Abstract
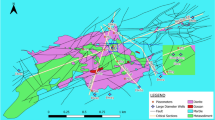
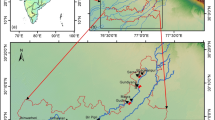
A container yard of around 100 Ha area was developed as part of the fourth terminal for Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT) in Navi Mumbai by means of reclamation in sea over soft, compressible marine clay. Ground improvement of the subsoil was warranted in order that the finished reclamation satisfies the stringent serviceability criteria.
Extensive offshore geotechnical investigation campaign comprised conventional borehole sampling, laboratory tests and various in situ field tests such as CPTu, field vane shear tests, etc. Investigations revealed clay thicknesses of 4 m–22 m, with top layer showing undrained shear strengths less than 7 kPa and increasing with depth, underlain by weathered basalt. The ground was improved using prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs) with preloading. Radial consolidation and cone dissipation tests were carried out to establish the coefficient of horizontal consolidation (ch).
The marine reclamation is confined on all sides by a perimeter bund with revetment, Stability analyses carried out for this bund showed that it was necessary to have overfill beyond the reclamation cope line along with tension geotextiles so as to achieve the prescribed factors of safety against slope failure. After removal of the preloading, the overfill was cut back to the final geometry and revetment was provided along the perimeter.
Extensive geotechnical instrumentation and monitoring were conducted using multilevel magnetic extensometers, settlement gauges, inclinometer and piezometers to monitor the behaviour and performance of ground improvement. Field ch and smear coefficients were back-calculated.
Around 200 confirmatory boreholes (CBH) were carried out after completion of ground improvement to ascertain the post-improvement and validate the design parameters, thus eliminating the risk of post-construction settlement.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manohar Varma G, Sravan Kanumuri, Ashok Kumar M (2016) Geotechnical investigations for reclamation of Mumbai port. In: Indian geotechnical conference, Chennai
Mesri G, Godlewski PM (1977) Time- and stress-compressibility interrelationship. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 103(5):417–430
Teh CI, Houlsby GT (1991) An analytical study of the cone penetration test in clay. Geotechnique 41(1):17–34
Jeevan Reddy, Pitchumani NK and Aminul Islam (2016) Stability analyses for reclamation bund on soft clay. In: Indian geotechnical conference, Chennai
IS 15284 Part 2 (2004) Design and construction for ground improvement – Guidelines
Geo-Slope International Ltd. (2012) Stability modelling with Slope/W Manual
IITK-GSDMA (2007) Guidelines for seismic design of earth dams and embankments
IS (1893) Part 1 (2002) Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structures. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi
Indraratna B, Bamunawita C, Redana IW, McIntosh G (2003) Modelling of prefabricated vertical drains in soft clay and evaluation of their effectiveness in practice. Ground Improv 7(3):127–137
Ashok Kumar M, Pitchumani NK, Aminul Islam (2016) Back analyses of PVD performance in Mumbai port. In: Indian geotechnical conference, Chennai
Sridharan A, Murthy NS, Prakash K (1987) Rectangular hyperbola method of consolidation analysis. Geotechnique 37(3):355–368
Asaoka A (1978) Observational procedure of settlement prediction. Soils Found 18(4):87–101
Hansbo S (1979) Consolidation of clay by band-shaped prefabricated drains. Ground Eng 12(5):16–25
Acknowledgement
We thank the entire AECOM team for having put in their full efforts in the design of every component of the project. We are thankful to ITD Cementation Ltd. for executing the project with the greatest diligence and professionalism. We are thankful to the consultants of the owner for ensuring top quality and robust designs from AECOM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitchumani N, K., Islam, A. Reclamation and Ground Improvement of Soft Marine Clay for Development of Offshore Terminal 4, JNPT, Navi Mumbai. Indian Geotech J 51, 502–519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-021-00521-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-021-00521-y