Abstract
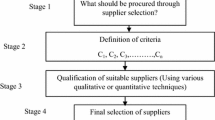
Due to highly competitive market environment, the supply chain network of business organization are not only efficient but also flexible. The flexible supply chain of business organization is greatly influenced by the suppliers. Hence, the selection of suppliers has to be flexible which not only take into account the quantitative factors but also take into account qualitative factors. In this paper, a novel attempt is conceptualized to model a flexible supplier selection (FSS) problem by integrating the qualitative and quantitative models for supplier selection problem. A MINLP, a quantitative model, is considered in the proposed FSS framework where factors such as lead time, quality, supplier’s capacity and transportation cost are considered. Similarly, in qualitative model factors such as loyalty, technology adaptability, CSR and environmental factors are considered. AHP and IRP, qualitative models, have been applied and compared for supplier’s ranking. An integrated ranking of AHP and IRP is used for modeling FSS problem. Finally, Integration of quantitative and qualitative model provides the set of deviation which measure the level of flexibility from pure solution of supplier selection problem by quantitative and qualitative model. The methodology of FSS problem is presented and demonstrated through an illustrative example of multi-product, multi-source and multi-period case.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akarte, M. M., Surendra, N. V., Ravi, B., & Rangaraj, N. (2001). Web based casting supplier evaluation using analytical hierarchy process. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 52, 511–522.
Amin, S. H., Razmi, J., & Zhang, G. (2011). Supplier selection and order allocation based on fuzzy SWOT analysis and fuzzy linear programming. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 334–342.
Bayazit, O. (2006). Use of analytic network process in vendor selection decisions. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 13(5), 566–579.
Bhutta, K. S., & Huq, F. (2002). Supplier selection problem: a comparison of the total cost of ownership and analytic hierarchy process approaches. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 7(3), 126–135.
Boer, L. D., Labro, E., & Morlacchi, P. (2001). A review of methods supporting supplier selection. European Journal of Purchasing & Supply Management, 7, 75–89.
Bruno, G., Esposito, E., Genovese, A., & Passaro, R. (2012). AHP-based approaches for supplier evaluation: Problems and perspectives. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 18, 159–172.
Chan, F. T. S., & Chan, H. K. (2004). Development of the supplier selection mode—a case study in the advanced technology industry. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 218, 1807–1824.
Chan, F. T. S., & Niraj, K. (2007). Global supplier development considering risk factors using fuzzy extended AHP-based approach. Omega, 35, 417–431.
Che, Z. H. (2010). A genetic algorithm-based model for solving multi-period supplier selection problem with assembly sequence. International Journal of Production Research, 48(15), 4355–4377.
Chia-Wei, H., & Allen, H. H. (2009). Applying hazardous substance management to supplier selection using analytic network process. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17, 255–264.
Demirtas, E. A., & Ustun, O. (2008). An integrated multi-objective decision making process for supplier selection and order allocation. Omega, 36, 76–90.
Demirtas, E. A., & Ustun, O. (2009). Analytical network process and multi-period goal programming interaction in purchasing decisions. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 56, 677–690.
Dempsey, (1978). Vendor selection and the buying process. Industrial Marketing Management, 7, 257–267.
Ding, H., Benyoucef, L., & Xie, X. (2005). A simulation optimization methodology for supplier selection problem. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 18(2–3), 210–224.
Gencer, C., & Gurpinar, D. (2007). Analytical network process in supplier selection: A case study in an electronic firm. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 31, 2475–2486.
Ghodsypour, S. H., & O’Brien, C. (2001). The total cost of logistics in supplier selection, under conditions of multiple sourcing, multiple criteria and capacity constraint. International Journal of Production Economics, 73, 15–27.
Ghodsypour, S. H., & O’Brine, C. (1998). A decision support system for supplier selection using an integrated analytic hierarchy process and linear programming. International Journal Production Economics, 56–57, 199–212.
Guneri, A. F., Yucel, A., & Ayyildiz, G. (2009). An integrated fuzzy-LP approach for supplier selection problem in supply chain management. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 9223–9228.
Haleem, A., Sushil, Qadri. M. A., & Kumar, Sanjay. (2012). Analysis of critical success factors of world-class manufacturing practices: an application of interpretative structural modelling and interpretative ranking process. Production Planning & Control, 23(10–11), 722–734.
