Abstract
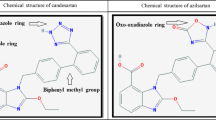
Fimasartan is the ninth, and most recent, angiotensin II receptor antagonist approved as an antihypertensive agent. Fimasartan, a pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivative of losartan with the imidazole ring replaced, which enables higher potency and longer duration than losartan. Fecal elimination and biliary excretion are the predominant elimination pathways of fimasartan and the urinary excretion was found to be less than 3 % 24 h after administration. Fimasartan is primarily catabolized by cytochrome P450 isoform 3A and no significant drug interaction was observed when used in combination with hydrochlorothiazide, amlodipine, warfarin, or digoxin. Fimasartan at a dosage range of 60–120 mg once daily showed an antihypertensive effect over 24 h. In a large, population-based observational study, fimasartan showed an excellent safety profile. Anti-inflammatory and organ-protecting effects of fimasartan have been shown in various preclinical studies, including aortic balloon injury, myocardial infarct ischemia/reperfusion, doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, and ischemic stroke models.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim TW, Yoo BW, Lee JK, Kim JH, Lee KT, Chi YH, et al. Synthesis and antihypertensive activity of pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives as losartan analogue for new angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012;22(4):1649–54.
Chi YH, Lee H, Paik SH, Lee JH, Yoo BW, Kim JH, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of fimasartan following single and repeated oral administration in the fasted and fed states in healthy subjects. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2011;11(5):335–46.
Ghim JL, Paik SH, Hasanuzzaman M, Chi YH, Choi HK, Kim DH, et al. Absolute bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist fimasartan in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;56(5):576–80.
Christ DD, Wong PC, Wong YN, Hart SD, Quon CY, Lam GN. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan potassium (DuP 753/MK 954) in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;268(3):1199–205.
Davi H, Tronquet C, Miscoria G, Perrier L, DuPont P, Caix J, et al. Disposition of irbesartan, an angiotensin II AT1-receptor antagonist, in mice, rats, rabbits, and macaques. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(1):79–88.
Ieiri I, Nishimura C, Maeda K, Sasaki T, Kimura M, Chiyoda T, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic profiles of telmisartan after the oral microdose and therapeutic dose. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011;21(8):495–505.
Kim TH, Shin S, Bashir M, Chi YH, Paik SH, Lee JH, et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolite profiling of fimasartan, a novel antihypertensive agent, in rats. Xenobiotica. 2014;44(10):913–25.
Flesch G, Muller P, Lloyd P. Absolute bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;52(2):115–20.
Schwocho LR, Masonson HN. Pharmacokinetics of CS-866, a new angiotensin II receptor blocker, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;41(5):515–27.
Lo MW, Goldberg MR, McCrea JB, Lu H, Furtek CI, Bjornsson TD. Pharmacokinetics of losartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, and its active metabolite EXP3174 in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1995;58(6):641–9.
Tenero D, Martin D, Ilson B, Jushchyshyn J, Boike S, Lundberg D, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously and orally administered eprosartan in healthy males: absolute bioavailability and effect of food. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1998;19(6):351–6.
Lee J, Han S, Jeon S, Hong T, Yim DS. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model of fimasartan applied to predict the influence of a high fat diet on its blood pressure-lowering effect in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;69(1):11–20.
Jeong ES, Kim YW, Kim HJ, Shin HJ, Shin JG, Kim KH, et al. Glucuronidation of fimasartan, a new angiotensin receptor antagonist, is mainly mediated by UGT1A3. Xenobiotica. 2015;45(1):10–8.
Shin KH, Kim TE, Kim SE, Lee MG, Song IS, Yoon SH, et al. The effect of the newly developed angiotensin receptor II antagonist fimasartan on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin in relation to OATP1B1 in healthy male volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011;58(5):492–9.
