Abstract
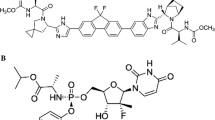
Ombitasvir is a potent, nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that is used in combination with other direct-acting antivirals for the treatment of chronic HCV infection. Ombitasvir is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism and is a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Ombitasvir displays linear pharmacokinetics with minimal accumulation and is eliminated via metabolism and biliary excretion. A negligible amount of unchanged drug is excreted in urine. Exposures are comparable across Chinese, Japanese, and non-Asian subjects. The pharmacokinetic characteristics of ombitasvir are similar in healthy subjects and HCV-infected patients, and are not appreciably altered by hepatic or renal impairment. Results from several drug interaction studies demonstrated that ombitasvir has a low potential for drug interactions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishnan P, Beyer J, Mistry N, Koev G, Reisch T, DeGoey D, et al. In vitro and in vivo antiviral activity and resistance profile of ombitasvir, an inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS5A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(2):979–87.
Menon RM, Polepally AR, Khatri A, Awni WM, Dutta S. Clinical pharmacokinetics of paritaprevir. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0520-x.
King JR, Zha J, Khatri A, Dutta S, Menon RM. Clinical pharmacokinetics of dasabuvir. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0519-3.
Kowdley KV, Lawitz E, Poordad F, Cohen DE, Nelson DR, Zeuzem S, et al. Phase 2b trial of interferon-free therapy for hepatitis C virus genotype 1. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(3):222–32.
Viekirax. Summary of product characteristics. UK: AbbVie Ltd; 2015.
Viekira Pak (ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir tablets; dasabuvir tablets) [US package insert]. North Chicago, IL; AbbVie Inc., 2016.
Technivie (ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir tablets). North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2016.
Chayama K, Notsumata K, Kurosaki M, Sato K, Rodrigues L Jr, Setze C, et al. Randomized trial of interferon- and ribavirin-free ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir in treatment-experienced hepatitis C virus-infected patients. Hepatology. 2015;61(5):1523–32.
Badri PS, King JR, Polepally AR, McGovern BH, Dutta S, Menon RM. Dosing recommendations for concomitant medications during 3D anti-HCV therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(3):275–95.
Dumas E, Lawal A, Menon RM, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of the HCV NS5A inhibitor ABT-267 following single and multiple doses in healthy adult volunteers. J Hepatol. 2011;54(Suppl 1):S475–6.
Epstein M, Felizarta F, Marbury T, Badri P, Mullally V, Pilot-Matias T, et al. Study of ABT-267 2-day monotherapy followed by 12-week combination therapy in treatment-naive patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. J Hepatol. 2013;58(Suppl):S484.
Shen J, Serby M, Surber B, Lee AJ, Ma J, Badri P, et al. Metabolism and disposition of pan-genotypic inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS5A ombitasvir in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016;44(8):1148–57.
Khatri A, Menon RM, Marbury TC, Lawitz EJ, Podsadecki TJ, Mullally VM, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of co-administered paritaprevir plus ritonavir, ombitasvir, and dasabuvir in hepatic impairment. J Hepatol. 2015;63(4):805–12.
Khatri A, Dutta S, Marbury T, Preston RA, Rodrigues L Jr, Wang H, et al. Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of anti-hepatitis C virus treatment with ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, in subjects with renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(2):153–63.
Pockros PJ, Reddy KR, Mantry PS, Cohen E, Bennett M, Sulkowski MS, et al. LO1: safety of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir plus dasabuvir for treating HCV GT1 infection in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease: The RUBY-I study. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S257.
Polepally AR, Badri PS, Eckert D, Mensing S, Menon RM. Effects of mild and moderate renal impairment on ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, dasabuvir, and ribavirin pharmacokinetics in patients with chronic HCV infection. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016. doi:10.1007/s13318-016-0341-6 (Epub 10 May 2016).
