Abstract
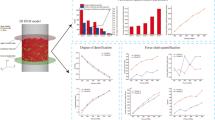
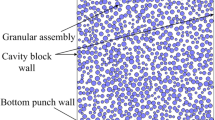
The flow and force chain characteristics of metal powder in high-velocity compaction are not fundamentally understood because of the complexities and discreteness of these particle systems. A 2D discrete element model of a metal powder subjected to uniaxial compaction is developed. The flow state of particles, the force chain distribution, and the influence of the main model parameters on the force chains are investigated. Results indicate a collisional particle flow stage at the beginning of compaction. Then, the flow state of particles can rapidly be classified as a dense particle flow. In addition, the contact force distribution for the collisional particle flow follows an exponential law, which is significantly different from that for dense particle flow. The probability distribution of contact forces changes as a power function in the dense particle flow. The force chains initially deviate in the y-axis direction and then in the x-axis direction with increasing friction coefficient, and the distribution and load-carrying rates of the weak force chains decrease with increasing friction coefficient. Moreover, the force chains deflect in the direction of the x-axis with increasing the particle diameter, and the distribution rate and load-carrying rate of the weak force chains decrease with increasing particle diameter. These changes in the direction of the force chains are similar to the density changes in the compacted blank part parts. The distribution rate and the load-carrying rate of the weak force chains decrease with increasing friction coefficient, and the density of the blank part depends on the direction of the entire force chains (vector sum of the force chains). Under the strength of the force chains with slight changes and when the entire force chains are inclined in the densification direction, the density of the compacted blank part increases.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
O.A. Waseem, H.J. Ryu, Sci Rep 7, 1926 (2017)
D. Wu, S.P. Wu, L. Yang, C.D. Shi, Y.C. Wu, W.M. Tang, Powder Metall 58, 100 (2015)
Z. Guo, D. Zhu, J. Pan, C. Yang, S. Li, T. Dong, H. Tian, X. Yan, Powder Technol 378, 19 (2021)
A. Db, B. Sat, A. Hpc, C. Map, Adv Powder Technol 31, 3474 (2020)
B. Zhang, M. Jain, C. Zhao, M. Bruhis, R. Lawcock, K. Ly, Powder Technol 204, 27 (2010)
B. Harthong, J.F. Jerier, P. Doremus, D. Imbault, F.V. Donze, Int J Solids Struct 46, 3357 (2009)
S. Yu, J. Zhou, W. Zhang, X. Zhang, K. Liu, CHN Mech Eng 29, 1120 (2018)
D. Souriou, P. Goeuriot, O. Bonnefoy, G. Thomas, F. Doré, Powder Technol 190, 152 (2009)
G. Sethi, E. Hauck, R.M. German, Mater Sci Tech 22, 955 (2006)
D.F. Khan, H.Q. Yin, H. Li, Z. Abideen, Q.X.H. Asadullah, M. Ellahi, Mater Design 54, 149 (2014)
D.F. Khan, H.Q. Yin, H. Li, X.H. Qu, M. Khan, S. Ali, Mater Design 50, 479 (2013)
K.Q. Zhang, H.Q. Yin, X. Jiang, X.Q. Liu, F. He, Z.H. Deng, D.F. Khan, Q.J. Zheng, X.H. Qu, Int J Min Mef Mater 26, 194 (2019)
J.Z. Wang, H.Q. Yin, X.H. Qu, J.L. Johnson, Powder Technol 195, 184 (2009)
J.Z. Wang, H.Q. Yin, X.H. Qu, Front Mater Sci China 3, 319 (2009)
T. Timo, A. Osmo, P. Arne, R. Heikki, E. Henrik, J. Anne, Y. Jouko, Int J Pharmaceut 566, 194 (2019)
B. Azhdar, B. Stenberg, L. Kari, Polym Test 24, 909 (2005)
Z.Q. Yan, F. Chen, Y.X. Cai, Powder Technol 208, 596 (2011)
P.G. De Gennes, Rev Mod Phys 71, 374 (1999)
W. Wang, Y. Liu, G.Q. Zhu, Wear 318, 114 (2014)
A. Tordesillas, D.W. Walker, Q. Lin, Phys Rev E 81, 011302 (2010)
W. Zhang, S. Zhang, J. Tan, J. Du, N. Zhang, J Phys Soc of JPN 89, 124602 (2020)
C.B. Eduardo, F.A. Ducha, A.P.F. Atman, Granul Matter 22, 61 (2020)
F.J. Meng, K. Liu, Z. Tang, W. Wang, X. Liu, Phys Scripta 89, 105702 (2014)
C.S. Campbell, Powder Technol 162, 208 (2006)
J.R. Darias, M.P. Madrid, L.A. Pugnaloni, Phys Rev E 101, 052905 (2020)
L. La Ragione, M. Gammariello, G. Recchia, Phys Rev E 94, 062904 (2016)
D. Bi, J. Zhang, B. Chakraborty, R.P. Behringer, Nature 480, 355 (2011)
J. Chang, W. Wang, M. Zhao, K. Liu, P I Mech Eng J-J Eng Tribol 231, 1371 (2017)
S. Ostojic, E. Somfai, B. Nienhuis, Nature 439, 828 (2006)
R. Arevalo, I. Zuriguel, D. Maza, Phys Rev E 81, 041302 (2010)
R. Radhakrishnan, J.R. Royer, W. Poon, J. Sun, Granul Matter 22, 1 (2020)
R. Artoni, A.C. Santomaso, M. Go, P. Canu, Phys Rev Lett 108, 238002 (2012)
P.A. Cundall, A. Strack, Geotechnique 29, 1 (1979)
F. Meng, K. Liu, Q. Tao, J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40, 430 (2018)
W. Wang, W. Gu, K. Liu, Tribol Trans 58, 197 (2015)
A. Albaba, S. Lambert, T. Faug, Phys Rev E 97, 052903 (2018)
Q. Tang, Y. Zhou, D. Zhao, Energy Sci Eng 3, 719 (2020)
D. Kawabata, M. Yoshida, A. Shimosaka, S. Yoshiyuki, Adv Powder Technol 31, 1381 (2020)
R.D. Mindlin, H. Deresiewicz, J Appl Mech 20, 327 (1953)
F.J. Meng, H.B. Liu, S.Z. Hua, M.H. Pang, Results Phys 25, 104328 (2021)
W. Zhang, K. Liu, J. Zhou, R. Chen, N. Zhang, G. Lian, Phys Scripta 95, 065704 (2020)
K.N. Elkholy, M.M. Khonsari, ASME J Tribol 129, 923 (2007)
W. Wang, Liu X J and Liu K. Tribol Lett 48, 229 (2012)
F. Meng, K. Liu, W. Wang, Tribol Tran 58, 70 (2015)
T. Majmudar, R. Behringer, Nature 435, 7045 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for its financial support under Grant No. 51605150. This work was also partly supported by Key Projects of Natural Science Research in Tongling Polytechnic (tlpt2020NK006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZY., Meng, FJ. Investigation of the flow and force chain characteristics of metal powder in high-velocity compaction based on a discrete element method. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 79, 455–467 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00241-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00241-9