Abstract
Purpose of Review
Patellar tendinopathy is a common cause of anterior knee pain. This review discusses the current concepts relating to the development of this condition and the best evidence on diagnosis and management of this condition.
Recent Findings
Patellar tendon biomechanics should be considered as a predisposing factor for development of patellar tendinopathy. Diagnosis is clinical and supported by ultrasound or MRI. The most reliable treatment is targeted exercise therapy with several useful adjunctive treatments available and undergoing more study. For refractory cases, minimally invasive and arthroscopic surgeries are preferred due to lower risk of complication and shorter recovery time. Surgical intervention for biomechanical deficits may be a useful strategy but requires more research.
Summary
Patellar tendinopathy is diagnosed clinically, and the most important treatment is physical therapy with surgery reserved for recalcitrant cases. Areas for future study include adjunctive treatments and surgical correction of the biomechanics of the patellar tendon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Dan M, Parr W, Broe D, Cross M, Walsh WR. Biomechanics of the knee extensor mechanism and its relationship to patella tendinopathy: a review. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(12):3105–12. A review of the function of the patella as the fulcrum of a lever system and how the biomechanics may contribute to patellar tendinopathy.
Tyler TF, Hershman EB, Nicholas SJ, Berg JH, McHugh MP. Evidence of abnormal anteroposterior patellar tilt in patients with patellar tendinitis with use of a new radiographic measurement. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(3):396–401.
Hansen P, Haraldsson BT, Aagaard P, Kovanen V, Avery NC, Qvortrup K, et al. Lower strength of the human posterior patellar tendon seems unrelated to mature collagen cross-linking and fibril morphology (1985). J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(1):47–52.
Millar NL, Silbernagel KG, Thorborg K, Kirwan PD, Galatz LM, Abrams GD, et al. Tendinopathy Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):1.
Lian OB, Engebretsen L, Bahr R. Prevalence of jumper’s knee among elite athletes from different sports: a cross-sectional study. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(4):561–7.
Zwerver J, Bredeweg SW, van den Akker-Scheek I. Prevalence of Jumper’s knee among nonelite athletes from different sports: a cross-sectional survey. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1984–8.
Fornaciari P, Kabelitz M, Fucentese SF. Die patellare Tendinopathie [Jumper’s Knee]. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2018;107(9–10):513-519. https://doi.org/10.1024/1661-8157/a002966.
Maffulli N, Oliva F, Loppini M, Aicale R, Spiezia F, King JB. The Royal London Hospital Test for the clinical diagnosis of patellar tendinopathy. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017;7(2):315–22.
Rath E, Schwarzkopf R, Richmond JC. Clinical signs and anatomical correlation of patellar tendinitis. Indian J Orthop. 2010;44(4):435–7.
Coombes BK, Mendis MD, Hides JA. Evaluation of patellar tendinopathy using the single leg decline squat test: is pain location important? Phys Ther Sport. 2020;46:254–9.
Morgan S, Coetzee FF. Proposing a patellar tendinopathy screening tool following a systematic review. S Afr J Physiother. 2018;74(1):454.
Blazina ME, Kerlan RK, Jobe FW, Carter VS, Carlson GJ. Jumper’s knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 1973;4(3):665–78.
Ferretti A, Conteduca F, Camerucci E, Morelli F. Patellar tendinosis: a follow-up study of surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(12):2179–85.
• Lun KK, Bennie S, Crowley JD, Lucas P, Cross M, Walsh WR, et al. Sagittal patellar flexion angle measurement determines greater incidence of patella alta in patellar tendinopathy patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(9):3115–23. This study evaluates a new radiological measurement which can identify patella alta in individuals with patellar tendinopathy.
• Park K, Salem G, Powers CM. Persons with patellar tendinopathy exhibit anatomical features that alter knee extensor mechanics: a comparison of persons with and without symptoms. J Biomech. 2022;144:111343. This study demonstrated that altered patellar tendon biomechanics caused increased patellar tendon force in these patients as a result of the anatomical abnormalities.
French C, Lee K, Jacobson J, Bureau NJ. Imaging of tendinopathies in advancing age. Radiol Clin North Am. 2022;60(4):583–92.
Bode G, Hammer T, Karvouniaris N, Feucht MJ, Konstantinidis L, Sudkamp NP, et al. Patellar tendinopathy in young elite soccer- clinical and sonographical analysis of a German elite soccer academy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):344.
