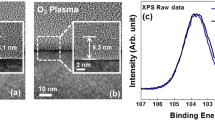
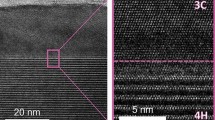
Abstract
Si3N4 wafers used for fabricating vertical 3D NAND flash memories are contaminated by various metallic, organic, and inorganic impurities. A process technology to effectively remove (NH4)2SiF6 powders generated on the surface of Si3N4 wafers processed by HF VPD was studied. It was confirmed that (NH4)2SiF6 powders were generated by a chemical reaction between Si3N4 and HF. In addition, the density and diameter of the powders depended on the thickness of the Si3N4 layers. The density of the powder increased from 317 to 2101 ea/mm2 as the thickness of the Si3N4 layer increased from 30 to 70 nm, and then rapidly decreased to 85 ea/mm2 for the 100-nm-thick Si3N4 layer. However, as the thickness of the Si3N4 layer increased from 30 to 70 nm, the diameter (approximately 10 μm) of the powder did not significantly change, but rapidly increased to approximately 30 μm when the Si3N4 layer thickness reached 100 nm. This was because more powders were generated by the thicker Si3N4 layer, but the powders generated on the 100-nm-thick Si3N4 layer aggregated more to reduce the surface energy. Moreover, we found that the heating and DIW cleaning processes effectively eliminated the (NH4)2SiF6 powders on the surface of the Si3N4 wafer processed by HF VPD. Furthermore, we determined the optimal heating and cleaning process conditions for complete decomposition: a temperature of 170 °C, time of 120 s, and pressure of 120 Torr in the vacuum oven for the heating process, and a temperature of 25 °C and time of 30 s for the cleaning process. Our proposed method for effectively eliminating (NH4)2SiF6 powder on Si3N4 wafers processed by HF VPD can be applied to monitor the level of impurity contamination in the fabrication process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.C. Jeong et al., 2018 IEEE Symp. on VLSI Tech. 59–60 (2018)
D. Ha et al., 2017 Symp. on VLSI Tech. T68–T69 (2017)
G. Bae et al., 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 28.7.1–28.7.4 (2018)
T.Z. Hong et al., 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 15–5 (2020)
K. Saga, ECS Trans. 86(10), 113–124 (2018)
H.B. Lim et al., IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 34(2), 140–144 (2021)
Y. Cho et al., J. Vac. Sci. 38(2), 022604 (2020)
D. Hellin et al., ECS Trans. 3(7), 173 (2006)
A. Shimazaki et al., Solid State Phenom. 145, 115–121 (2009)
V. Gorodokin, D. Zemlyanov, 2004 23rd IEEE Convention of Electrical and Electronics Engineers in Israel 157–160 (2004)
S.A. Ajuria et al., J. Electrochem. Soc. 140(7), L113–L115 (1993)
J. Bea et al., IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 32(1), 66–68 (2010)
K.W. Lee et al., IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 14(1), 451–462 (2013)
M.L. Polignano et al., ECS Trans. 16(6), 195 (2008)
C.J. Hsiao et al., Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA) 16–64 (2013)
M. Soha et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 520, 146299 (2020)
A. Krushevska et al., J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 15(9), 1211–1216 (2000)
M. Beebe, S. Anderson, Microelectron. Eng. 87(9), 1701–1705 (2010)
M.B. Shabani et al., J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 102(1–3), 238–246 (2003)
M.P. Yeh et al., Surf. Interface Anal. 40(1), 60–66 (2008)
E.J. Ferrero, D. Posey, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 17(9), 1194–1201 (2002)
V.K. Karandashev et al., Inorg. Mater. 49(14), 1249–1263 (2013)
M.A. Reddy et al., Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 180, 106184 (2021)
K.S. Seol et al., 2010 IEEE Symp. VLSI Circuits Dig. Tech. Pap. 127–128 (2010).
T.Y. Lee et al., Solid-State Electron. 164, 107713 (2020)
C.J. Wang et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52(7), 070201 (2013)
B.D. Bois et al., Sensor Technology 2001 (Springer, Dordrecht, 2001), pp.131–136
H.C. Zeng, Curr. Nanosci. 3(2), 177–181 (2007)
B. Liu, H.C. Zeng, Small 1(5), 566–571 (2005)
I. Gosens et al., Part. Fibre Toxicol. 7(1), 1–11 (2010)
G. Vereecke et al., J. Electochem. Soc. 147(4), 1499–1501 (2000)
E.J. Song et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57(10), 106505 (2018)
N. Posseme et al., J. Vac. Sci 34(6), 061301 (2016)
N. Miyoshi et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 56(6S2), 06HB01 (2017)
J. Frayret et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 427(4–6), 356–364 (2006)
Y. Elyamani et al., J. Fluor. Chem. 247, 109796 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A4A1052085) and by the Brain Korea 21 PLUS Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, HJ., Park, JG. Effective methods for eliminating (NH4)2SiF6 powders generated on Si3N4 wafers processed by HF VPD. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 81, 903–909 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-022-00625-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-022-00625-5