified are relatively unrelated to pharmacotherapy compared with other identified comorbidities [24]. These protective factors may act as a confounder or possibly compete with the risk of readmissions where patients readmitted for these causes are less likely to have the opportunity for a drug-related readmission. A systematic review has identified the Charlson Comorbidity Index score as a prominent risk factor of drug-related readmissions, although specific conditions were not explored further. Conflicting results have been found in past papers regarding age and sex; however, this review found no association between these factors and readmissions [15].
Use of high-risk medications, often to treat comorbidities such as those identified in this review, has also been associated with an increased risk of readmission. Anticoagulants, antibiotics, psychotropics and chemotherapy agents were the most common drug classes identified by this review [23, 25]. Past reviews identified these drug classes as risk factors in past reviews along with other drug classes such as opioids, antihypertensives, diuretics and corticosteroids. In particular, anticoagulants were found to be most associated with preventable drug-related readmissions [15, 16]. These drug classes align with the APINCHS [33] (Antimicrobials, Potassium, Insulin, Narcotics and other sedatives, Chemotherapeutic agents, Heparin and other anticoagulants and Systems) acronym classifying high-risk medications [34]. In particular, anticoagulant and psychotropic use is often seen in longer term care of older patients, increasing the likelihood of ADEs [34,35,36]. Gastrointestinal bleeds and falls were the most common clinical presentations identified in this review, which are potentially preventable ADRs of anticoagulants and psychotropics.
Along with specific medication classes, taking an increasing number of medications was linked to an increased risk of readmission. Polypharmacy is a well-established issue, particularly in the older population, which is associated with an increased risk of medication regimen complexity, ADEs, MEs and drug–drug interactions, which can lead to an increased burden on individual health and the healthcare system [37]. Importantly, DRPs that can occur from polypharmacy can be prevented through rational prescribing and deprescribing initiatives [38,39,40].
Risk factors including the use of high-risk medications and polypharmacy can be managed through the implementation of targeted interventions addressing these issues. One study [24] suggests the causes of potentially preventable readmissions were inadequate treatment (undertreatment, low dose or a lack of treatment, wrong or inappropriate treatment), a lack of monitoring or follow-up and a lack of investigations or diagnostics. Past studies suggest that communication issues and a lack of medication management are barriers to effective transitions in care that can possibly increase the risk of hospitalisation [41,42,43]. Pharmacist-led interventions during hospital stay, discharge and post-discharge may reduce potentially inappropriate medication use and ADEs. Interventions that have been studied in the past include improved discharge planning, medication reconciliation and patient education, a medication care plan on discharge and follow-up monitoring by a pharmacist [44,45,46,47].
4.1 Strengths and Limitations
This review had several strengths, particularly the extensive search strategy and extraction of data. The extensive search strategy included multiple databases that minimised the chances of relevant studies being missed by the search. The screening and extraction process involved three independent reviewers that minimised the risk of bias. However, there were some limitations in this review. The heterogeneity between the studies included in the review and the number of studies included suggests the calculated prevalence should be interpreted with caution. The search was limited to the English language and excluded unpublished articles, which increased the likelihood of excluding relevant studies. Some studies did not report on the risk factors and/or drug classes associated with drug-related readmissions, which may have led to underestimation or underreporting of information. The studies included in the review present data from European countries and therefore the results from this study may not be generalisable to healthcare systems in other countries. Furthermore, ICD-10 codes were used by a few studies to identify cases of drug-related readmissions; however, this method of identification has limited sensitivity and specificity, which may have missed eligible cases in the identification process [48].
4.2 Implications for Practice, Policy and Future Research
Despite its high impact on health burden and healthcare costs, there is currently a lack of studies exploring drug-related readmissions in older adults and current studies are difficult to compare. A recent systematic review suggests further investigations using a more standardised approach to define drug-related readmissions and preventability to help gain a deeper understanding of possible causes and risk factors associated with readmissions [15]. This review has also emphasised the role of comorbidities and polypharmacy in contributing to drug-related readmissions; however, further investigations are required to identify other possible risk factors, including sociodemographic and environmental factors, which can contribute to readmissions. Further research is also required to investigate other common DRPs including ADEs and MEs. An increased understanding of risk factors and causes of preventable readmissions will help inform the development of targeted interventions in healthcare settings to optimise the quality use of medicines in older adults.
5 Conclusions
This systematic review and meta-analysis found that almost one in ten older adults discharged from hospital experienced a drug-related hospital readmission, with one fifth of these being preventable. Several comorbidities and the use of polypharmacy were identified as prominent risk factors for readmission, with the most common drug classes involved including anticoagulants, antibiotics, chemotherapy agents and psychotropics. Further research is needed to explore possible causes of drug-related readmissions in older adults for a more guided approach to the development of effective medication management interventions.
References
Kanasi E, Ayilavarapu S, Jones J. The aging population: demographics and the biology of aging. Periodontol 2000. 2016;72(1):13–8.
Aidoud A, Gana W, Poitau F, Debacq C, Leroy V, Nkodo JA, et al. High prevalence of geriatric conditions among older adults with cardiovascular disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023;12(2): e026850.
