Abstract
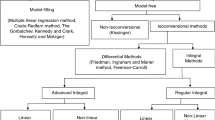
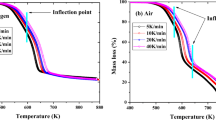
Thermogravimetry analyzer was used for the study of thermal degradation of plywood under air and nitrogen environment. The investigation was carried out at a heating rate in the range of 5–100 K min−1 from a temperature atmosphere to 1050 K. Thermal decomposition steps dehydration, oxidative reaction (air environment), pyrolysis degradation (nitrogen environment) and char degradation with temperature evolution were reported. Kinetic parameters of thermal degradation step were investigated with model fitting Coats–Redfern method. Arrhenius kinetic reaction model was used for oxidative and pyrolysis reaction degradation stages kinetic parameter estimation. Model kinetic triplets were estimated for different heating rates of the thermal degradation step. The experimental data deviation percentage with the proposed model was found to be below 5% with reasonable accuracy for different heating rates.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- m :
-
Mass initial and mass at a time (mg)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- W :
-
Normalized mass
- α :
-
Conversion
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- dα/dt :
-
Conversion rate
- dW/dt :
-
Normalized DTG (s−1)
- dm/dt :
-
Experimental DTG data (mg s−1)
- K(T):
-
Reaction rate constant (s)
- f(α):
-
Reaction model
- A :
-
Pre-exponential factor (s−1)
- R :
-
Gas constant, 8.314 (J mol−1 K−1)
- n :
-
Reaction order
- β :
-
Heating rate (K min−1)
- g(α):
-
Reaction model integral form
- N :
-
Number of data points
- E :
-
Activation energy (J mol−1)
- o :
-
Initial
- f :
-
Final
- exp:
-
Experimental
- theo:
-
Theoretical
- i :
-
Different heating rate values
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetry analysis
- DTG:
-
Differential thermogravimetry
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- RMSD:
-
Root-mean-square deviation
References
H.J. Park, H.S. Heo, K.S. Yoo, J.H. Yim, J.M. Sohn, K.E. Jeong, J.K. Jeon, Y.K. Park, Thermal degradation of plywood with block polypropylene in TG and batch reactor system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 17, 549–533 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2010.11.002
D.A. Tillman, Biomass cofiring: the technology, the experience, the combustion consequences. Biomass Bioenergy 19(6), 365–384 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0961-9534(00)00049-0
T. Fateh, T. Rogaume, J. Luche, F. Richard, F. Jabouille, Kinetic and mechanism of the thermal degradation of a plywood by using thermogravimetry and fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy analysis in nitrogen and air atmosphere. Fire Saf. J. 58, 25–37 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2013.01.019
F. C. Beall, H. W. Eickner, Thermal degradation of wood components: a review of the literature. U.S.D.A. Forest Serv. Res. Pap. FPL 130 (1970)
G.A. Byrne, D. Gardiner, F.H. Holmes, The pyrolysis of cellulose and the action of flame-retardants. J. Appl. Chem. 16(3), 81–88 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5010160303
K. Suresh, K. Gulati, S. Kumar, A. Singh, Kinetic study of thermal degradation of varieties of plywood by using thermogravimetry under nitrogen atmosphere. Int. J. Adv. Res. Manag. 3(8), 177–183 (2018)
T. Fateh, T. Rogaume, F. Richard, Multi-scale modeling of the thermal decomposition of fire retardant plywood. Fire Saf. J. 64, 36–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2014.01.007
M. Wu, W. Song, Y. Wu, W. Qu, Preparation and characterization of the flame retardant decorated plywood based on the intumescent flame retardant adhesive. Materials (Basel) 13(3), 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030676
F. Wang, Z. Gao, M. Zheng, J. Sun, Thermal degradation and fire performance of plywood treated with expanded vermiculite. Fire Mater. 40(3), 427–433 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2297
C. Branca, C. Di Blasi, Global interinsic kinetics of wood oxidation. Fuel. 83(1), 81–87 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00220-5
C. Di Blasi, Modeling chemical and physical processes of wood and biomass pyrolysis. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 34(1), 47–90 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2006.12.001
A. Sharma, B. Mohanty, Non-isothermal TG/DTG-FTIR kinetic study for devolatilization of dalbergia sissoo wood under nitrogen atmosphere. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09978-0
A. Coats, J. Redfern, Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 201(4916), 68–69 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/201068a0
S. Ceylan, Y. Topçu, Pyrolysis kinetics of hazelnut husk using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 156, 182–188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.040
A.K. Varma, P. Mondal, Physicochemical characterization and kinetic study of pine needle for pyrolysis process. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 124(1), 487–497 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-5126-7
J.J.M. Orfão, F.J.A. Antunes, J.L. Figueiredo, Pyrolysis kinetics of lignocellulosic materials - three independent reactions model. Fuel. 78(3), 349–358 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00156-2
É.D.G. Baroni, K. Tannous, Y.J. Rueda-Ordóñez, L.K. Tinoco-Navarro, Tinoco-Navarro LK. The applicability of isoconversional models in estimating the kinetic parameters of biomass pyrolysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 123(2), 909–917 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4707-9
F.C.R. Lopes, K. Tannous, Y.J. Rueda-Ordóñez, Combustion reaction kinetics of guarana seed residue applying isoconversional methods and consecutive reaction scheme. Bioresour. Technol. 219, 392–402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.099
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge CSIR-Central Building Research Institute, Roorkee, India, for financial support and permission for the activity.
Funding
Funding was provided by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India (Grant No. HCP-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A.A., Kumar, R., Ansari, A.A. et al. Non-isothermal Degradation Analysis of Plywood and Determination of Kinetic Parameters Using Coats–Redfern Method. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 102, 249–255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-021-00215-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-021-00215-3