Abstract
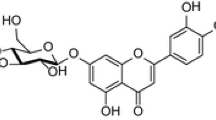
Wool and silk fibres have been effectively dyed with an aqueous extract of C. sinensis from an acidic dye bath (pH ~ 4.0). Methanol extract of the dye has been used for measuring different kinetic and thermodynamic parameters. The results indicate that the dye has an affinity for wool and silk. The standard affinity value of C. sinensis for wool fibre is greater than that for the silk fibre and it increases with the increase in temperature. Rate of dyeing for wool is lower as compared to that of silk. Studies on adsorption isotherm indicate that this dye is adsorbed on protein fibres chiefly following Langmuir adsorption mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, The wealth of India, a dictionary of Indian raw materials and industrial products. Raw Mater. II, 26–49 (1950)
S. Scion, Biosynthesis of precursors for liquor and flavour characteristics in black tea, in Global Advances in Tea Science, ed. by N.K. Jain (Aravali Books International (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 1999), p. 723
D. Das, S.C. Bhattacharya, S. Ray Maulik, Int. J. Tea Sci. 4(3 & 4), 17–25 (2005)
H.T. Deo, B.K. Desai, J. Soc. Dyers Col. 115, 224–227 (1999)
M.D. Teli, R.V. Adivarekar, P.D. Pardeshi, Colourage 69(10), 23–28 (2002)
M.L. Gulrajani, D. Gupta, S. Roy Maulik, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 24(2), 131–135 (1999)
S. Roy Maulik, Asian Dyer 12(1), 29–32 (2015)
E.R. Trotman, Dyeing and Chemical Technology of Textile Fibres (B I Publications Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, 1994)
D. Das, A.K. Samanta, P.C. Dasgupta, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 22(1), 53–60 (1997)
M.L. Gulrajani, D. Gupta, S. Roy Maulik, J. Indian, Fibre Text. Res. 24(3), 223–225 (1999)
M.L. Gulrajani, S. Bhaumik, W. Oppermann, G. Hardtmann, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 27, 91–94 (2002)
M.L. Gulrajani, D. Gupta, S.R. Maulk, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 24(4), 294–296 (1999)
A. Johnson, The Theory of Colouration of Textiles (Dyers Co. Publications Trust, West Yorkshire, 1989)
S.R. Sivaraja Iyer, D.J. Srinivasan, Soc. Dyer Col. 100, 63–65 (1984)
C. L. Bird, Theory and Practice of Wool Dyeing, (Soc Dyers Col, Bradford, England, 1982)
F. Sadov, M. Korchagin, A. Matetsky, Chemical Technology of Fibrous Materials (Mir Publishers, Moscow, 1978)
E.P.G. Gohl, L.D. Vilensky, Textile Science: An Explanation of Fibre Properties (Longman Cheshire Pvt, Ltd, 1983)
C. Duckworth, Engineering in Textile Colouration (Dyers Co. Publications Trust, Bradford, 1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy Maulik, S. Studies on Dyeing Parameters of Colourants Extracted from Camellia sinensis. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 99, 157–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-018-0124-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-018-0124-5