Abstract
Background
Water pre-load affects insulin secretion by altering the level of copeptin (C-terminal component of the arginine vasopressin hormone (AVP)) and preventing obesity by reducing food intake.
Aims
The present randomized controlled trial (RCT) aimed to investigate the effects of pre-meal water intake on type 2 diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Materials and methods
In this study, 40 patients with T2DM were randomly assigned to two intervention groups for 8 weeks; a) drinking 1 liter of water per day before each main meal (PW group)., and b) no water consumption before any meal (NPW group). At the beginning and at the end of the study, blood samples were taken to assess glycemic indices, lipid profile, copeptin and anthropometric indices.
Results
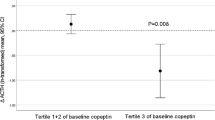
Pre-meal water intake was associated with lower energy intake, BMI, waist circumference (WC) and greater weight loss, in compared with the controls (P < 0.0001) after 8 weeks. At the end of the trial, the concentrations of fasting blood sugar (FBS) (P < 0.0001), triglyceride (TG) (P < 0.05), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (P < 0.05) and copeptin (P < 0.05) were significantly reduced following water drinking before meals.
Conclusion
To sum up, the present study revealed that pre-meal water intake is associated with lower BMI, body weight, WC, FBS, TG, LDL-C and copeptin levels in patients with T2DM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotfy M, Adeghate J, Kalasz H, Singh J, Adeghate E. Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: a mini review. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(1):3–10.
Tabrizi R, Nowrouzi-Sohrabi P, Hessami K, Rezaei S, Jalali M, Savardashtaki A, et al. Effects of Ginkgo biloba intake on cardiometabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. 2020.
Wannamethee SG, Welsh P, Papacosta O, Lennon L, Whincup PH, Sattar N. Copeptin, insulin resistance, and risk of incident diabetes in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2015;100(9):3332–9.
Clark AG, Dennis Parker EA, Savla JS, Davy KP. Is increased water consumption among older adults associated with improvements in glucose homeostasis? 2013.
Agrawal S, Gensure R. Commentary on the impact of obesity on pediatric diabetes. Clin Ther. 2018;40(10):1631–7.
Nowrouzi-Sohrabi P, Tabrizi R, Rezaei S, Jafari F, Hesami K, Abedi M, et al. The effect of voglibose on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials; 2020. p. 104988.
Daniels MC, Popkin BM. Impact of water intake on energy intake and weight status: a systematic review. Nutr Rev. 2010;68(9):505–21.
Popkin BM, Barclay DV, Nielsen SJ. Water and food consumption patterns of US adults from 1999 to 2001. Obes Res. 2005;13(12):2146–52.
Muckelbauer R, Sarganas G, Grüneis A, Müller-Nordhorn J. Association between water consumption and body weight outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(2):282–99.
Parretti HM, Aveyard P, Blannin A, Clifford SJ, Coleman SJ, Roalfe A, et al. Efficacy of water preloading before main meals as a strategy for weight loss in primary care patients with obesity: RCT. Obesity. 2015;23(9):1785–91.
Van Walleghen EL, Orr JS, Gentile CL, Davy BM. Pre-meal water consumption reduces meal energy intake in older but not younger subjects. Obesity. 2007;15(1):93–9.
Davy BM, Dennis EA, Dengo AL, Wilson KL, Davy KP. Water consumption reduces energy intake at a breakfast meal in obese older adults. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(7):1236–9.
Abbasi A, Corpeleijn E, Meijer E, Postmus D, Gansevoort RT, Gans RO, et al. Sex differences in the association between plasma copeptin and incident type 2 diabetes: the prevention of renal and vascular Endstage disease (PREVEND) study. Diabetologia. 2012;55(7):1963–70.
Enhörning S, Wang TJ, Nilsson PM, Almgren P, Hedblad B, Berglund G, et al. Plasma copeptin and the risk of diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2010;121(19):2102–8.
Enhörning S, Tasevska I, Roussel R, Bouby N, Persson M, Burri P, et al. Effects of hydration on plasma copeptin, glycemia and gluco-regulatory hormones: a water intervention in humans. Eur J Nutr. 2019;58(1):315–24.