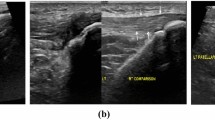
Nishida Y, Nishino T, Tanaka K, Onishi S, Kanamori A, Yamazaki M. An objective measure of patellar tendon thickness based on ultrasonography and MRI in university athletes. J Clin Med. 2021;10(18):4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184092.
Aicale R, Oliviero A, Maffulli N. Management of Achilles and patellar tendinopathy: what we know, what we can do. J Foot Ankle Res. 2020;13(1):59.
Schwartz A, Watson JN, Hutchinson MR. Patellar tendinopathy. Sports Health. 2015;7(5):415–20.
Reinking MF. Current concepts in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(6):854–66.
Quinlan JI, Narici MV, Reeves ND, Franchi MV. Tendon adaptations to eccentric exercise and the implications for older adults. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2019;4(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk4030060.
Andriolo L, Altamura SA, Reale D, Candrian C, Zaffagnini S, Filardo G. Nonsurgical treatments of patellar tendinopathy: multiple injections of platelet-rich plasma are a suitable option: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(4):1001–18.
Muaidi QI. Rehabilitation of patellar tendinopathy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4):535–40.
Marigi EM, Buckley P, Razi F, Abbas MJ, Jildeh TR, Camp CL, et al. Patellar tendinopathy: critical analysis review of current nonoperative treatments. JBJS Rev. 2022;10(3). https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.21.00168.
Breda SJ, Oei EHG, Zwerver J, Visser E, Waarsing E, Krestin GP, et al. Effectiveness of progressive tendon-loading exercise therapy in patients with patellar tendinopathy: a randomised clinical trial. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(9):501–9.
Lim HY, Wong SH. Effects of isometric, eccentric, or heavy slow resistance exercises on pain and function in individuals with patellar tendinopathy: a systematic review. Physiother Res Int. 2018;23(4): e1721.
Lorenz DS, Bailey L, Wilk KE, Mangine RE, Head P, Grindstaff TL, et al. Blood flow restriction training. J Athl Train. 2021;56(9):937–44.
Anderson AB, Owens JG, Patterson SD, Dickens JF, LeClere LE. Blood flow restriction therapy: from development to applications. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27(3):119–23.
Burton I, McCormack A. Blood flow restriction resistance training in tendon rehabilitation: a scoping review on intervention parameters, physiological effects, and outcomes. Front Sports Act Living. 2022;4: 879860.
Burton I. Interventions for prevention and in-season management of patellar tendinopathy in athletes: a scoping review. Phys Ther Sport. 2022;55:80–9.
Kongsgaard M, Kovanen V, Aagaard P, Doessing S, Hansen P, Laursen AH, et al. Corticosteroid injections, eccentric decline squat training and heavy slow resistance training in patellar tendinopathy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009;19(6):790–802.
Nuhmani S, Ahsan M, Bari MA, Malhotra D, Al Muslem WH, Alsaadi SM, et al. Patellar tendinopathy-does injection therapy have a role? A systematic review of randomised control trials. J Clin Med. 2022;11(7):2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11072006.
Yelland MJ, Sweeting KR, Lyftogt JA, Ng SK, Scuffham PA, Evans KA. Prolotherapy injections and eccentric loading exercises for painful Achilles tendinosis: a randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(5):421–8.
Rabago D, Nourani B. Prolotherapy for osteoarthritis and tendinopathy: a descriptive review. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(6):34.
Reeves KD, Sit RW, Rabago DP. Dextrose prolotherapy: a narrative review of basic science, clinical research, and best treatment recommendations. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2016;27(4):783–823.
Alfredson H, Ohberg L, Forsgren S. Is vasculo-neural ingrowth the cause of pain in chronic Achilles tendinosis? An investigation using ultrasonography and colour Doppler, immunohistochemistry, and diagnostic injections. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003;11(5):334–8.
Morath O, Beck M, Taeymans J, Hirschmuller A. Sclerotherapy and prolotherapy for chronic patellar tendinopathies - a promising therapy with limited available evidence, a systematic review. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):89.
Crimaldi S, Liguori S, Tamburrino P, Moretti A, Paoletta M, Toro G, et al. The role of hyaluronic acid in sport-related tendinopathies: a narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(10):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101088.
Oliva F, Marsilio E, Asparago G, Frizziero A, Berardi AC, Maffulli N. The impact of hyaluronic acid on tendon physiology and its clinical application in tendinopathies. Cells. 2021;10(11):3081. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113081.
Barman A, Sinha MK, Sahoo J, Jena D, Patel V, Patel S, et al. Platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2022;34(1):22.