Sinclair AJ, Abdelhafiz AH. Multimorbidity, frailty and diabetes in older people-identifying interrelationships and outcomes. J Pers Med. 2022;12(11):1911.
Zazzara MB, Palmer K, Vetrano DL, Carfì A, Onder G. Adverse drug reactions in older adults: a narrative review of the literature. Eur Geriatr Med. 2021;12(3):463–73.
Wastesson JW, Morin L, Tan ECK, Johnell K. An update on the clinical consequences of polypharmacy in older adults: a narrative review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2018;17(12):1185–96.
Hsu HF, Chen KM, Belcastro F, Chen YF. Polypharmacy and pattern of medication use in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review. J Clin Nurs. 2021;30(7–8):918–28.
Garcia-Caballos M, Ramos-Diaz F, Jimenez-Moleon JJ, Bueno-Cavanillas A. Drug-related problems in older people after hospital discharge and interventions to reduce them. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):430–8.
Plácido AI, Herdeiro MT, Morgado M, Figueiras A, Roque F. Drug-related problems in home-dwelling older adults: a systematic review. Clin Ther. 2020;42(4):559-72.e14.
Maher RL, Hanlon J, Hajjar ER. Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(1):57–65.
Chiatti C, Bustacchini S, Furneri G, Mantovani L, Cristiani M, Misuraca C, et al. The economic burden of inappropriate drug prescribing, lack of adherence and compliance, adverse drug events in older people. Drug Saf. 2012;35(1):73–87.
Alqenae FA, Steinke D, Keers RN. Prevalence and nature of medication errors and medication-related harm following discharge from hospital to community settings: a systematic review. Drug Saf. 2020;43(6):517–37.
Parameswaran Nair N, Chalmers L, Peterson GM, Bereznicki BJ, Castelino RL, Bereznicki LR. Hospitalization in older patients due to adverse drug reactions: the need for a prediction tool. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:497–505.
Salvi F, Marchetti A, D’Angelo F, Boemi M, Lattanzio F, Cherubini A. Adverse drug events as a cause of hospitalization in older adults. Drug Saf. 2012;35(1):29–45.
Angamo MT, Chalmers L, Curtain CM, Bereznicki LRE. Adverse-drug-reaction-related hospitalisations in developed and developing countries: a review of prevalence and contributing factors. Drug Saf. 2016;39(9):847–57.
El Morabet N, Uitvlugt EB, Bemt BJF, Bemt P, Janssen MJA, Karapinar-Carkit F. Prevalence and preventability of drug-related hospital readmissions: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66(3):602–8.
Linkens AEMJH, Milosevic V, van der Kuy PHM, Damen-Hendriks VH, Mestres Gonzalvo C, Hurkens KPGM. Medication-related hospital admissions and readmissions in older patients: an overview of literature. Int J Clin Pharm. 2020;42(5):1243–51.
Ruiz-Ramos J, Juanes-Borrego A, Puig-Campany M, Blazquez-Andión M, López-Vinardell L, Gilabert-Perramon A, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of implementing a secondary prevention programme in those patients who visited an emergency department for drug-related problems. Int J Pharm Pract. 2022;30(5):434–40.
Wright EA, Graham JH, Maeng D, Tusing L, Zaleski L, Martin R, et al. Reductions in 30-day readmission, mortality, and costs with inpatient-to-community pharmacist follow-up. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2019;59(2):178–86.
Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe. Classification for drug related problems. The PCNE classification V 6.2. https://www.pcne.org/upload/files/11_PCNE_classification_V6-2.pdf. Accessed 27 May 2023.
Nebeker JR, Barach P, Samore MH. Clarifying adverse drug events: a clinician’s guide to terminology, documentation, and reporting. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(10):795–801.
Leendertse AJ, Egberts ACG, Stoker LJ, van den Bemt PMLA. Frequency of and risk factors for preventable medication-related hospital admissions in the Netherlands. Arch Inern Med. 2008;168(17):1890–6.
National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. http://www.nccmerp.org/sites/default/files/nccmerp_fact_sheet_2015-02-v91.pdf. Accessed 27 May 2023.
Hauviller L, Eyvrard F, Garnault V, Rousseau V, Molinier L, Montastruc JL, et al. Hospital re-admission associated with adverse drug reactions in patients over the age of 65 years. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;72(5):631–9.
Kempen TGH, Hedman AN, Hadziosmanovic N, Lindner KJ, Melhus H, Nielsen EI, et al. Risk factors for and preventability of drug-related hospital revisits in older patients: a post-hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023;89(5):1575–87.
Ekerstad N, Bylin K, Karlson BW. Early rehospitalizations of frail elderly patients: the role of medications: a clinical, prospective, observational trial. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2017;9:77–88.
Parekh N, Ali K, Stevenson JM, Davies JG, Schiff R, Van der Cammen T, et al. Incidence and cost of medication harm in older adults following hospital discharge: a multicentre prospective study in the UK: incidence and cost of medication harm in older adults. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84(8):1789–97.
