Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of dietary nitrate on secretory function of pancreatic islet and oxidative stress status in streptozotocin (STZ) induced type 1 diabetes in absence or presence of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (L-NAME).
Methods
Fifty adult male sprague-dawly rats were divided into 5 groups: controls (C), diabetes (D), diabetes+nitrate (DN), diabetes +L-NAME (D + Ln), and diabetes+nitrate+L-NAME (DN + Ln) for 45 days. The concentrations of sodium nitrate and L-NAME were respectively 80 mg/L in drinking water and 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally. Body weight gain, plasma levels of glucose and insulin, islet insulin secretion and content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in the pancreas of rats were determined.
Results
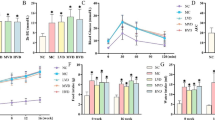
Compared to control group, the body weight gain and plasma insulin level were significantly decreased and plasma glucose and pancreatic NO and MDA concentrations and antioxidant enzymes activities were significantly increased in the STZ diabetic rats. In the diabetic rats, nitrate alone significantly reduced plasma glucose and increased pancreatic SOD and GPx activity. Reduced plasma glucose, pancreatic MDA and NO concentrations and increased plasma insulin level and pancreatic islet insulin secretion were observed in D + Ln and DN + Ln groups. Antioxidant enzymes activities were increased in diabetic rats which received combination of nitrate and L-NAME.
Conclusions
Our results showed that nitrate without effect on pancreatic islet insulin content and secretion decreased the blood glucose and slightly moderate oxidative stress and its effects in the presence of L-NAME on glucose hemostasis and pancreatic insulin secretion higher than those of nitrate alone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(2):156–67.
Omar SA, Webb AJ, Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E. Therapeutic effects of inorganic nitrate and nitrite in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J Intern Med. 2016;279(4):315–36.
McNally B, Griffin JL, Roberts LD. Dietary inorganic nitrate: from villain to hero in metabolic disease? Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016;60(1):67–78.
Lundberg JO, Gladwin MT, Ahluwalia A, Benjamin N, Bryan NS, Butler A, et al. Nitrate and nitrite in biology, nutrition and therapeutics. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5(12):865–9.
Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S. Potential therapeutic effects of nitrate/nitrite and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;11(2):63–4.
El-Wakf AM, Hassan HA, Mahmoud AZ, Habza MN. Fenugreek potent activity against nitrate-induced diabetes in young and adult male rats. Cytotechnology. 2015;67(3):437–47.
Novelli M, Pocai A, Lajoix AD, Beffy P, Bezzi D, Marchetti P, et al. Alteration of beta-cell constitutive NO synthase activity is involved in the abnormal insulin response to arginine in a new rat model of type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;219(1–2):77–82.
Lajoix AD, Reggio H, Chardes T, Peraldi-Roux S, Tribillac F, Roye M, et al. A neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase expressed in pancreatic beta-cells controls insulin secretion. Diabetes. 2001;50(6):1311–23.
Broniowska KA, Oleson BJ, Corbett JA. Chapter Twelve - β-Cell Responses to Nitric Oxide. In: Litwack G, editor. Vitamins & Hormones. Cambridge: Academic Press; 2014. p. 299–322.
Smukler SR, Tang L, Wheeler MB, Salapatek AM. Exogenous nitric oxide and endogenous glucose-stimulated beta-cell nitric oxide augment insulin release. Diabetes. 2002;51(12):3450–60.
Henningsson R, Salehi A, Lundquist I. Role of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in glucose-stimulated insulin release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283(1):C296–304.
Jones PM, Persaud SJ, Bjaaland T, Pearson JD, Howell SL. Nitric oxide is not involved in the initiation of insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1992;35(11):1020–7.
Salehi A, Meidute Abaraviciene S, Jimenez-Feltstrom J, Ostenson CG, Efendic S, Lundquist I. Excessive islet NO generation in type 2 diabetic GK rats coincides with abnormal hormone secretion and is counteracted by GLP-1. PLoS One. 2008;3(5):e2165.
Ghasemi A, Jeddi S. Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide. 2017;70:9–24.
Pitocco D, Tesauro M, Alessandro R, Ghirlanda G, Cardillo C. Oxidative stress in diabetes: implications for vascular and other complications. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(11):21525–50.
Wang J, Wang H. Oxidative stress in pancreatic Beta cell regeneration. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1930261–9.
Carlström M, Larsen FJ, Nyström T, Hezel M, Borniquel S, Weitzberg E, et al. Dietary inorganic nitrate reverses features of metabolic syndrome in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(41):17716–20.
Gadek-Michalska A, Bugajski J. Role of nitric oxide in the nicotine-induced pituitary-adrenocortical response. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004;55(2):443–55.
Farrokhfall K, Khoshbaten A, Zahediasl S, Mehrani H, Karbalaei N. Improved islet function is associated with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and hypoglycemic potential of cinnamaldehyde on metabolic syndrome induced by high tail fat in rats. J Funct Foods. 2014;10:397–406.
Safayee S, Karbalaei N, Noorafshan A, Nadimi E. Induction of oxidative stress, suppression of glucose-induced insulin release, ATP production, glucokinase activity, and histomorphometric changes in pancreatic islets of hypothyroid rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;791:147–56.
Karbalaei N, Noorafshan A, Hoshmandi E. Impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and reduced beta-cell mass in pancreatic islets of hyperthyroid rats. Exp Physiol. 2016;101(8):1114–27.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72(1):248–54.