Cho WS, Chung SG, Kim W, Jo CH, Lee SU, Lee SY. Mesenchymal stem cells use in the treatment of tendon disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical studies. Ann Rehabil Med. 2021;45(4):274–83.
Russo V, Mauro A, Peserico A, Di Giacinto O, Khatib ME, Citeroni MR, et al. Tendon healing response is dependent on epithelial-mesenchymal-tendon transition state of amniotic epithelial stem cells. Biomedicines. 2022;10(5):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051177.
Mirghaderi SP, Valizadeh Z, Shadman K, Lafosse T, Oryadi-Zanjani L, Yekaninejad MS, et al. Cell therapy efficacy and safety in treating tendon disorders: a systemic review of clinical studies. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):85.
Morton S, Chan O, King J, Perry D, Crisp T, Maffulli N, et al. High volume image-guided Injections for patellar tendinopathy: a combined retrospective and prospective case series. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(2):214–9.
Verlinde M, Hollmann MW, Stevens MF, Hermanns H, Werdehausen R, Lirk P. Local anesthetic-induced neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(3):339.
Dedes V, Stergioulas A, Kipreos G, Dede AM, Mitseas A, Panoutsopoulos GI. Effectiveness and safety of shockwave therapy in tendinopathies. Mater Sociomed. 2018;30(2):131–46.
Challoumas D, Pedret C, Biddle M, Ng NYB, Kirwan P, Cooper B, et al. Management of patellar tendinopathy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised studies. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021;7(4):e001110.
Steunebrink M, Zwerver J, Brandsema R, Groenenboom P, van den Akker-Scheek I, Weir A. Topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(1):34–9.
Naterstad IF, Joensen J, Bjordal JM, Couppe C, Lopes-Martins RAB, Stausholm MB. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in patients with lower extremity tendinopathy or plantar fasciitis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2022;12(9):e059479.
Lavagnino M, Arnoczky SP, Dodds J, Elvin N. Infrapatellar straps decrease patellar tendon strain at the site of the jumper’s knee lesion: a computational analysis based on radiographic measurements. Sports Health. 2011;3(3):296–302.
Rosen AB, Ko J, Brown CN. Single-limb landing biomechanics are altered and patellar tendinopathy related pain is reduced with acute infrapatellar strap application. Knee. 2017;24(4):761–7.
Dar G, Mei-Dan E. Immediate effect of infrapatellar strap on pain and jump height in patellar tendinopathy among young athletes. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2019;43(1):21–7.
Chalian M, Nacey NC, Rawat U, Knight J, Lancaster T, Deal DN, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous needle tenotomy using Tenex system for refractory lateral epicondylitis; short and long-term effectiveness and contributing factors. Skeletal Radiol. 2021;50(10):2049–57.
Stuhlman CR, Stowers K, Stowers L, Smith J. Current concepts and the role of surgery in the treatment of jumper’’s knee. Orthopedics. 2016;39(6):e1028–35.
Lavallee M, Bush C. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous tenotomy and its associated pain reduction and functionality outcomes in nonelite active adults. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;100(4):349–53.
Dunkow PD, Jatti M, Muddu BN. A comparison of open and percutaneous techniques in the surgical treatment of tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 2004;86(5):701–4.
• F Morrey B. A new safe and effective treatment for chronic refractory tendinopathy. Orthopedics and Rheumatology Open Access Journal. 2018;11(4):96-99. Ultrasound guided percutaneous tenotomy is shown to be effective and safe with very few complications.
• Cognetti DJ, Sheean AJ, Arner JW, Wilkerson D, Bradley JP. Surgical management of patellar tendinopathy results in improved outcomes and high rates of return to sport: a systematic review. J Knee Surg. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1757701. This was a thorough review of the use of surgery in the management of patellar tendinopathy.
•• Dan MJ, Cadman J, McMahon J, Parr WCH, Broe D, Cross M, et al. Distalising tibial tubercle osteotomy decreases patellar tendon force - a treatment rationale for recalcitrant patellar tendinopathy. Knee. 2020;27(3):871–7. This study demonstrated that distalising tibial tubercle osteotomy could reduce patellar tendon force.
•• Dan MJ, Walsh WR, Cross MJ, Caldwell B. Treatment of patella tendinopathy by distalising tibial tubercle osteotomy. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(7):e229209. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2019-229209. This is the first reported use of the distalising tibial tubercle osteotomy to alter the biomechanics of the patellar tendon for recalcitrant patellar tendinopathy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Drakes, S.M.A. Patellar Tendinopathy: Diagnosis and Management. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 11, 344–351 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-023-00407-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-023-00407-5