Abstract
Purpose
Patients with diabetic neuropathy usually suffer from impaired balance, pain, and decreased sole-foot sensation. The present research was designed to appraise the relic of whole-body vibration (WBV) on balance, pain, and sole-foot sensation in diabetic neuropathy patients.
Methods
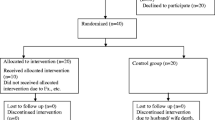
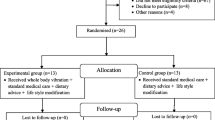
Present study was a single-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Thirty-four patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy were randomly divided into intervention groups (n=17) and control (n=17). The therapeutic program in the intervention group included standing on the platform of the WBV device, and in the control group included using the device in off mode. Dynamic balance (including overall, anterior-posterior, and medial-lateral stability indices) was measured using Biodex device, functional balance with timed up and go (TUG) test, pain using the visual analog scale (VAS), and sole-foot sensation of both feet with a monofilament. The outcomes were measured in both groups before and after the interventions.
Results
Sixteen people in each group were analyzed. Intra-group comparison showed a significant improvement in the mean pain (P = 0.000), functional balance (P = 0.011), right and left sole-foot sensation (P = 0.001), and overall (P = 0.000), anterior-posterior (P = 0.000) and medial-lateral (P = 0.000) stability indices for the intervention group in post-intervention compared to pre-intervention. However, changes in the control group were not statistically significant. Results of inter-group comparison indicated a significant improvement in all parameters in the intervention group, except for functional balance.
Conclusion
WBV can be effective in reducing pain and improving the sole-foot sensation and dynamic balance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rossi G, Association AD. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2018;33(Suppl 1):S62–S9.
Akbari NJ, Hosseinifar M, Naimi SS, Mikaili S, Rahbar S. The efficacy of physiotherapy interventions in mitigating the symptoms and complications of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders. 2020; Oct 12:1–0.
Cancelliere P. A review of the pathophysiology and clinical sequelae of diabetic polyneuropathy in the feet. J Diabetes Metab Disord Control. 2016;3(2):00062.
Han J, Anson J, Waddington G, Adams R, Liu Y. The role of ankle proprioception for balance control in relation to sports performance and injury. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015.
Hong J. Whole body vibration therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a case report. Health Sci J. 2011;5(1):66.
Lamb SE, Becker C, Gillespie LD, Smith JL, Finnegan S, Potter R, et al. Reporting of complex interventions in clinical trials: development of a taxonomy to classify and describe fall-prevention interventions. Trials. 2011;12(1):1–8.
Delbaere K, Bourgois J, Van Den Noortgate N, Vanderstraeten G, Willems T, Cambier D. A home-based multidimensional exercise program reduced physical impairment and fear of falling. Acta Clin Belg. 2006;61(6):340–50.
Zhang J, Zhang H, Kan L, Zhang C, Wang P. The effect of whole body vibration therapy on the physical function of people with type II diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(9):2675–80.
Javed S, Alam U, Malik RA. Treating diabetic neuropathy: present strategies and emerging solutions. The review of diabetic studies: RDS. 2015;12(1–2):63.
del Pozo-Cruz J, Alfonso-Rosa RM, Ugia JL, McVeigh JG, del Pozo-Cruz B, Sañudo B. A primary care-based randomized controlled trial of 12-week whole-body vibration for balance improvement in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(11):2112–8.
Lu J, Xu G, Wang Y. Effects of whole body vibration training on people with chronic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2015;22(3):161–8.
Yang X, Zhou Y, Wang P, He C, He H. Effects of whole body vibration on pulmonary function, functional exercise capacity and quality of life in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(5):419–31.
Zafar H, Alghadir A, Anwer S, Al-Eisa E. Therapeutic effects of whole-body vibration training in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(8):1525–32.
Guest A, Apgar M. Promoting and prescribing exercise for the elderly. Americ family physician. 2002;65(3).
Cheung W-H, Mok H-W, Qin L, Sze P-C, Lee K-M, Leung K-S. High-frequency whole-body vibration improves balancing ability in elderly women. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(7):852–7.
Daenen L, Van Oosterwijck J, Meeus M, Roussel N, Cras P, Nijs J. 10 Evaluatie en behandeling van patiënten met chronische whiplashgeassocieerde aandoeningen. Jaarboek Fysiotherapie Kinesitherapie 2012: Springer; 2012. p. 151–61.
Johnson PK, Feland JB, Johnson AW, Mack GW, Mitchell UH. Effect of whole body vibration on skin blood flow and nitric oxide production. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2014;8(4):889–94.
Palma FH, Antigual DU, Martínez SF, Monrroy MA, Gajardo RE. Static balance in patients presenting diabetes mellitus type 2 with and without diabetic polyneuropathy. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia. 2013;57(9):722–6.
Ziaee A, Hashemipour S, Ghavam S, Javadi A, Ghavam R, Barikani A, et al. Comparison of metformin and pioglitazone on hs-CRP levels in patients with type II diabetes. 2013.