Lee JY, Choi YJ, Oh SJ, Chi YH, Paik SH, Lee KH, et al. Characterization of fimasartan metabolites in human liver microsomes and human plasma. Xenobiotica. 2015;46(1):50–1.
Kim CO, Lee HW, Oh ES, Seong SJ, Kim do Y, Lee J, et al. Influence of hepatic dysfunction on the pharmacokinetics and safety of fimasartan. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013;62(6):524–9.
Kim S, Lee J, Shin D, Lim KS, Kim YS, Jang IJ, et al. Effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics of fimasartan: a single-dose, open-label, phase I study. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:1723–31.
Dreisbach AW, Lertora JJ. The effect of chronic renal failure on drug metabolism and transport. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2008;4(8):1065–74.
Yi S, Kim TE, Yoon SH, Cho JY, Shin SG, Jang IJ, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction of fimasartan, a new angiotensin II receptor antagonist, with amlodipine in healthy volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011;57(6):682–9.
Jeon H, Lim KS, Shin KH, Kim J, Yoon SH, Cho JY, et al. Assessment of the drug-drug interactions between fimasartan and hydrochlorothiazide in healthy volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;59(1):84–91.
Gu N, Kim BH, Lim KS, Kim SE, Nam WS, Yoon SH, et al. The effect of fimasartan, an angiotensin receptor type 1 blocker, on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin in healthy Korean male volunteers: a one-sequence, two-period crossover clinical trial. Clin Ther. 2012;34(7):1592–600.
Yi S, Kim JW, Kim TE, Kim J, Jun YK, Choi J, et al. Effect of multiple doses of fimasartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of digoxin in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;49(5):321–7.
Kim JW, Yi S, Kim TE, Lim KS, Yoon SH, Cho JY, et al. Increased systemic exposure of fimasartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, by ketoconazole and rifampicin. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53(1):75–81.
Lee H, Yang HM, Lee HY, Kim JJ, Choi DJ, Seung KB, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of once-daily oral fimasartan 20 to 240 mg/d in Korean patients with hypertension: findings from two phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Clin Ther. 2012;34(6):1273–89.
Lee SE, Kim YJ, Lee HY, Yang HM, Park CG, Kim JJ, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of fimasartan, a new angiotensin receptor blocker, compared with losartan (50/100 mg): a 12-week, phase III, multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, dose escalation clinical trial with an optional 12-week extension phase in adult Korean patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. Clin Ther. 2012;34(3):552–68, 68 e1–9.
Lee H, Kim KS, Chae SC, Jeong MH, Kim DS, Oh BH. Ambulatory blood pressure response to once-daily fimasartan: an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active-comparator, parallel-group study in Korean patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Clin Ther. 2013;35(9):1337–49.
Israili ZH. Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2000;14(Suppl 1):S73–86.
Taylor AA, Siragy H, Nesbitt S. Angiotensin receptor blockers: pharmacology, efficacy, and safety. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011;13(9):677–86.
Rhee MY, Baek SH, Kim W, Park CG, Park SW, Oh BH, et al. Efficacy of fimasartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination in hypertensive patients inadequately controlled by fimasartan monotherapy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:2847–54.
Park JB, Sung KC, Kang SM, Cho EJ. Safety and efficacy of fimasartan in patients with arterial hypertension (Safe-KanArb study): an open-label observational study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2013;13(1):47–56.
Sanchez-Lemus E, Murakami Y, Larrayoz-Roldan IM, Moughamian AJ, Pavel J, Nishioku T, et al. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the rat adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 2008;149(10):5177–88.
Zhou J, Ando H, Macova M, Dou J, Saavedra JM. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade abolishes brain microvascular inflammation and heat shock protein responses in hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25(7):878–86.
Bregonzio C, Armando I, Ando H, Jezova M, Baiardi G, Saavedra JM. Anti-inflammatory effects of angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonism prevent stress-induced gastric injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;285(2):G414–23.