Zhu W, Chen M, Shou Q, Li Y, Hu F. Biological activities of Chinese Propolis and Brazilian Propolis on Streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:1–8.
Broulik PD, Haluzik M, Skrha J. The influence of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME on bones of male rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Physiol Res. 2003;52(6):729–34.
Ogur R, Coskun O, Korkmaz A, Oter S, Yaren H, Hasde M. High nitrate intake impairs liver functions and morphology in rats; protective effects of alpha-tocopherol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20(1):161–6.
National TP. Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of sodium nitrite (CAS NO. 7632-00-0) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (drinking water studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2001;495:7–273.
Til HP, Kuper CF, Falke HE. Nitrite-induced adrenal effects in rats and the consequences for the no-observed-effect level. Food Chem Toxicol. 1997;35(3–4):349–55.
Khalifi S, Rahimipour A, Jeddi S, Ghanbari M, Kazerouni F, Ghasemi A. Dietary nitrate improves glucose tolerance and lipid profile in an animal model of hyperglycemia. Nitric Oxide. 2015;44:24–30.
Akasha M, A. K, A. AS. Effect of Nitrate on the Body Weight, Food and Water Consumption and Thyroid Hormone in Hybrid Female Rabbits. J Vet Adv. 2015;5(5):912–8.
Kato Y, Miura Y, Yamamoto N, Ozaki N, Oiso Y. Suppressive effects of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibitor on pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetologia. 2003;46(9):1228–33.
Muhammed SJ, Lundquist I, Salehi A. Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction, expression of iNOS and the effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors in human pancreatic islets of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(11):1010–9.
Bedoya FJ, Salguero-Aranda C, Cahuana GM, Tapia-Limonchi R, Soria B, Tejedo JR. Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell survival by nitric oxide: clinical relevance. Islets. 2012;4(2):108–18.
McDaniel ML, Kwon G, Hill JR, Marshall CA, Corbett JA. Cytokines and nitric oxide in islet inflammation and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996;211(1):24–32.
Yang T, Peleli M, Zollbrecht C, Giulietti A, Terrando N, Lundberg JO, et al. Inorganic nitrite attenuates NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide generation in activated macrophages via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;83:159–66.
Carlström M, Liu M, Yang T, Zollbrecht C, Huang L, Peleli M, et al. Cross-talk between nitrate-nitrite-NO and NO synthase pathways in control of vascular NO homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;23(4):295–306.
Jiang H, Torregrossa AC, Potts A, Pierini D, Aranke M, Garg HK. Dietary nitrite improves insulin signaling through GLUT4 translocation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;67:51–7.
Ohtake K, Nakano G, Ehara N, Sonoda K, Ito J, Uchida H. Dietary nitrite supplementation improves insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic KKA(y) mice. Nitric Oxide. 2015;44:31–8.
Nino Fong R, Fatehi-Hassanabad Z, Lee SC, Lu H, Wheeler MB, Chan CB. Uncoupling protein-2 increases nitric oxide production and TNFAIP3 pathway activation in pancreatic islets. J Mol Endocrinol. 2011;46(3):193–204.
Cnop M, Welsh N, Jonas JC, Jorns A, Lenzen S, Eizirik DL. Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: many differences, few similarities. Diabetes. 2005;54(Suppl 2):S97–S107.
Qader SS, Ekelund M, Andersson R, Obermuller S, Salehi A. Acute pancreatitis, expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and defective insulin secretion. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;313(3):271–9.
Rains JL, Jain SK. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;50(5):567–75.
Pacher P, Obrosova IG, Mabley JG, Szabo C. Role of nitrosative stress and peroxynitrite in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Emerging new therapeutical strategies. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(3):267–75.
Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB 3rd. Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003;17(1):24–38.
Tiedge M, Lortz S, Munday R, Lenzen S. Protection against the co-operative toxicity of nitric oxide and oxygen free radicals by overexpression of antioxidant enzymes in bioengineered insulin-producing RINm5F cells. Diabetologia. 1999;42(7):849–55.
Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M. Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(6):1583–606.
Seven A, Guzel S, Seymen O, Civelek S, Bolayirli M, Yigit G, et al. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition by L-NAME in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats: impacts on oxidative stress. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2003;199(4):205–10.
Sheweita SA, Mashaly S, Newairy AA, Abdou HM, Eweda SM. Changes in oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in Streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats: role of Alhagi maurorum extracts. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:5264064.
Carlstrom M, Persson AE, Larsson E, Hezel M, Scheffer PG, Teerlink T. Dietary nitrate attenuates oxidative stress, prevents cardiac and renal injuries, and reduces blood pressure in salt-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;89:574–85.
Acknowledgements
The present work was financially supported by Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran (grant no. 12977); it is a part of Ms. Thesis by Zahra Shabgard Shahraki. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis and preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to the conception and design of the research. Z.S.S, M.N. performed the experiments/analysis. N.K. conceived the study. All authors have participated in drafting the article or revising it and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahraki, Z.S., Karbalaei, N. & Nemati, M. Improving effect of combined inorganic nitrate and nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on pancreatic oxidative stress and impaired insulin secretion in streptozotocin induced-diabetic rats. J Diabetes Metab Disord 19, 353–362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00516-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00516-1