Abstract
Background
The in vivo assessment of a novel compound is a pivotal step in the development of a new drug. In this study, we selected 1-(2-bromophenyl)-1,11-dihydro-3H-benzo[h]pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-3,12(2H)-dione (2-BDBPQD), identified as an exemplary α-glucosidase inhibitor in preliminary in vitro assays, for further evaluation in an in vivo anti-diabetic context.
Methods
The in vivo anti-diabetic effect of 2-BDBPQD was assessed using a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic Wistar rat model. Recognizing the relevance of lipid factors in diabetes, we also investigated the impact of this compound on the lipid profile of diabetic Wistar rats. In silico studies, encompassing docking studies and pharmacokinetic predictions of 2-BDBPQD, were conducted.
Results
The results obtained indicated a significant reduction in blood glucose levels with 2-BDBPQD treatment compared to acarbose. However, no significant effects on the lipid profile were observed. In silico studies revealed that 2-BDBPQD interacted with key residues in the α-glucosidase active site and exhibited favorable pharmacokinetic properties.
Conclusion
In summary, the study demonstrated the in vivo anti-hyperglycemic activity of 2-BDBPQD. Nevertheless, further in vivo evaluations are recommended to comprehensively assess its potential as a new drug for the treatment of diabetes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- T1DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- T1DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2
- 2-BDBPQD:
-
1-(2-bromophenyl)-1,11-dihydro-3H-benzo[h]pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-3,12(2H)-dione
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- BGL:
-
Blood glucose level
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- BBB:
-
Blood brain barrier
- HIA:
-
Human intestinal absorption
References
Lotfy M, Adeghate J, Kalasz H, Singh J, Adeghate E. Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: a mini review. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(1):3–10.
Oguntibeju OO. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: examining the links. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2019;11(3):45.
Leon BM, Maddox TM. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: epidemiology, biological mechanisms, treatment recommendations and future research. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(13):1246.
Mukhtar Y, Galalain A, Yunusa U. A modern overview on diabetes mellitus: a chronic endocrine disorder. Eur J Biol Biotechnol. 2020;5(2):1–4.
Whalen K, Miller S, Onge ES. The role of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Clin Ther. 2015;37(6):1150–66.
Corder AM, Henry RJ. Carbohydrate-degrading enzymes in germinating wheat. Cereal Chem. 1989;66(5):435–9.
Eldor R, DeFronzo RA, Abdul-Ghani M. In vivo actions of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors: glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(Supplement_2):S162–74.
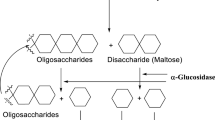
Chiba S. Molecular mechanism in α-glucosidase and glucoamylase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1997;61(8):1233–9.
Wu B, Yan J, Yang J, Xia Y, Li D, Zhang F, Cao H. Extension of the life span by Acarbose: is it mediated by the gut microbiota? Aging Dis. 2022;13(4):1005.
Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani M, Nori M, Valizadeh Y, Javanshir S, Dastyafteh N, Moaazam A, Hosseini S, Larijani B, Adibi H, Biglar M, Hamedifar H. New 4-phenylpiperazine-carbodithioate-N-phenylacetamide hybrids: synthesis, in vitro and in silico evaluations against cholinesterase and α-glucosidase enzymes. Arch Pharm. 2022;355(5):2100313.
Nikookar H, Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani M, Imanparast S, Faramarzi MA, Ranjbar PR, Mahdavi M, Larijani B. Design, synthesis and in vitro α-glucosidase inhibition of novel dihydropyrano [3, 2-c] quinoline derivatives as potential anti-diabetic agents. Bioorg Chem. 2018;77:280–6.
Lee BH, Lee CC, Wu SC. Ice plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum) improves hyperglycaemia and memory impairments in a Wistar rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Sci Food Agric. 2014;94(11):2266–73.
Chinthala Y, Thakur S, Tirunagari S, Chinde S, Domatti AK, Arigari NK, Srinivas KV, Alam S, Jonnala KK, Khan F, Tiwari A. Synthesis, docking and ADMET studies of novel chalcone triazoles for anti-cancer and anti-diabetic activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;93:564–73.
Seul SC. Bioinformatics and Molecular Design Research Center. PreADMET program. 2004. http://preadmet.bmdrc.org.
Noori M, Davoodi A, Iraji A, Dastyafteh N, Khalili M, Asadi M, Mohammadi Khanaposhtani M, Mojtabavi S, Dianatpour M, Faramarzi MA, Larijani B. Design, synthesis, and in silico studies of quinoline-based-benzo [d] imidazole bearing different acetamide derivatives as potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):14019.
Noori M, Rastak M, Halimi M, Ghomi MK, Mollazadeh M, Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani M, Sayahi MH, Rezaei Z, Mojtabavi S, Faramarzi MA, Larijani B. Design, synthesis, in vitro, and in silico enzymatic evaluations of thieno [2, 3-b] quinoline-hydrazones as novel inhibitors for α-glucosidase. Bioorg Chem. 2022;127:105996.
Taj S, Ahmad M, Ashfaq UA. Exploring of novel 4-hydroxy-2H-benzo [e][1, 2] thiazine-3-carbohydrazide 1, 1-dioxide derivative as a dual inhibitor of α-glucosidase and α-amylase: molecular docking, biochemical, enzyme kinetic and in-vivo mouse model study. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;207:507–21.
Khan HA, Sobki SH, Khan SA. Association between glycaemic control and serum lipids profile in type 2 diabetic patients: HbA 1c predicts dyslipidaemia. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2007;7:24–9.
Acknowledgments
The ethics code for this work is IR. IAU. AMOL. REC. 1400.010. Furthermore, the authors thankfully acknowledge the scientific support provided by Research and Technology Empowerment Committee of Babol University of Medical Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zare, N., Bandarian, F., Esfahani, E.N. et al. In vivo and in silico evaluations of a synthetic pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline derivative as a potent anti-diabetic agent. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01355-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01355-6