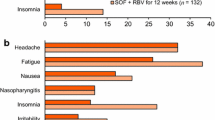
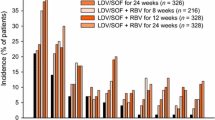
Abstract
A fixed-dose combination tablet comprising the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitor elbasvir and the HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor grazoprevir (elbasvir/grazoprevir; Zepatier™) was recently approved for the treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1 and 4 infection in the EU and the USA. In phase III trials, 12 or 16 weeks of treatment with once-daily elbasvir/grazoprevir (fixed-dose tablet or as individual agents), taken with or without ribavirin, generally provided high rates of sustained virological response at 12 weeks (SVR12) in treatment-naive and -experienced adult patients with chronic HCV genotype 1a, 1b or 4 infection, including those with or without compensated cirrhosis, HIV co-infection, inherited blood disorders or chronic kidney disease or patients receiving opioid agonist therapy or of Japanese origin. Elbasvir/grazoprevir was generally well tolerated. Thus, elbasvir/grazoprevir, with or without ribavirin, represents an effective new option for the treatment of adults with chronic HCV genotype 1 and 4 infection, including a number of difficult-to-treat populations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myers RP, Shah H, Burak KW, et al. An update on the management of chronic hepatitis C: 2015 consensus guidelines from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;29(1):19–34.
European Medicines Agency. Zepatier (elbasvir/grazoprevir) film-coated tablets: EU summary of product characteristics. 2016. http://www.ema.europa.eu/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Merck & Co., Inc. Zepatier™ (elbasvir and grazoprevir) tablets, for oral use: US prescribing information 2016. http://www.merck.com/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Merck & Co., Inc. Merck to present new data on Zepatier™ (elbasvir/grazoprevir) and chronic hepatitis C clinical development programs at The Liver Meeting® [media release]. 3 October 2016. http://www.businesswire.com/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Coburn CA, Meinke PT, Chang W, et al. Discovery of MK-8742: an HCV NS5A inhibitor with broad genotype activity. Chemmedchem. 2013;8(12):1930–40.
European Medicines Agency. Assessment report: Zepatier (elbasvir/grazoprevir). 2016. http://www.ema.europa.eu/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Summa V, Ludmerer SW, McCauley JA, et al. MK-5172, a selective inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease with broad activity across genotypes and resistant variants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(8):4161–7.
Kwo PY, Gane E, Peng C-Y, et al. Effectiveness of elbasvir and grazoprevir combination, with or without ribavirin, for treatment-experienced patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):164–75.
Rockstroh JK, Nelson M, Katlama C, et al. Efficacy and safety of grazoprevir (MK-5172) and elbasvir (MK-8742) in patients with hepatitis C virus and HIV co-infection (C-EDGE CO-INFECTION): a non-randomised, open-label trial. Lancet HIV. 2015;2(8):e319–27.
Dore GJ, Altice F, Litwin AH, et al. Elbasvir–grazoprevir to treat hepatitis C virus infection in persons receiving opioid agonist therapy: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2016;165(9):625–34.
Zeuzem S, Ghalib R, Reddy KR, et al. Grazoprevir-elbasvir combination therapy for treatment-naive cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1, 4, or 6 Infection: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(1):1–13.
Forns X, Gordon SC, Zuckerman E, et al. Grazoprevir and elbasvir plus ribavirin for chronic HCV genotype-1 infection after failure of combination therapy containing a direct-acting antiviral agent. J Hepatol. 2015;63(3):564–72.
George J, Burnevich E, Sheen I, et al. Efficacy and safety of elbasvir/grazoprevir in treatment-naive subjects with chronic HCV GT 1, GT 4 and GT 6 infection (C-CORAL): a phase III randomized multinational clinical trial [abstract no. 76 plus conference report]. Hepatology. 2016;64(Suppl 1):41A.
Hezode C, Colombo M, Bourliere M, et al. Elbasvir/grazoprevir for patients with hepatitis C virus infection and inherited blood disorders: a phase III study. Hepatology. 2017. doi:10.1002/hep.29139.
Kumada H, Suzuki F, Karino Y, et al. The combination of elbasvir and grazoprevir for the treatment of chronic HCV infection in Japanese patients: a randomized phase II/III study. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52(4):520–33.