Ryu S, Shin JS, Cho YW, Kim HK, Paik SH, Lee JH, et al. Fimasartan, anti-hypertension drug, suppressed inducible nitric oxide synthase expressions via nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein-1 inactivation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(3):467–74.
Munger MA. Use of Angiotensin receptor blockers in cardiovascular protection: current evidence and future directions. P T. 2011;36(1):22–40.
Lee JY, Lee CW, Kim WJ, Ahn JM, Park DW, Kang SJ, et al. Antiatherosclerotic effects of the novel angiotensin receptor antagonist fimasartan on plaque progression and stability in a rabbit model: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013;62(2):229–36.
Fliss H, Gattinger D. Apoptosis in ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res. 1996;79(5):949–56.
Lee SW, Won JY, Lee HY, Lee HJ, Youn SW, Lee JY, et al. Angiopoietin-1 protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury through VE-cadherin dephosphorylation and myocardiac integrin-beta1/ERK/caspase-9 phosphorylation cascade. Mol Med. 2011;17(9–10):1095–106.
Solaini G, Harris DA. Biochemical dysfunction in heart mitochondria exposed to ischaemia and reperfusion. Biochem J. 2005;390(Pt 2):377–94.
Han J, Park SJ, Thu VT, Lee SR, le Long T, Kim HK, et al. Effects of the novel angiotensin II receptor type I antagonist, fimasartan on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(3):2851–9.
Chang SA, Lim BK, Lee YJ, Hong MK, Choi JO, Jeon ES. A novel angiotensin type I receptor antagonist, fimasartan, prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(5):559–68.
Lou M, Blume A, Zhao Y, Gohlke P, Deuschl G, Herdegen T, et al. Sustained blockade of brain AT1 receptors before and after focal cerebral ischemia alleviates neurologic deficits and reduces neuronal injury, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24(5):536–47.
Hosomi N, Nishiyama A, Ban CR, Naya T, Takahashi T, Kohno M, et al. Angiotensin type 1 receptor blockage improves ischemic injury following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2005;134(1):225–31.
Sandset EC, Bath PM, Boysen G, Jatuzis D, Korv J, Luders S, et al. The angiotensin-receptor blocker candesartan for treatment of acute stroke (SCAST): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9767):741–50.
Diener HC, Sacco RL, Yusuf S, Cotton D, Ounpuu S, Lawton WA, et al. Effects of aspirin plus extended-release dipyridamole versus clopidogrel and telmisartan on disability and cognitive function after recurrent stroke in patients with ischaemic stroke in the Prevention Regimen for Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes (PRoFESS) trial: a double-blind, active and placebo-controlled study. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(10):875–84.
Kim CK, Yang XL, Kim YJ, Choi IY, Jeong HG, Park HK, et al. Effect of long-term treatment with fimasartan on transient focal ischemia in rat brain. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:295925.
Kim C KM, Kang DR, Kim JY, Park JB, On behalf of the K-MetS study investigators. The efficacy of fimasartan for cardiovascular events and metabolic syndrome (K-MetS Study): rationale, design and participant characteristics. Pulse (Basel). 2013;1(1):177–85.
Acknowledgments
Drs. B.H. Oh and H.Y. Lee each contributed to writing the manuscript and figure creation. Drs. B.H. Oh and H.Y. Lee contributed equally to the data collection, data interpretation, and literature search, and were involved in all stages of manuscript development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was used in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Dr. B.H. Oh has been involved in the study design of fimasartan phase II and III studies and received consulting fees from Boryung Pharmaceuticals for this. Dr. H.Y. Lee has received a basic research grant from Boryung Pharmaceuticals. Drs. B.H. Oh and H.Y. Lee have given several lectures including discussion of fimasartan in scientific sessions. Drs. B.H. Oh and H.Y. Lee declare that they have no other conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HY., Oh, BH. Fimasartan: A New Angiotensin Receptor Blocker. Drugs 76, 1015–1022 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0592-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0592-1