Abstract
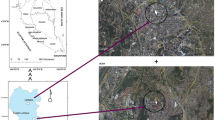
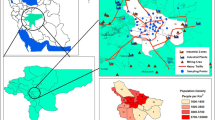
Haze weather frequently occurs in many cities in China. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) in fine particulate matter(PM2.5) can adversely affect the environment and human health. In this paper, PM2.5 samples were collected at nine sites in a city in northeastern China from September 2013 to October 2014. Sixteen USEPA(US Evironment Protection Agency) priority PAHs in PM2.5 were analyzed to determine their spatial and temporal distribution characteristics. The source apportionment of PAHs was conducted with the Positive Matrix Factorization(PMF) model. The results indicate that the concentrations of total PAHs(T-PAHs) in PM2.5 are within the range of 0.26 to 72.48 ng/m3. The seasonal variation of T-PAHs is winter>spring>autumn>summer, and the space distribution of PAHs is JZP>DP>BFH>LP> EESA>IPT>CP>HZMC>JYP. In all types of PAHs, three-ring and five-ring PAHs are significantly prominent(62%) in the heating period due to petrogenic sources and traffic emissions. Middle- and high-ring PAHs in the non-heating period are caused by coal combustion and vehicle exhaust, which accounts for 77% of the total emissions. The source apportionment results obtained by the diagnostic ratio of PAHs reflect that coal burning, traffic and other sources have a distinct influence on PAH emissions in this city. Six factors are defined by PMF v5.0, namely, coke oven emissions(7.7%), biomass burning(44.3%), petrogenic sources(10.7%), coal combustion(10.4%), gasoline engine emissions(16.7%), and diesel engine emissions(10.3%). The results indicate that the PAHs in PM2.5 in the city are primarily caused by combustion processes and vehicle exhaust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobson M. C., Hansson H. C., Noone K. J., Charlson R. J., Reviews of Geophysics, 2000, 38(2), 267
Meng Q. Z., Fan S. X., He J. B., Zhang J., Sun Y., Zhang Y., Zu F., Particuology, 2015, 18(1), 127
Lu G. H., Chen W., Li Y., Zhu Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2011, 27(3), 413
Wang C., Zhang L. L., Dao X., Teng E. J., Li G. G., China Environmental Science, 2015, 35, 1
Amato F., Hopke P. K., Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 46(3), 329
Qin Y. J., Kim E., Hopke P. K., Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(2), S312
Hopke P. K., Journal of Chemometrics, 2003, 17(5), 255
Zhang D. H., Ma Y. L., He K. B., Duan F. K., Jia Y. T., Okuda T., Tanaka. S., Environmental Science, 2006, 27(7), 1269
Li W. F., Bai Z. P., Wei J. D., Liu A. X., Zhao Y. J., Jin T. S., China Environmental Science, 2008, 28(6), 481
Li J., Zhang G., Qi S. H., Environmental Science, 2004, 25(3), 7
Xu P., Zhang Z. E., Zhang F., Qiu D. L., Shen J. S., Modern Chemical Industry, 2016, 36(2), 46
Yang L. L., Wang M. F., Zhang Y. Y., Hu E. Y., Wu L. J., Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(1), 53
Zhang Y., Liu H., Zhang J. Q., Zhou J. J., Xu H. M., Zheng J. R., Yao R. Z., Xiao W. S., Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2014, 21(2), 28
Gao B., Wang X. M., Zhao X. Y., Ding X., Fu X. X., Zhang Y. L., He Q. F., Zhang Z., Liu T. Y., Huang Z. Z., Chen L. G., Peng Y., Guo H., Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 103, 114
Wang J. Z., Zhu C. Z., Chen T. H., Environmental Science Processes & Impacts, 2013, 15(6), 104
Wang J., Geng N. B., Xu Y. F., Environ Monitor Assess, 2014, 186(11), 7461
Hanedar A., Alp K., Kaynak B., Baek J., Avsar E., Odman M. T., Atmospheric Research, 2011, 99(3/4), 391
Norris G., Vedantham R., Wade K., Brown S., Prouty J., Foley C., EPA Positive Matrix Factorization(PMF) 3.0. Fundamentals User Guide, USEnvironmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Washington DC,2008
Molnár P., Johannesson S., Quass U., Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2014, 14(3), 725
Liu G., Li J. H., Wu D., Xu H., Particuology, 2015, 18(1), 135
