Abstract
Purpose
Recently, an association has been observed between metabolic syndrome and erectile dysfunction (ED). This study aimed to evaluate the cardiometabolic index (CMI) in patients with ED.
Methods
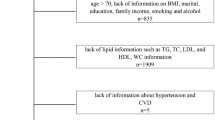
This cross-sectional study was performed on 144 patients with ED who were referred to a urology clinic in Rasht, Iran, from 2019 to 2021. Metabolic syndrome was evaluated according to National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel (NCEP) and Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) criteria which are considered three positive criteria from five. Also, the ED severity was classified as weak, moderate, and severe based on the five-item International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF5) questionnaire.
Results
The mean age of participants was 53.46 ± 10.58 years. 56.9% had abdominal obesity, 48.6% had hypertriglyceridemia, 34.7% had low HDL-C, 55.6% had hypertension and 56.9% had elevated fasting blood sugar (FBS). 43.8% had diabetes and 13.2% had cardiovascular disease. The mean CMI was 2.51 ± 1.57. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 50.7%. Body mass index (BMI) was significantly associated with metabolic syndrome and CMI (P = 0.001). The severity of ED had a significant relationship with high FBS in patients. CMI and components of abdominal obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL-C had no statistically significant relationship with ED. However, the incidence of moderate and severe ED increased with increasing the number of metabolic syndrome components.
Conclusion
ED is not significantly associated with metabolic syndrome and CMI, however, the severity of this disorder increases with increasing the number of components of metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP III:
-
Adult Treatment Panel III
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CMI:
-
Cardiometabolic index
- ED:
-
Erectile dysfunction
- FBS:
-
Fasting blood suger
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- IIEF:
-
International Index of Erectile Function
- NCEP:
-
National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- WHtR:
-
Waist-to-height ratio
References
Muneer A, Kalsi J, Nazareth I et al. Erectile Dysfunct Bmj. 2014;348.
Kessler A, Sollie S, Challacombe B et al. The global prevalence of erectile dysfunction: a review. BJU Int. 2019.
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6.
Rew KT, Heidelbaugh JJ. Erectile Dysfunction. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:820–7.
Yafi FA, Jenkins L, Albersen M, et al. Erectile dysfunction. Nat Reviews Disease Primers. 2016;2:16003.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, et al. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61.
Grover SA, Lowensteyn I, Kaouache M, et al. The prevalence of erectile dysfunction in the primary care setting: importance of risk factors for diabetes and vascular disease. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:213–9.
Kloner RA. Erectile dysfunction in the cardiac patient. Curr Urol Rep. 2003;4:466–71.
Dursun M, Besiroglu H, Otunctemur A, et al. Association between cardiometabolic index and erectile dysfunction: a new index for predicting cardiovascular disease. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016;32:620–3.
Liu X, Wu Q, Yan G, et al. Cardiometabolic index: a new tool for screening the metabolically obese normal weight phenotype. J Endocrinol Investig. 2021;44:1253–61.
Zou J, Xiong H, Zhang H, et al. Association between the cardiometabolic index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: insights from a general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:1–10.
Hamidi Madani A, Heidarzadeh A, Akbari Parsa N, et al. A survey on relative frequency of metabolic syndrome and testosterone deficiency in men with erectile dysfunction. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44:667–72.
Huang PL. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Models Mech. 2009;2:231–7.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, et al. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1997;49:822–30.
Wakabayashi I, Daimon T. The “cardiometabolic index” as a new marker determined by adiposity and blood lipids for discrimination of diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;438:274–8.
Shi W-R, Wang H-Y, Chen S, et al. Estimate of prevalent diabetes from cardiometabolic index in general chinese population: a community-based study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17:236.
Smarr KL, Keefer AL. Measures of depression and depressive symptoms: Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II), Center for epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), geriatric Depression Scale (GDS), hospital anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63(Suppl 11):454–66.
Shabsigh R, Arver S, Channer K, et al. The triad of erectile dysfunction, hypogonadism and the metabolic syndrome. Int J Clin Pract. 2008;62:791–8.
Thethi TK, Asafu-Adjaye NO, Fonseca VA. Erectile dysfunction. Clin Diabetes. 2005;23:105–13.
Carson CC. Erectile dysfunction: evaluation and new treatment options. Psychosom Med. 2004;66:664–71.
Farmanfarma KK, Kaykhaei MA, Adineh HA, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Iran: a meta-analysis of 69 studies. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2019;13:792–9.
Gorgel SN, Gorgel A, Sefik E. Sexual function in male patients with metabolic syndrome and effective parameters on erectile dysfunction. Int braz j urol. 2014;40:56–61.
Besiroglu H, Otunctemur A, Ozbek E. The relationship between metabolic syndrome, its components, and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1309–18.
Demir T. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome. Int J Urol. 2006;13:385–8.
Traish AM, Feeley RJ, Guay A. Mechanisms of obesity and related pathologies: androgen deficiency and endothelial dysfunction may be the link between obesity and erectile dysfunction. FEBS J. 2009;276:5755–67.
Vlachopoulos C, Rokkas K, Ioakeimidis N, et al. Inflammation, metabolic syndrome, Erectile Dysfunction, and coronary artery disease: common links. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1590–600.
Kupelian V, Shabsigh R, Araujo AB, et al. Erectile dysfunction as a predictor of the metabolic syndrome in aging men: results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 2006;176:222–6.
Sood R, Sharma D, Goel H, et al. The correlation between erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome in an indian population: a cross-sectional observational study. Arab J Urol. 2019;17:221–7.
Espinosa-Marrón A, Quiñones-Capistrán CA, Rubio-Blancas A et al. Hyperglycemia: the metabolic syndrome component that aggravates erectile dysfunction in Mexican patients. Revista mexicana de urología. 2019;79.
Xu Y, Zhang Y, Yang Y, et al. Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction in type 2 diabetic men: a population-based cross-sectional study in chinese men. Int J Impot Res. 2019;31:9–14.
Shiferaw WS, Akalu TY, Aynalem YA. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus and its association with body mass index and Glycated hemoglobin in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Endocrinol. 2020;2020.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHM: Conceptualization, Project administration, Review & editing. AK: Supervision, Project administration, Review & editing. MHM: Conceptualization, Project administration. ASF: Investigation, Data curation. SE: Project administration, Investigation, Data curation. SM: Supervision, Investigation, Data curation. SMZ: Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis. PZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Formal analysis. HR: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Review & editing. BN: Investigation, Data curation, Review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guilan University of Medical Sciences (IR.GUMS.REC.1400.015) and it was under the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed written consent form was completed by every participant.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Madani, A.H., Akhavan, A., Madani, M.H. et al. Evaluation of the frequency of metabolic syndrome and assessment of cardiometabolic index among men with erectile dysfunction: a prospective cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Metab Disord 22, 1191–1196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01231-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01231-3