Hallas J, Harvald B, Gram LF, Grodum E, Brøsen K, Haghfelt T, et al. Drug related hospital admissions: the role of definitions and intensity of data collection, and the possibility of prevention. J Intern Med. 1990;228(2):83–90.
Howard RL, Avery AJ, Howard PD, Partridge M. Investigation into the reasons for preventable drug related admissions to a medical admissions unit: observational study. Qual Saf Health Care. 2003;12(4):280–5.
Olivier P, Caron J, Haramburu F, Imbs J-L, Jonville-Béra A-P, Lagier G, et al. Validation of a measurement scale: example of a French Adverse Drug Reactions Preventability Scale. Therapie. 2005;60(1):39–45.
Kimmick GG, Fleming R, Muss HB, Balducci L. Cancer chemotherapy in older adults: a tolerability perspective. Drugs Aging. 1997;10(1):34–49.
García-Pérez L, Linertová R, Lorenzo-Riera A, Vázquez-Díaz JR, Duque-González B, Sarría-Santamera A. Risk factors for hospital readmissions in elderly patients: a systematic review. QJM. 2011;104(8):639–51.
Kim IH, Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Aging and liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015;31(3):184–91.
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. APINCHS classification of high risk medicines. https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/medication-safety/high-risk-medicines/apinchs-classification-high-risk-medicines. Accessed 27 May 2023.
Wojt IR, Cairns R, Gillooly I, Patanwala AE, Tan ECK. Clinical factors associated with increased length of stay and readmission in patients with medication-related hospital admissions: a retrospective study. Res Soc Admin Pharm. 2022;18(7):3184–90.
Ćurković M, Dodig-Ćurković K, Erić AP, Kralik K, Pivac N. Psychotropic medications in older adults: a review. Psychiatr Danub. 2016;28(1):13–24.
Parks ALMD, Fang MCMDMPH. Anticoagulation in older adults with multimorbidity. Clin Geriatr Med. 2016;32(2):331–46.
Pazan F, Wehling M. Polypharmacy in older adults: a narrative review of definitions, epidemiology and consequences. Eur Geriatr Med. 2021;12(3):443–52.
NSW Therapeutic Advisory Group Inc. Deprescribing tools. https://www.nswtag.org.au/deprescribing-tools/. Accessed 27 May 2023.
Kurczewska-Michalak M, Lewek P, Jankowska-Polańska B, Giardini A, Granata N, Maffoni M, et al. Polypharmacy management in the older adults: a scoping review of available interventions. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 734045.
Verma A, Saha S, Jarl J, Conlon E, McGuinness B, Trépel D. An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses on the effect of medication interventions targeting polypharmacy for frail older adults. J Clin Med. 2023;12(4):1379.
Liebzeit D, Rutkowski R, Arbaje AI, Fields B, Werner NE. A scoping review of interventions for older adults transitioning from hospital to home. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(10):2950–62.
Ozavci G, Bucknall T, Woodward-Kron R, Hughes C, Jorm C, Joseph K, et al. A systematic review of older patients’ experiences and perceptions of communication about managing medication across transitions of care. Res Soc Admin Pharma. 2021;17(2):273–91.
Lee JY, Yang YS, Cho E. Transitional care from hospital to home for frail older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Geriatr Nurs. 2022;43:64–76.
İlkin N. Preventable hospitalizations in older adults: a dream or reality? İstanbul Med J. 2017;18(3):114–9.
Villeneuve Y, Courtemanche F, Firoozi F, Gilbert S, Desbiens M-P, Desjardins A, et al. Impact of pharmacist interventions during transition of care in older adults to reduce the use of healthcare services: a scoping review. Res Soc Admin Pharm. 2021;17(8):1361–72.
Riordan DO, Walsh KA, Galvin R, Sinnott C, Kearney PM, Byrne S. The effect of pharmacist-led interventions in optimising prescribing in older adults in primary care: a systematic review. SAGE Open Med. 2016;4:2050312116652568.
Uchida M, Suzuki S, Sugawara H, Suga Y, Nakagawa T, Takase H. Multicentre prospective observational study on community pharmacist interventions to reduce inappropriate medications. Int J Pharm Pract. 2022;30(5):427–33.
Quan H, Li B, Duncan Saunders L, Parsons GA, Nilsson CI, Alibhai A, et al. Assessing validity of ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data in recording clinical conditions in a unique dually coded database: assessing validity of ICD-9-CM and ICD-10. Health Serv Res. 2008;43(4):1424–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions.
Conflicts of interest
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
All data and material accessed for the review are included in the article (either within the article or as part of the supplementary material).
Code availability
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
All authors were involved in the concept and design of the study. NP, EL and IW were involved in title and abstract screening, full-text screening and data extraction. NP and EL performed the quality assessment for included studies. NP prepared the initial draft of the review and EL, IW, JP, ZDK and ET provided critical feedback and amendments to revise the initial draft.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, N., Lau, E.C.Y., Wojt, I. et al. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Drug-Related Readmissions in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drugs Aging 41, 1–11 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-023-01076-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-023-01076-8