Abstract
Background and Objective
Levetiracetam is available in China as adjunctive oral therapy for partial-onset seizures. This study was conducted to evaluate the bioequivalence between single-dose intravenous infusion and oral levetiracetam 1500 mg (Part A), and to assess the pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose intravenous infusion at the same dose (Part B) in healthy Chinese subjects.
Methods
Part A was an open-label, crossover comparison (intravenous vs. oral), while Part B was a double-blind, parallel-group study of intravenous levetiracetam versus intravenous placebo administered for 5 days.
Results
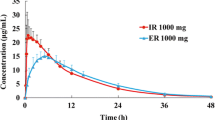
Bioequivalence was demonstrated between the 45-min intravenous infusion and oral tablets, with geometric mean area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) from time 0 to infinity (AUC∞) 492.3 and 506.8 μg⋅h/mL, and geometric mean maximum concentration (C max) 65.12 and 55.93 μg/mL for intravenous infusion and oral dosing, respectively. Linear pharmacokinetics were demonstrated (geometric least-squares mean AUC during the dosing interval τ at steady state (AUC τ,ss) 475.6 μg⋅h/mL; geometric least-squares mean AUC∞ after single dose 501.7 μg⋅h/mL; linearity factor = 0.948). Geometric mean C max (77.44 μg/mL) and AUC τ,ss (475.6 μg⋅h/mL) of intravenous infusion levetiracetam 1500 mg after multiple doses were within the expected range, based on their respective single-dose values and the terminal half-life of levetiracetam after a single dose (7.13 h). A theoretical accumulation of approximately 40 % would be expected after multiple doses, which is consistent with the calculated accumulation of 18.0 and 43.5 % (R max and R AUC, respectively).
Conclusions
Intravenous infusion of levetiracetam is bioequivalent to oral levetiracetam in healthy Chinese subjects and is a suitable alternative for levetiracetam administration in patients who are temporarily unable to take their medication orally.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patsalos PN. Pharmacokinetic profile of levetiracetam: toward ideal characteristics. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;85:77–85.
Perucca E, Gidal BE, Baltès E. Effects of antiepileptic comedication on levetiracetam pharmacokinetics: a pooled analysis of data from randomized adjunctive therapy trials. Epilepsy Res. 2003;53:47–56.
Ramael S, De Smedt F, Toublanc N, Otoul C, Boulanger P, Riethuisen JM, et al. Single-dose bioavailability of levetiracetam intravenous infusion relative to oral tablets and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and tolerability of levetiracetam intravenous infusion compared with placebo in healthy subjects. Clin Ther. 2006;28:734–44.
Ramael S, Daoust A, Otoul C, Toublanc N, Troenaru M, Lu Z, et al. Levetiracetam intravenous infusion: a randomized, placebo-controlled safety and pharmacokinetic study. Epilepsia. 2006;47(7):1128–35.
Baulac M, Brodie MJ, Elger CE, Krakow K, Stockis A, Meyvisch P, et al. Levetiracetam intravenous infusion as an alternative to oral dosing in patients with partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia. 2007;48(3):589–92.
Yamamoto J, Toublanc N, Kumagai Y, Stockis A. Levetiracetam pharmacokinetics in Japanese subjects with renal impairment. Clin Drug Investig. 2014;34:819–28.
Stockis A, Lu S, Tonner F, Otoul C. Clinical pharmacology of levetiracetam for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2009;2(4):339–50.
Zhao Q, Jiang J, Li XM, Lu Z, Hu P. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in healthy Chinese male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(5):614–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fiona Swain (Mediwrite Ltd, UK) for providing medical writing support funded by UCB Pharma, and Barbara Pelgrims and Azita Tofighy (UCB Pharma) for editorial support and coordinating the manuscript development process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by UCB Pharma, who were involved in the design and conduct of the study, and collection, management, and analysis of the data.
Conflicts of interest
Nathalie Toublanc, Xinlu Du, Armel Stockis, Pritibha Singh and Robert Chan were employees of UCB Pharma at the time the study was conducted. Yun Liu and Qian Chen were employees of the Clinical Research Unit at Shanghai Xuhui Central Hospital, which conducted the clinical phase of the study for UCB Pharma, and have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The research followed the ethical principles for medical research set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki 1964, as modified by subsequent revisions. Approval for the study was obtained from an Independent Review Board and informed consent was obtained in writing from all participants prior to initiating any study-related medical procedure.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toublanc, N., Du, X., Liu, Y. et al. Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Bioequivalence of Levetiracetam Intravenous Infusion and Oral Tablets in Healthy Chinese Subjects. Clin Drug Investig 35, 495–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0303-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0303-9