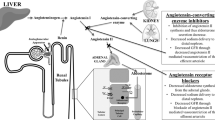
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global health problem and is strongly associated with hypertension (HTN) and impaired quality of life. Managing HTN with agents that block the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) remains the gold standard, however there is a misleading impression that patients with impaired renal function or those receiving hemodialysis should not be treated with RAAS inhibitors. To date, only a few data in this field are available, given that this population subset is systematically excluded from many major clinical trials. The purpose of this review was to solve the difficult equation regarding the optimal use of RAAS blockade in patients with CKD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395(10225):709–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3.
Mills KT, Stefanescu A, He J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(4):223–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0244-2.
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19.1 million participants. Lancet. 2017;389(10064):37–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31919-5.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1269–324. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYP.0000000000000066.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021–104. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339.
KDIGO Executive Committee. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO clinical practice guideline on the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. KDIGO. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/KDIGO-BP-Management-in-CKD-GL-public-review-draft-Jan-31-2020.pdf. Accessed Jan 2020.
Pugh D, Gallacher PJ, Dhaun N. Management of hypertension in chronic kidney disease. Drugs. 2019;79(4):365–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-1064-1.
Cheung AK, Rahman M, Reboussin DM, Craven TE, Greene T, Kimmel PL, et al. Effects of intensive BP control in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(9):2812–23. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017020148.
Remuzzi G, Perico N, Macia M, Ruggenenti P. The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;99:S57-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.09911.x.
Zhang F, Liu H, Liu D, Liu Y, Li H, Tan X, et al. Effects of RAAS inhibitors in patients with kidney disease. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017;19(9):72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0771-9.
Siragy HM, Carey RM. Role of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2010;31(6):541–50. https://doi.org/10.1159/000313363.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(20):1456–62. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199311113292004.
Maschio G, Alberti D, Janin G, Locatelli F, Mann JF, Motolese M, et al. Effect of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor benazepril on the progression of chronic renal insufficiency. The Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibition in Progressive Renal Insufficiency Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(15):939–45. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199604113341502.
Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Mosconi L, Matalone M, Tognoni G, Remuzzi G, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of effect of ramipril on decline in glomerular filtration rate and risk of terminal renal failure in proteinuric, non-diabetic nephropathy The GISEN Group (Gruppo Italiano di Studi Epidemiologici in Nefrologia). Lancet. 1997;349(9069):1857–63.
Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Gherardi G, Garini G, Zoccali C, Salvadori M, et al. Renoprotective properties of ACE-inhibition in non-diabetic nephropathies with non-nephrotic proteinuria. Lancet. 1999;354(9176):359–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(98)10363-X.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):861–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011161.
Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P, et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):870–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011489.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):851–60. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011303.
Agodoa LY, Appel L, Bakris GL, Beck G, Bourgoignie J, Briggs JP, et al. Effect of ramipril vs amlodipine on renal outcomes in hypertensive nephrosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285(21):2719–28. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.21.2719.
Wright JT Jr, Bakris G, Greene T, Agodoa LY, Appel LJ, Charleston J, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease: results from the AASK trial. JAMA. 2002;288(19):2421–31. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.19.2421.
Viberti G, Wheeldon NM. Microalbuminuria reduction with VSI. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation. 2002;106(6):672–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000024416.33113.0a.
Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva A, Iliev IP, Chiurchiu C, Rubis N, et al. Effects of verapamil added-on trandolapril therapy in hypertensive type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria: the BENEDICT-B randomized trial. J Hypertens. 2011;29(2):207–16.
Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, Bruno S, Iliev IP, Brusegan V, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(19):1941–51.
Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, et al. Prevention of transition from incipient to overt nephropathy with telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(6):1577–8. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-1998.
Heerspink HJ, Persson F, Brenner BM, Chaturvedi N, Brunel P, McMurray JJ, et al. Renal outcomes with aliskiren in patients with type 2 diabetes: a prespecified secondary analysis of the ALTITUDE randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(4):309–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00469-6.
Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(Suppl 2):B54-64.
Rahman M, Ford CE, Cutler JA, Davis BR, Piller LB, Whelton PK, et al. Long-term renal and cardiovascular outcomes in Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) participants by baseline estimated GFR. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(6):989–1002. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.07800811.
DREAM Trial Investigators, Dagenais GR, Gerstein HC, Holman R, Budaj A, Escalante A, et al. Effects of ramipril and rosiglitazone on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in people with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: results of the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) trial. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(5):1007–14. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-1868.
Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L, Cavalli A. Inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system in chronic kidney disease: a critical look to single and dual blockade. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009;113(4):c286–93. https://doi.org/10.1159/000235946.
Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9638):547–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61236-2.
Xie X, Liu Y, Perkovic V, Li X, Ninomiya T, Hou W, et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD: a bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;67(5):728–41. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.10.011.
Potier L, Roussel R, Elbez Y, Marre M, Zeymer U, Reid CM, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in high vascular risk. Heart. 2017;103(17):1339–46. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310705.
Lin CC, Wu YT, Yang WC, Tsai MJ, Liu JS, Yang CY, et al. Angiotensin receptor blockers are associated with lower mortality than ACE inhibitors in predialytic stage 5 chronic kidney disease: a nationwide study of therapy with renin-angiotensin system blockade. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(12):e0189126. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189126.
Bakris G, Burgess E, Weir M, Davidai G, Koval S, AMADEO Study Investigators. Telmisartan is more effective than losartan in reducing proteinuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2008;74(3):364–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2008.204.
Galle J, Schwedhelm E, Pinnetti S, Boger RH, Wanner C, Investigators V. Antiproteinuric effects of angiotensin receptor blockers: telmisartan versus valsartan in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(10):3174–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfn230.
Brown T, Gonzalez J, Monteleone C. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: a review of the literature. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2017;19(12):1377–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13097.
Brookhart MA, Wyss R, Layton JB, Sturmer T. Propensity score methods for confounding control in nonexperimental research. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2013;6(5):604–11. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.113.000359.
Makani H, Messerli FH, Romero J, Wever-Pinzon O, Korniyenko A, Berrios RS, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized trials of angioedema as an adverse event of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(3):383–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.03.034.
Schmidt M, Mansfield KE, Bhaskaran K, Nitsch D, Sorensen HT, Smeeth L, et al. Serum creatinine elevation after renin-angiotensin system blockade and long term cardiorenal risks: cohort study. BMJ. 2017;356:j791. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j791.
Turgut F, Balogun RA, Abdel-Rahman EM. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade effects on the kidney in the elderly: benefits and limitations. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(7):1330–9. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.08611209.
Goncalves AR, Khwaja A, Ahmed AK, El Kossi M, El Nahas M. Stopping renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in chronic kidney disease: predictors of response. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;119(4):c348–54. https://doi.org/10.1159/000330289.
Ahmed AK, Kamath NS, El Kossi M, El Nahas AM. The impact of stopping inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(12):3977–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfp511.
Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(5 Suppl 1):S1-290.
Qiao Y, Shin JI, Chen TK, Inker LA, Coresh J, Alexander GC, et al. Association between renin-angiotensin system blockade discontinuation and all-cause mortality among persons with low estimated glomerular filtration rate. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(5):718–26. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0193.
Inrig JK. Antihypertensive agents in hemodialysis patients: a current perspective. Semin Dial. 2010;23(3):290–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-139X.2009.00697.x.
Karaboyas A, Xu H, Morgenstern H, Locatelli F, Jadoul M, Nitta K, et al. DOPPS data suggest a possible survival benefit of renin angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and other antihypertensive medications for hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2018;94(3):589–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.03.013.
Moist LM, Port FK, Orzol SM, Young EW, Ostbye T, Wolfe RA, et al. Predictors of loss of residual renal function among new dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(3):556–64.
Yoo KD, Kim CT, Kwon S, Lee J, Oh YK, Kang SW, et al. Renin angiotensin aldosterone system blockades does not protect residual renal function in patients with hemodialysis at 1 year after dialysis initiation: a prospective observational cohort study. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):18103. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54572-6.
Bhandari S, Ives N, Brettell EA, Valente M, Cockwell P, Topham PS, et al. Multicentre randomized controlled trial of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker withdrawal in advanced renal disease: the STOP-ACEi trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(2):255–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfv346.
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(20):1892–903. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1303154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was used to assist in the preparation of this review.
Conflicts of interest
Elias Sanidas, Dimitrios Papadopoulos, Michalis Chatzis, Maria Velliou, and John Barbetseas have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The authors declare that all relevant data are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author contributions
All authors contributed equally to this review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanidas, E., Papadopoulos, D., Chatzis, M. et al. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Difficult Equation. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 21, 619–627 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40256-021-00467-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40256-021-00467-9