Abstract
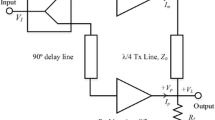
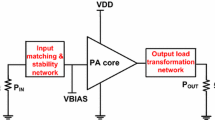
In this paper, a comparative study of different efficiency enhancement architectures for power amplifiers (PA) has been undertaken. Architectures such as Doherty, Outphasing and Envelope tracking have been discussed in this paper. These architectures can be used individually or a combination of these can be used. The Doherty power amplifier (DPA) is one of the most regularly utilized power amplifier topologies in cellular systems. The advantages of Doherty architecture are the flexibility and simple design, whereas the disadvantages include the inherent bandwidth restrictions because of the use of narrow-band quarter-wavelength transmission lines for impedance transformation. The outphasing method provides good efficiency, but branch loading creates a problem. The Envelope tracking (ET) approach uses drain-bias modulation to amplify a modulated signal with a high peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). To achieve flawless envelope tracking, the supply control signal and the radio frequency (RF) input envelope should be time-matched.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.L. Krauss, C.W. Bostian, F.H. Raab, Solid State Radio Engineering (Wiley, New York, 1980)
F.H. Raab, R. Caverly, R. Campbell, M. Eron, J.B. Hecht, A. Mediano, D.P. Myer, J.L. Walker, HF, VHF, and UHF systems and technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 50(3), 888–899 (2002)
G.I. Haddad, R.J. Trew, Microwave solid-state active devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 50(3), 760–779 (2002)
Weiss Manoja D, Z. Popovic, A 10 GHz high-efficiency active antenna, in IEEE Microwave Symposium Digest vol. 3, No. 1 (1999), pp. 663–666
R. Van Nee, R. Prasad, OFDM for Wireless Multimedia Communications (Artech House Inc., 2000)
P.B. Kenington, High Linearity RF Amplifier Design (Artech House, Boston, 2000)
S.C. Cripps, RF Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communications (Artech House, 2006)
W.H. Doherty, A new high efficiency power amplifier for modulated waves. Proc. Inst. Radio Eng. 24(9), 1163–1182 (1936)
S.C. Cripps, Advanced Techniques in RF Power Amplifier Design (Artech House, Boston, 2002)
M. Iwamoto, A. Williams, P.-F. Chen, A.G. Metzger, L.E. Larson, P.M. Asbeck, An extended Doherty amplifier with high efficiency over a wide power range. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 49(12), 2472–2479 (2001)
D.Y.-T. Wu, S. Boumaiza, A mixed-technology asymmetrically biased extended and reconfigurable Doherty amplifier with improved power utilization factor. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(5), 1946–1956 (2013)
Y. Park, J. Lee, S. Kim, D. Minn, B. Kim, Analysis of average power tracking Doherty power amplifier. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 25(7), 481–483 (2015)
F.H. Raab, Efficiency of Doherty RF power-amplifier systems. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 3, 77–83 (1987)
M. Özen, K. Andersson, C. Fager, Symmetrical Doherty power amplifier with extended efficiency range. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 64(4), 1273–1284 (2016)
J. Qureshi, N. Li, W. Neo, F. Van Rijs, I. Blednov, L. de Vreede, A wideband 20W LMOS Doherty power amplifier, in 2010 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IEEE, 2010) pp. 1504–1507
M.N.A. Abadi, H. Golestaneh, H. Sarbishaei, S. Boumaiza, An extended bandwidth Doherty power amplifier using a novel output combiner, in 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2014) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 1–4
Y. Cho, D. Kang, J. Kim, K. Moon, B. Park, B. Kim, Linear Doherty power amplifier with an enhanced back-off efficiency mode for handset applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 62(3), 567–578 (2014)
R. Giofre, L. Piazzon, P. Colantonio, F. Giannini, A distributed matching/combining network suitable for Doherty power amplifiers covering more than an octave frequency band, in 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2014) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 1–3
D. Gustafsson, C.M. Andersson, C. Fager, A modified Doherty power amplifier with extended bandwidth and reconfigurable efficiency. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(1), 533–542 (2013)
D.Y.-T. Wu, S. Boumaiza, A modified Doherty configuration for broadband amplification using symmetrical devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 60(10), 3201–3213 (2012)
P. Saad, P. Colantonio, L. Piazzon, F. Giannini, K. Andersson, C. Fager, Design of a concurrent dual-band 1.8–2.4 GHz GaNHEMT Doherty power amplifier. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 60(6), 1840–1849 (2012)
G. Lv, W. Chen, X. Chen, F.M. Ghannouchi, Z. Feng, A compact Ka/Q dual-band GaAs MMIC Doherty power amplifier with simplified offset lines for 5G applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 67(7), 3110–3121 (2019)
X.A. Nghiem, J. Guan, T. Hone, R. Negra, Design of concurrent multiband Doherty power amplifiers for wireless applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(12), 4559–4568 (2013)
A.M.M. Mohamed, S. Boumaiza, R.R. Mansour, Reconfigurable Doherty power amplifier for multi frequency wireless radio systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(4), 1588–1598 (2013)
A.M.M. Mohamed, S. Boumaiza, R.R. