Abstract
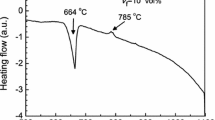
An Al2O3P/Al composite was successfully synthesized using a displacement reaction between 80 wt% Al and 20 wt% CuO powders at a heating rate of 5 °C/min. Two different sizes CuO particles were used, and all the experiments were conducted under an argon atmosphere. To analyze the microstructural evolution during synthesis, the Al–20 wt% CuO samples were heated to the temperatures selected according to the differential scanning calorimetry curve and then immediately quenched with water. The phase composites and microstructure of the water-quenching samples were investigated using X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectrometry. The results indicate that the CuO particle size has a significant effect on the microstructural evolution of the samples during the heating stage and on the microstructure of synthesized composites. Smaller CuO particles can decrease the reaction temperature, narrow the reaction temperature range at the different reaction stages during the heating stage and make the size and distribution of in situ Al2O3 particles more uniform. The reaction between Al and CuO can be complete as the temperature rises to 900 °C. The size of the in situ Al2O3 particles is approximately 5 μm when the size of the CuO particles is less than 6 μm. This sample has a relatively high Rockwell hardness of 60 HRB.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M.L. Wu, G.W. Han, Mater. Charact. 58, 416 (2007)
Z. Razavi Hesabi, A. Simchi, S.M. Seyed Reihani, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 428, 159 (2006)
M. Rahimian, N. Ehasani, N. Parvin, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 5387 (2009)
J. Hashim, L. Looney, M.S.J. Hashmi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 123, 257 (2002)
S.C. Tjong, Z.Y. Ma, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 29, 49 (2000)
P. Yu, C.K. Kwok, C.Y. To, T.K. Li, D.H.L. Ng, Compos. B 39, 327 (2008)
S. Dadbakhsh, L. Hao, Adv. Eng. Mater. 14, 45 (2012)
C.F. Feng, L. Froyen, Compos. A 31, 385 (2000)
P. Yu, C.J. Deng, N.G. Ma, D.H.L. Ng, Mater. Lett. 58, 679 (2004)
Z.J. Huang, B. Yang, H. Cui, J.S. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 351, 15 (2003)
B. Dikici, M. Gavgali, J. Alloys Compd. 551, 101 (2013)
G.H. Zahid, T. Azhar, M. Musaddiq, Mater. Des. 32, 1630 (2011)
B. Yang, M. Sun, G.S. Gan, C.G. Xu, Z.J. Huang, H.B. Zhang, Z.G. Zak Fang, J. Alloys Compd. 494, 261 (2010)
G. Chen, G.X. Sun, Z.G. Zhu, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 251, 226 (1998)
P. Yu, C.J. Deng, N.G. Ma, M.Y. Yau, D.H.L. Ng, Acta Mater. 51, 3445 (2003)
H. Arami, A. Simchi, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 464, 225 (2007)
K. Song, J.D. Xing, Q.M. Dong, P. Liu, B.H. Tian, X.J. Cao, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 380, 117 (2004)
E.Q. Mokhnache, G.S. Qang, L. Geng, Acta. Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett) 27, 930 (2014)
K.L. Tee, L. Lu, M.O. Lai, Compos. Struct. 47, 589 (1999)
G. Lasko, U. Weber, S. Schmauder, Acta. Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 27, 853 (2014)
Y.Z. Wan, Y.L. Wang, H.L. Luo, X.H. Dong, G.X. Cheng, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 18, 1059 (1999)
T.G. Durai, K. Das, S. Das, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 445–446, 100 (2007)
S.M. Umbrajkar, M. Schoenitz, E.L. Dreizin, Thermochim. Acta 451, 34 (2006)
Z.H. Cai, D.L. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 419, 310 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 2012MS0801 and 2013MS0804).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Shi, ZM. & Zhang, RY. Effect of CuO Particle Size on the Microstructure Evolution of Al2O3P/Al Composites Prepared Via Displacement Reactions in the Al/CuO System. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 28, 699–706 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0250-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0250-8