Mensing S, Eckert D, Sharma S, Polepally AR, Khatri A, Podsadecki TJ, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of paritaprevir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir, ritonavir and ribavirin in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: analysis of six phase III trials. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. doi:10.1111/bcp.13138 (Epub 23 Sep 2016).
Holkira Pak (ombitasvir/pritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir) product monograph. St-Laurent, QC: AbbVie Corporation; 2016.
Menon RM, Badri PS, Wang T, Polepally AR, Zha J, Khatri A, et al. Drug-drug interaction profile of the all-oral anti-hepatitis C virus regimen of paritaprevir/ritonavir, ombitasvir, and dasabuvir. J Hepatol. 2015;63(1):20–9.
Badri PS, Dutta S, Wang H, Podsadecki TJ, Polepally AR, Khatri A, et al. Drug interactions with the direct-acting antiviral combination of ombitasvir and paritaprevir-ritonavir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;60(1):105–14.
Badri P, Dutta S, Coakley E, Cohen D, Ding B, Podsadecki T, et al. Pharmacokinetics and dose recommendations for cyclosporine and tacrolimus when coadministered with ABT-450, ombitasvir, and dasabuvir. Am J Transplant. 2015;15(5):1313–22.
Badri PS, Parikh A, Coakley EP, Ding B, Awni WM, Dutta S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus and cyclosporine in liver transplant recipients receiving 3 direct-acting antivirals as treatment for hepatitis C infection. Ther Drug Monit. 2016;38(5):640–5.
Bow DAJ, Liu J, Kavetskaia O, Menon R, de Morais SM, Nijsen M. A mechanistic non-clinical assessment of drug-drug interactions (metabolism and transporters) with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) regimen: ABT-450/r, ombitasvir and dasabuvir. AASLD/EASL Special Conference on Hepatitis C. New York, NY. 3–5 October, 2014.
Khatri A, Dutta S, Dunbar M, Podsadecki T, Trinh R, Awni W, et al. Evaluation of drug-drug interactions between direct-acting anti-hepatitis C Virus combination regimens and the HIV-1 antiretroviral agents raltegravir, tenofovir, emtricitabine, efavirenz, and rilpivirine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(5):2965–71.
Polepally AR, King JR, Ding B, Shuster DL, Dumas EO, Khatri A, et al. Drug-drug interactions between the anti-hepatitis C virus 3D regimen of ombitasvir, paritaprevir/ritonavir, and dasabuvir and eight commonly used medications in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(8):1003–14.
Khatri A, Dutta S, Wang H, Podsadecki T, Trinh R, Awni W, et al. Evaluation of drug-drug interactions between hepatitis C antiviral agents ombitasvir, paritaprevir/ritonavir, and dasabuvir and HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(8):972–9.
King JR, Dutta S, Cohen D, Podsadecki TJ, Ding B, Awni WM, et al. Drug-drug interactions between sofosbuvir and ombitasvir-paritaprevir-ritonavir with or without dasabuvir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;60(2):855–61.
Zha J, Badri PS, Ding B, Uchiyama N, Alves K, Rodrigues-Jr L, et al. Drug interactions between hepatoprotective agents ursodeoxycholic acid or glycyrrhizin and ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir in healthy Japanese subjects. Clin Ther. 2015;37(11):2560–71.
Khatri A, Trinh R, Zhao W, Podsadecki T, Menon R. Drug-drug interaction between the direct-acting antiviral regimen of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir plus dasabuvir and the HIV antiretroviral agents dolutegravir or abacavir plus lamivudine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(10):6244–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank AbbVie employees Allison M. Kitten and Sonja J. Causemaker for medical writing support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The studies summarized in this report were supported by AbbVie, who contributed to the study designs, research, and interpretation of data, and the writing, reviewing, and approving of the publication.
Conflict of interest
Prajakta S. Badri, Diana L. Shuster, Sandeep Dutta, and Rajeev M. Menon are current or former AbbVie employees and may own AbbVie stock or stock options.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badri, P.S., Shuster, D.L., Dutta, S. et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ombitasvir. Clin Pharmacokinet 56, 1103–1113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0518-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0518-4