Abstract
Purpose
Oral administration of Iodine−131 (I−131) solutions causes high risk of contamination for patients and dispensers. The objective of the study was to adapt hard gelatin capsules (HGCs) for filling with radiopharmaceutical solutions without deformation.
Methods
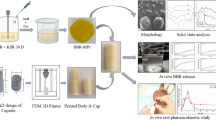
Polystyrene (PS) internally lining films with different thicknesses were used to protect HGCs. The insulated HGCs were evaluated for their physicochemical characteristics and rupturing time in different dissolution media. HGCs internally lined with PS were examined for withstand loading with different volumes and radioactivities of I−131 solutions. Radioactivity release was studied in deionized water and acidic media. Quality control of released I−131 was inspected for radiochemical purities.
Results
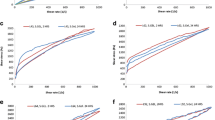
There was a directly proportion between PS lining thickness and stability of HGCs after filling with 500 μl aqueous methylene blue solution. HGCs internally lined with PS 100 μm thickness withstand deformation for ˃ two months; however showed fast in-vitro rupturing time in different dissolution media. Internally lined HGCs loaded with different volumes and radioactivities of I−131 solutions resisted for one week without radioactive leakage. Yet, revealed complete release of I−131 after 20 min in dissolution media with great radiochemical purity.
Conclusion
The study promises safely I−131 aqueous solution delivery via adapted HGCs.

Oral administration of radiopharmaceuticals









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GC-MS:
-
Gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy
- HGCs:
-
Hard gelatin capsules
- I−131 :
-
Radioactive Iodine−131 solutions
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- PS:
-
Polystyrene
References
Saha GB. Characteristics of specific radiopharmaceuticals (chap. 7). Fundamentals of Nuclear Pharmacy 6th ed. New York: Springer; 2010. p. 115–52.
Santos-Oliveira R, Antunes LJ. Radiopharmaceutical research and production in Brazil: a 30-year history of participation in the nuclear medicine scenario. J Nucl Med Technol. 2011;39(3):237–9.
Garcia-Peña E, Caravalho J, Watkins JW, Leifer ES. Esophageal passage of iodine-131 capsules. J Nucl Med Technol. 1997;25(1):55–8.
Kristensen K, Nørbygaard E, editors. Safety and efficacy of radiopharmaceuticals. 4. 1984th ed: pub. Springer Science & Business Media 2012. p. 85–98.
Hung JC. Radioiodine dispensing and usage in a centralized hospital nuclear pharmacy. Thyroid. 1997;7(2):289–94.
Kamalakkannan V, Puratchikody A, Masilamani K, Senthilnathan B. Solubility enhancement of poorly soluble drugs by solid dispersion technique–a review. J Pharm Res. 2010;3(9):2314–21.
Marques MR, Cole E, Kruep D, Gray V, Murachanian D, Brown WE, et al., editors. Liquid-filled gelatin capsules. Pharmacopeial forum; 2009.
Kuentz M, Röthlisberger D. Determination of the optimal amount of water in liquid-fill masses for hard gelatin capsules by means of texture analysis and experimental design. Int J Pharm. 2002;236(1):145–52.
Howard SS, Alexander S. Capsule containing a pharmaceutically useful radioactive material. U.S. patent no. 3,121,041. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office; 1964.
Takada K, Murakami M. Glycyrrhizin preparations for transmucosal absorption. U.S. patent no. 6,890, vol. 547. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office; 2005.
El-Aasser MS, Fitch RM. Future directions in polymer colloids: Springer Science & Business Media; 2012;138.
Sterns RH, Rojas M, Bernstein P, Chennupati S. Ion-exchange resins for the treatment of hyperkalemia: are they safe and effective? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21(5):733–5.
Iconomopoulou S, Andreopoulou A, Soto A, Kallitsis J, Voyiatzis G. Incorporation of low molecular weight biocides into polystyrene–divinyl benzene beads with controlled release characteristics. J Control Release. 2005;102(1):223–33.
Patil P, Paradkar A. Porous polystyrene beads as carriers for self-emulsifying system containing loratadine. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006;7(1):E199–205.
Maria AVW, Margarida MCO, Marcela Z, Ariane JSB, Mohammed Q, Ralph SO. Nanoradiopharmaceuticals for nanomedicine: building the future. Recent Pat Nanomed. 2014;4(2):90–4.
Sanagi MM, Lu LS, Nasir Z, Ibrahim WAW, Ahmedy AN. Determination of residual volatile organic compounds migrated from polystyrene food packaging into food simulant by headspace solid phase micro extraction-gas chromatography. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences. 2008;12(3):542–51.
Rosell M, Ginebreda A, Barceló D. Simultaneous determination of methyl tert.-butyl ether and its degradation products, other gasoline oxygenates and benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes in Catalonian groundwater by purge-and-trap-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2003;995(1):171–84.
Perkasa DP, Erizal E, Darmawan D, Rasyid A. Effect of gamma irradiation on mechanical and thermal properties of fish gelatin film isolated from lates calcarifer scales. Indonesian Journal of Chemistry. 2013;13(1):28–35.
Cilurzo F, Selmin F, Minghetti P, Montanari L, Lenardi C, Orsini F, et al. Comparison between gamma and beta irradiation effects on hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and gelatin hard capsules. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2005;6(4):E586–E93.
Rockville M. Disintegration and dissolution of dietary supplements h2040i. USP USP 31–NF 262008. p. 732–6.
IAEA-TECDOC M. 1340. Manual for reactor produced radioisotope. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency; 2003.
Roydan. United States pharmacopeia (USP 32) and the 27th edition of the national formulary (NF 27). Rockville: The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. Pustaka Kesehatan. 2008;2 (3):422–6.
Socrates G. Six membered ring heterocyclic compounds, In: Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts 3rd ed: Wiley 2001 p. 171.
Ofner CM, Zhang YE, Jobeck VC, Bowman BJ. Crosslinking studies in gelatin capsules treated with formaldehyde and in capsules exposed to elevated temperature and humidity. J Pharm Sci. 2001;90(1):79–88.
Suriyanarayanan S. Cywinski PJ, Moro A. J., Mohr G. J. and Kutner W. Chemosensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. In: Haupt K, editor. molecular imprinting Top Curr Chem. 325: Springer Science & Business Media; 2012.
Shepson P, Edney E, Corse E. Ring fragmentation reactions in the photooxidations of toluene and o-xylene. J Phys Chem. 1984;88(18):4122–6.
Digenis GA, Gold TB, Shah VP. Cross-linking of gelatin capsules and its relevance to their in vitro-in vivo performance. J Pharm Sci. 1994;83(7):915–21.
Ellis B, Smith R. Oriented polystyrene sheet and film. In: Polymers: a property database. 2nd Ed. ed: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group; 2008. p. 327–8.
Bullwinkel M, Gu J, Campbell G, Sukanek P. The effect of polymer molecular weight and solvent type on the planarization of spin-coated films. J Electrochem Soc. 1995;142(7):2389–94.
Islam MM, Zaman A, Islam MS, Khan MA, Rahman MM. Physico-chemical characteristics of gamma-irradiated gelatin. Prog Biomater. 2014;3(1):21.
Chiwele I, Jones BE, Podczeck F. The shell dissolution of various empty hard capsules. Chem Pharm Bull. 2000;48(7):951–6.
Zhang X, Do MD, Casey P, Sulistio A, Qiao GG, Lundin L, et al. Chemical cross-linking gelatin with natural phenolic compounds as studied by high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(4):1125–32.
Mercade-Prieto R, Sahoo PK, Falconer RJ, Paterson WR, Wilson DI. Polyelectrolyte screening effects on the dissolution of whey protein gels at high pH conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2007;21(8):1275–84.
Duconseille A, Astruc T, Quintana N, Meersman F, Sante-Lhoutellier V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: a review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015;43:360–76.
Yang XJ, Zheng PJ, Cui ZD, Zhao NQ, Wang YF, De Yao K. Swelling behaviour and elastic properties of gelatin gels. Polym Int. 1997;44(4):448–52.
Miyawaki O, Norimatsu Y, Kumagai H, Irimoto Y, Kumagai H, Sakurai H. Effect of water potential on sol-gel transition and intermolecular interaction of gelatin near the transition temperature. Biopolymers. 2003;70(4):482–91.
Swidan M, Sakr T, Motaleb M, El-Bary AA, El-Kolaly M. Preliminary assessment of radioiodinated fenoterol and reproterol as potential scintigraphic agents for lung imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2015;303(1):531–9.
Swidan M, Sakr T, Motaleb M, El-Bary AA, El-Kolaly M. Radioiodinated acebutolol as a new highly selective radiotracer for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Label Compd Radiopharm. 2014;57(10):593–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omar, S.M., Abdel-Rashid, R.S., AlAssaly, M.K. et al. Adaptation of hard gelatin capsules for oral delivery of aqueous radiopharmaceuticals. DARU J Pharm Sci 27, 295–305 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-019-00275-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-019-00275-2