Ioannou GN, Bryson CL, Boyko EJ. Prevalence and trends of insulin resistance, impaired fasting glucose, and diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2007;21(6):363–70.
Emami S, Saraf-Bank S, Rouhani MH, Azadbakht L. Diet quality and total daily price of foods consumed among Iranian diabetic patients. Int J Prev Med. 2019;10:50. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_334_16.
Ashabi G, Khalaj L, Khodagholi F, Goudarzvand M, Sarkaki A. Pre-treatment with metformin activates Nrf2 antioxidant pathways and inhibits inflammatory responses through induction of AMPK after transient global cerebral ischemia. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30(3):747–54.
Lemetais G, Melander O, Vecchio M, Bottin JH, Enhörning S, Perrier ET. Effect of increased water intake on plasma copeptin in healthy adults. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(5):1883–90.
Villela-Torres MDLL, Higareda-Mendoza AE, Gómez-García A, Alvarez-Paredes AR, García-López E, Stenvikel P, et al. Copeptin plasma levels are associated with decline of renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Med Res. 2018;49(1):36–43.
Boone M, Deen PM. Physiology and pathophysiology of the vasopressin-regulated renal water reabsorption. Pflügers Archiv-European J Physiol. 2008;456(6):1005–24.
Stoiser B, Mörtl D, Hülsmann M, Berger R, Struck J, Morgenthaler N, et al. Copeptin, a fragment of the vasopressin precursor, as a novel predictor of outcome in heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006;36(11):771–8.
Taveau C, Chollet C, Waeckel L, Desposito D, Bichet DG, Arthus M-F, et al. Vasopressin and hydration play a major role in the development of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis in obese rats. Diabetologia. 2015;58(5):1081–90.
Clark WF, Sontrop JM, Macnab JJ, Suri RS, Moist L, Salvadori M, et al. Urine volume and change in estimated GFR in a community-based cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(11):2634–41.
Sontrop JM, Dixon SN, Garg AX, Buendia-Jimenez I, Dohein O, Huang S-HS, et al. Association between water intake, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data. Am J Nephrol. 2013;37(5):434–42.
Dennis EA, Dengo AL, Comber DL, Flack KD, Savla J, Davy KP, et al. Water consumption increases weight loss during a hypocaloric diet intervention in middle-aged and older adults. Obesity. 2010;18(2):300–7.
Duffey KJ, Popkin BM. Shifts in patterns and consumption of beverages between 1965 and 2002. Obesity. 2007;15(11):2739–47.
Stookey JD, Constant F, Popkin BM, Gardner CD. Drinking water is associated with weight loss in overweight dieting women independent of diet and activity. Obesity. 2008;16(11):2481–8.
Rothermel J, Kulle A, Holterhus PM, Toschke C, Lass N, Reinehr T. Copeptin in obese children and adolescents: relationships to body mass index, cortisol and gender. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016;85(6):868–73.
Lewandowski KC, Lewiński A, Skowrońska-Jóźwiak E, Stasiak M, Horzelski W, Brabant G. Copeptin under glucagon stimulation. Endocrine. 2016;52(2):344–51.
Saleem U, Khaleghi M, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A, Struck J, Mosley TH Jr, et al. Plasma carboxy-terminal provasopressin (copeptin): a novel marker of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2009;94(7):2558–64.
Tenderenda-Banasiuk E, Wasilewska A, Filonowicz R, Jakubowska U, Waszkiewicz-Stojda M. Serum copeptin levels in adolescents with primary hypertension. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014;29(3):423–9.
Acknowledgements
This article was extracted from a master’s degree thesis in nutrition. The authors are grateful to Research Vice Chancellor of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences for financial support and to all patients for their sincere cooperation to this study.
Funding
Research Deputy of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran financially supported the present study (grant No. 8984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FM and GS contributed to study design and concept. MAK visited patients. GS and SS contributed to data collection. FM and AD contributed to data analyses. FM, GS, MK and MAK contributed to drafting and reviewing the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedaghat, G., Montazerifar, F., Keykhaie, M.A. et al. Effect of pre-meal water intake on the serum levels of Copeptin, glycemic control, lipid profile and anthropometric indices in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord 20, 171–177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00724-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00724-9