Abstract
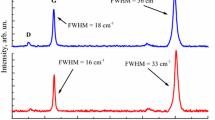
Temperature-dependent Raman scattering provides valuable information on electron–phonon coupling and phonon anharmonicity of graphene. In this study, we show an enhancement of Joule heating in graphene by confining the current flow in a narrow channel. In addition, we performed a detailed analysis of the anharmonic effect in the hBN/monolayer graphene/hBN heterostructure based on the behaviour of the full-width at half maximum of the G mode with increasing electric power: a non-monotonic trend, leading to the key of approximation of the electronic temperature in graphene. We believe our results could offer a convenient analysis tool to study electron–phonon coupling and anharmonic phonon-decay processes in a high-temperature regime.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 January 2021
The article was revised to change copy right year.
References
E. Gruber et al., Nat. Commun. 7, 13948 (2016)
C.R. Dean et al., Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 722–726 (2010)
L. Wang et al., Science 342, 614–617 (2013)
S. Son et al., 2D Materials 5(1), 011006 (2017)
Y.D. Kim et al., Nano Lett. 18(2), 934–940 (2018)
F. Luo et al., ACS Photon. 6(8), 2117–2125 (2019)
D. Chae, B. Krauss, K. Klitzing, J.H. Smet, Nano Lett. 10(2), 466–471 (2010)
H.-N. Liu, X. Cong, M.-L. Lin, P.-H. Tan, Carbon 152, 451–458 (2019)
N. Bonini, M. Lazzeri, N. Marzari, F. Mauri, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 176802 (2007)
Y. Yang et al., Nano Lett. 19(12), 8526–8532 (2019)
Y.J. Yu et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 183105 (2011)
M. Freitag et al., Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 497–501 (2010)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A. 362, 2477–2512 (2004)
A.C. Ferrari et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 187401 (2006)
A.C. Ferrari, D.M. Basko, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 235–246 (2013)
L.M. Malard, M.A. Pimenta, G. Dresselhaus, M.S. Dresselhaus, Phys. Rep. 473, 51–87 (2009)
G. Froehlicher, S. Berciaud, Phys. Rev. B 91, 205413 (2015)
C. Ferrante et al., Nat. Commun. 9, 308 (2018)
D. Yoon, Y. Son, H. Cheong, Nano Lett. 11(8), 3227–3231 (2011)
M. Lazzeri, M. Calandra, F. Mauri, Phys. Rev. B 68, 220509(R) (2003)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Research Funds of Mokpo National University in 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, M., Kim, DH., Lee, JH. et al. Electronic-temperature estimation of Joule-heated graphene via Raman investigations. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 78, 164–168 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-020-00054-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-020-00054-2