Mansha M., Ghauri B., Rahman S., Amman A., Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 425(3), 176
Wang S. R., Yu Y. Y., Wang Q. G., Lu Y., Yin L. N., Zhang Y. Y., Lu X. B., China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(12), 3535
Chen Y., Zeng Y., Zhang Q., Peng Q. Q., Luo Y. P., Li W., Sichuan Environment, 2014, 33(6), 81
Wei Y. X., Tong Y. Q., Yin Y., Chen K., Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2009, 32(3), 451
Pan B. F., Zhao Y. L., Li J. J., Wang R. B., Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 25(6), 41
Zhang Z. X., Study on the Distribution Characters of PAHs in Particulate Matter in Typical Cities of Jilin Province, Jilin University, Changchun, 2012
Dong H. L., Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Inhalable Particulate Matter and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Handan City, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 2008
Yunker M. B., Macdonld R. W., Vingarzanr R., Mitchell R. H., Goyette D., Sylvestre S., Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(4), 489
Meng Q. Z., Fan S. X., He J. B., Zhang J., Sun Y., Zhang Y., Zu F., Particuology, 2015, 18(1), 127
Hou X. M., Zhuang G. S., Sun Y. L., An Z. S., Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(18), 3251
Akyüz M., Çabuk H., Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(22), 5550
Vasilakos C., Levi N., Maggos T., Hatzianestis J., Michopoulos J., Helmis C., Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 140(1/2), 45
Torre-Roche D. L., Roberto J., Lee W. Y., Campos-Díaz S. I., Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 163(2/3), 946
Khan M. F., Latif M. T., Lim C. H., Amil N., Jaafar S. A., Dominick D., Nadzir M. S. M., Sahani M., Tahir N. M., Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 106(178), 178
Akyüz M., Çabuk H., Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 170(1), 13
Mantis J., Chaloulakou A., Samara C., Chemosphere, 2005, 59(5), 593
Wang J., Li X., Jiang N., Zhang W. K., Zhang R. Q., Tang X. Y., Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 104, 228
Wang X., Cheng H., Xu X., Zhuang G., Zhao C., Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 157(1), 47
Chen X. Y., Study on the Composition Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Typical Particulate Matter Pollution Sources, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 2005
Guo L., Analysis on the PAHs and Their Sources on Fine Particulate Matter(PM2.5) of Nanchang City, Nanchang University, Nanchang, 2007
Liu Y., Chen L., Huang Q. H., Li W. Y., Tang Y. J., Zhao J. F., Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(8), 2931
Sarkar S., Khillare P. S., Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(2), 1199
Li C. K., Kamens R. M., Atmospheric Environment Part A General Topics, 1993, 27(4), 523
Harrison R. M.D., Smith J. T., Luhana L., Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(3), 825
Miguel A. H., Kirchstetter T. W., Harley R. A., Hering S. V., Environmental Science Technology, 1998, 32(4), 450
Mu L., Emission Characteristics of Particulates and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Coking Processes, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, 2010
Wang Q. F., Application of UNMIX-CMB Combined Model to Source Apportionment of PAHs in Ambient Air, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, 2011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Foundation of Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department, China(No.20130204051SF) and the Foundation of Jilin Provincial Environment Protection Department, China(No.2013EP01-03).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yang, L., Ma, T. et al. Source apportionment research of fine particulate matter in the atmosphere by PAHs. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 32, 746–753 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-016-5516-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-016-5516-9