Kumar, Sanjay., Parashar, N., & Haleem, A. (2009). Analytical hierarchy process applied to vendor selection problem: Small scale, medium scale and large scale industries. Business Intelligence Journal, 2(2), 355–362.
Mithat, Z., Cuneyt, C., & Cemal, C. (2011). A combined methodology for supplier selection and performance evaluation. Expert Systems with Applications, 8, 2741–2751.
Nydik, R. L., & Hill, R. P. (1992). Using the analytic hierarchy process to structure the supplier selection procedure. International Journal of Purchasing and Materials Management, 28(2), 31–36.
Ozgen, D., Onut, S., Gulsun, B., Tuzkaya, U. R., & Tuzkya, G. (2006). A two-phased possibilistic linear programming methodology for multi-objective supplier evaluation and order allocation problems. Information Sciences, 178, 485–500.
Razmi, J., & Rafiei, H. (2010). An integrated analytical network process with mixed-interger non-linear programming to supplier selection and order allocation. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 49, 1195–1208.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytical hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. New York: Mcgraw-Hill.
Saaty, T. L. (1990). How to make decision: the analytical decision process. European Journal of Operation Research, 48, 9–26.
Sanayei, A., Mousavi, S. F., Abdi, M. R., & Mohaghar, A. (2008). An integrated group decision-making process for supplier selection and order allocation using multi-attribute utility theory and linear programming. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 345, 731–747.
Shahanaghi, K., & Yazdian, S. A. (2009). Vendor selection using a new fuzzy group TOPSIS approach. Journal of Uncertain Systems, 3(3), 221–231.
Shipley, D., Colin, E., & Scott, E. (1991). Meeting source selection criteria: Direct versus distributor channels. Industrial Marketing Management, 20, 297–303.
Soukup, W. R. (1987). Supplier selection strategies. Journal of Purchasing and Materials Management, 50(1), 2–18.
Sushil, (2000). SAP-LAP models of inquiry. Management Decision, 38(5), 347–353.
Sushil, (2001). SAP-LAP framework. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 2(1), 51–55.
Sushil, (2005). Interpretive matrix: A tool to aid interpretation of management and social research. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 6(2), 27–30.
Sushil, (2009a). SAP-LAP linkages—a generic interpretive framework for analyzing managerial contexts. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 10(2), 11–20.
Sushil, (2009b). Interpretive ranking process. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 10(4), 1–10.
Thomas, J. K., & Srinivas, T. (2008). A supply risk reduction model using integrated multi-criteria decision making. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 55(3), 409–419.
Wadhwa, V., & Ravindran, A. R. (2007). Vendor selection in outsourcing. Computers & Operations Research, 34, 3725–3737.
Wang, J. W., Cheng, C. H., & Chen, H. K. (2009). Fuzzy hierarchical TOPSIS for supplier selection. Applied Soft Computing, 9, 377–386.
Ware, N. R., Singh, S. P., & Banwet, D. K. (2012). Supplier selection problem: A state-of-the-art review. Management Science Letters, 2(5), 1465–1490.
Ware, N. R., Singh, S. P., & Banwet, D. K. (2014a). A mixed integer non linear program to model dynamic supplier selection. Expert System with Application, 41, 671–678.
Ware, N. R., Singh, S. P., & Banwet, D. K. (2014b). Analyzing the effect of demand variation on multi-product, multi-source, multi-period model for supplier selection problem. Industrial Engineering Journal, 7(2), 13–18.
Weber, C. A., Current, J. R., & Benton, W. C. (1991). Vendor selection criteria and methods. European Journal of Operational Research, 50, 2–18.
Weber, C. A., & John, R. C. (1993). A multi-objective approach to vendor selection. European Journal of Operational Research, 68, 173–184.
Yeh, W. C., & Chuang, M. C. (2011). Using multi-objective genetic algorithm for partner selection in green supply chain problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 4244–4253.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See the Appendix Tables 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ware, N.R., Singh, S.P. & Banwet, D.K. Modeling Flexible Supplier Selection Framework. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 15, 261–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-014-0070-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-014-0070-0