Lahser FC, Bystol K, Curry S, et al. The combination of grazoprevir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor, and elbasvir, an HCV NS5A inhibitor, demonstrates a high genetic barrier to resistance in HCV genotype 1a replicons. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(5):2954–64.
US FDA. Application number: 208261Orig1s000 clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s). 2015. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Roth D, Nelson DR, Bruchfeld A, et al. Grazoprevir plus elbasvir in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (the C-SURFER study): a combination phase 3 study. Lancet. 2015;386(10003):1537–45.
US National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02252016. 2017. https://clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Sperl J, Horvath G, Halota W, et al. Efficacy and safety of elbasvir/grazoprevir and sofosbuvir/pegylated interferon/ribavirin; a phase III randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2016;65(6):1112–9.
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Recommendations for testing, managing and treating hepatitis C. 2016. http://hcvguidelines.org/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2016. J Hepatol. 2017;66(1):153–94.
Data on file, Merck & Co., Inc. 2017.
Buti M, Gordon SC, Zuckerman E, et al. Grazoprevir, elbasvir, and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection after failure of pegylated interferon and ribavirin with an earlier-generation protease inhibitor: Final 24-week results from C-SALVAGE. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(1):32–6.
Arduino JM, Jiang Z, Shaughnessy M, et al. C-EDGE Co-Infection: impact of 12-week oral regimen of grazoprevir (GZR, MK-5172)/elbasvir (EBR, MK-8742) on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in treatment-naive patients with HCV/HIV co-infection [abstract no. 729 plus conference report]. Hepatology. 2015;62(Suppl 1):572-3A.
Arduino JM, Shibolet O, Litwin AH, et al. C-EDGE CO-STAR: favorable impact of elbasvir and grazoprevir on health-related quality of life in treatment-naive HCV-infected persons who inject drugs receiving opioid agonist therapy [abstract no. THU-225 plus conference report]. J Hepatol. 2016;64(Suppl 2):S403–4.
Arduino JM, Wang Y, Brown DD, et al. C-EDGE TN: impact of 12-week oral regimen of grazoprevir (GZR, MK-5172)/elbasvir (EBR, MK-8742) on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype (GT) 1, 4, or 6 infection [abstract no. 717 plus conference report]. Hepatology. 2015;62(Suppl 1):565-6A.
Zeuzem S, Ghalib R, Reddy KR, et al. Final SVR24 data from the phase 3 C-EDGE treatment-naive study of elbasvir/grazoprevir in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1, 4 or 6 infection [abstract no. SAT-266 plus conference report]. J Hepatol. 2016;64(Suppl 2):S821.
Dusheiko GM, Manns MP, Vierling JM, et al. Safety and tolerability of grazoprevir/elbasvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C (HCV) infection: integrated analysis of phase 2–3 trials [abstract no. 712 plus conference report]. Hepatology. 2015;62(Suppl 1):562A.
Zhang J, Nguyen D, Hu KQ. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of current direct-acting antiviral treatment strategies. N Am J Med Sci (Boston). 2016;9(2):47–54.
Asselah T, Boyer N, Saadoun D, et al. Direct-acting antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection: optimizing current IFN-free treatment and future perspectives. Liver Int. 2016;36(Suppl 1):47–57.
US FDA. Clinical review appendum. 2016. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Woolston SL, Kim N. Cost and access to direct-acting antiviral agents. 2016. http://www.hepatitisc.uw.edu/. Accessed 4 Apr 2017.
Rosenthal ES, Graham CS. Price and affordability of direct-acting antiviral regimens for hepatitis C virus in the United States. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016;11:24.
Acknowledgements
During the peer review process, the manufacturer of elbasvir/grazoprevir was also offered an opportunity to review this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Conflict of interest
Zaina T. Al-Salama and Emma D. Deeks are salaried employees of Adis/Springer, are responsible for the article content and declare no relevant conflicts of interest
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: A. Ascione, Department of Internal Medicine, Centre for Liver Disease, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, Naples, Italy; N. Izumi, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Musashino Red-Cross Hospital, Tokyo, Japan; S. Karatapanis, First Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Rhodes, Rhodes, Greece.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Salama, Z.T., Deeks, E.D. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir: A Review in Chronic HCV Genotypes 1 and 4. Drugs 77, 911–921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0739-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0739-8