Abstract
Introduction
Elagolix is a novel, orally active, non-peptide, competitive gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonist in development for the management of endometriosis with associated pain and heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids. The pharmacokinetics of elagolix have been well-characterized in phase I studies; however, elagolix population pharmacokinetics have not been previously reported. Therefore, a robust model was developed to describe elagolix population pharmacokinetics and to evaluate factors affecting elagolix pharmacokinetic parameters.
Methods
The data from nine clinical studies (a total of 1624 women) were included in the analysis: five phase I studies in healthy, premenopausal women and four phase III studies in premenopausal women with endometriosis.
Results
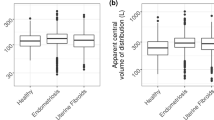
Elagolix population pharmacokinetics were best described by a two-compartment model with a lag time in absorption. Of the 15 covariates tested for effect on elagolix apparent clearance (CL/F) and/or volume of distribution only one covariate, organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1 genotype status, had a statistically significant, but not clinically meaningful, effect on elagolix CL/F.
Conclusion
Elagolix pharmacokinetics were not affected by patient demographics and were similar between healthy women and women with endometriosis.
Clinical Trial Registration Numbers NCT01403038, NCT01620528, NCT01760954, NCT01931670, NCT02143713.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy S, Bergqvist A, Chapron C, et al. ESHRE guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2005;20(10):2698–704.
Viganò P, Parazzini F, Somigliana E, Vercellini P. Endometriosis: epidemiology and aetiological factors. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;18(2):177–200.
Facchin F, Barbara G, Saita E, et al. Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and mental health: pelvic pain makes the difference. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 2015;36(4):135–41.
Struthers RS, Chen T, Campbell B, et al. Suppression of serum luteinizing hormone in postmenopausal women by an orally administered nonpeptide antagonist of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (NBI-42902). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(10):3903–7.
Struthers RS, Nicholls AJ, Grundy J, et al. Suppression of gonadotropins and estradiol in premenopausal women by oral administration of the nonpeptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist elagolix. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(2):545–51.
Ng J, Chwalisz K, Carter DC, Klein CE. Dose-dependent suppression of gonadotropins and ovarian hormones by elagolix in healthy premenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(5):1683–91.
Carr B, Dmowski WP, O’Brien C, et al. Elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist, versus subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for the treatment of endometriosis: effects on bone mineral density. Reprod Sci. 2014;21(11):1341–51.
Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):28–40.
Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice LC, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of elagolix treatment in women with endometriosis-associated pain: primary results from two phase 3 extension studies [abstract no. O-233]. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3 Suppl):e95–6.
Archer D, Ng J, Chiu Y-L, Klein C, Chwalisz K. Dose-dependent suppression of ovulation and ovarian activity by elagolix in healthy premenopausal women. Society for Reproductive Investigation (SRI) 64th annual meeting, 15–18 Mar 2017, Orlando.
Ng J, Chiu Y-L, Chwalisz K, Klein C. Effects of elagolix, an oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), on gonadotropins and ovarian sex hormones in healthy premenopausal women [poster no. PS02-003]. World Congress on Endometriosis (WCE), 17–20 May 2017, Vancouver.
Ng J, Archer D, Chiu Y-L, Klein C, Chwalisz K. Effects of elagolix, an oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), on ovulation, ovarian activity, and ovarian reserve in healthy premenopausal women [poster no. PS02-004]. World Congress on Endometriosis (WCE), 17–20 May 2017, Vancouver.
Chen C, Wu D, Guo Z, et al. Discovery of sodium r-(+)-4-{2-[5-(2-fluoro-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-(2-fluoro-6-[trifluoromethyl]benzyl)-4-methyl-2,6-dioxo-3,6-dihydro-2h-pyrimidin-1-yl]-1-phenylethylamino}butyrate (elagolix), a potent and orally available nonpeptide antagonist of the human gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. J Med Chem. 2008;51(23):7478–85.
Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Organic anion transporting polypeptides of the OATP/SLC21 family: Phylogenetic classification as OATP/SLCO superfamily, new nomenclature and molecular/functional properties. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447(5):653–65.
Ng J, Salem AH, Carter D, Williams LA, Klein CE. Effects of the coadministration of single and multiple doses of rifampin on the pharmacokinetics and safety of elagolix in healthy premenopausal females [poster no. PI-089]. American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (ASCPT), 8–12 Mar 2016, San Diego.
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011;13(2):143–51.
Acknowledgements
We thank AbbVie employee Sonja Kemmis Causemaker for medical writing support for this manuscript. We also thank AbbVie employee Xiaohua Du for dataset programming efforts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design and analysis and interpretation of the data. All authors participated in the drafting and revising of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
AbbVie provided financial support for the study and participated in the design, study conduct, analysis, and interpretation of data as well as the writing, review, and approval of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Insa Winzenborg, Ahmed Nader, Akshanth R. Polepally, Mohan Liu, Jacob Degner, Cheri E. Klein, Nael M. Mostafa, Peter Noertersheuser, and Juki Ng are employees of AbbVie, Inc. and may hold stock or stock options.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winzenborg, I., Nader, A., Polepally, A.R. et al. Population Pharmacokinetics of Elagolix in Healthy Women and Women with Endometriosis. Clin Pharmacokinet 57, 1295–1306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0629-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0629-6