Baum K, Votteler T, Schiab J. Efficiency of vibration exercise for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Int J Med Sci. 2007;4(3):159.
Yoosefinejad AK, Shadmehr A, Olyaei G, Talebian S, Bagheri H, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR. Short-term effects of the whole-body vibration on the balance and muscle strength of type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy: a quasi-randomized-controlled trial study. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders. 2015;14(1):1–8.
Miri F, Khodaveisi M, Karami M, Mohammadi N. The effect of training home care to type-2 diabetic patients on controlling blood glucose levels in patients admitted to the diabetes research center of Hamadan. Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care. 2014;22(3):24–32.
Hassanzade S, Raz A, Mansouri M, Mirzaeezadeh Z, Larijani B. Assessment of the relationship between (thr399ile) polymorphism of tlr4 gene with diabetic foot ulcer in type 2 diabetic patients referred to the clinic of diabetes & metabolic diseases. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2016;16(1):9–16.
Arnold BL, Schmitz RJ. Examination of balance measures produced by the biodex stability system. J Athl Train. 1998;33(4):323.
FATHI RZ. Aslankhani MA. Abdoli B, ZAMANI SS. A comparison of three functional tests of balance in identifying fallers from non-fallers in elderly people: Farsi AR; 2010.
Moghtaderi A, Bakhshipour A, Rashidi H. Validation of Michigan neuropathy screening instrument for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006;108(5):477–81.
Herman W, Pop-Busui R, Braffett B, Martin C, Cleary P, Albers J, et al. Use of the Michigan neuropathy screening instrument as a measure of distal symmetrical peripheral neuropathy in type 1 diabetes: results from the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications. Diabet Med. 2012;29(7):937–44.
Delgado DA, Lambert BS, Boutris N, McCulloch PC, Robbins AB, Moreno MR, et al. Validation of digital visual analog scale pain scoring with a traditional paper-based visual analog scale in adults. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Global research & reviews. 2018;2(3).
Mahbub M, Hase R, Yamaguchi N, Hiroshige K, Harada N, Bhuiyan A, et al. Acute effects of whole-body vibration on peripheral blood flow, Vibrotactile perception and balance in older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(3):1069.
Dolny DG, Reyes GFC. Whole body vibration exercise: training and benefits. Current sports medicine reports. 2008;7(3):152–7.
Sa-Caputo DC, Paineiras-Domingos L, Oliveira R, Neves MF, Brandão A, Marin PJ, et al. Acute effects of whole-body vibration on the pain level, flexibility, and cardiovascular responses in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Dose-Response. 2018;16(4):1559325818802139.
Niajalili M, Sedaghat M, Reza Soltani A, Akbarzadeh Baghban A, Naimi SS. The effect of Tecar therapy on pain and tactile sensation of the foot in patients with type II diabetes. Archives of Rehabilitation 2020 Sep 10;21(3):0–5.
Talimkhani A, Nodehi Moghadam A, Ghamkhar L, Amiri AS. The immediate effect of the whole body vibration on postural control in young adults. Journal of Modern Rehabilitation. 2016;9(7):28–36.
Torvinen S, Kannus P, SievaÈnen H, JaÈrvinen TA, Pasanen M, Kontulainen S, et al. Effect of a vibration exposure on muscular performance and body balance. Randomized cross-over study. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2002;22(2):145–52.
Murakami M, Itotani K, Maeda N, Otani Y, Koeda H, Kato J. Influences on Electromyography Activities of Lower Limbs and Postural Balance during Whole Body Vibration (WBV) in Young People. 神戸国際大学紀要. 2014(86):25–30.
Pollock RD, Woledge RC, Martin FC, Newham DJ. Effects of whole body vibration on motor unit recruitment and threshold. J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(3):388–95.
Freitas ED, Frederiksen C, Miller RM, Heishman A, Anderson M, Pardo G, et al. Acute and chronic effects of whole-body vibration on balance, postural stability, and mobility in women with multiple sclerosis. Dose-Response. 2018;16(4):1559325818816577.
Morales-Vargas R, Valdes-Badilla P, Guzmán-Muñoz E. Relationship between the anthropometric profile and physical fitness of surfers and their dynamic postural balance. Camp d. 2021 Mar;107.
Naghdi S, Khalifeloo M, Ansari NN, Akbari M, Jalaie S, Jannat D. The short-term effects of plantar vibration on balance disorder after stroke. Audiology. 2013;22(22):104–9.
Pollock RD, Provan S, Martin FC, Newham DJ. The effects of whole body vibration on balance, joint position sense and cutaneous sensation. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(12):3069–77.
Schlee G, Reckmann D, Milani TL. Whole body vibration training reduces plantar foot sensitivity but improves balance control of healthy subjects. Neurosci Lett. 2012;506(1):70–3.
Conflict of interest
The responsible author declares that no conflict of interest exists on behalf of all other authors. The financial support center did not have any funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohrabzadeh, E., Kalantari, K.K., Naimi, S.S. et al. The immediate effect of a single whole-body vibration session on balance, skin sensation, and pain in patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21, 43–49 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00933-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00933-w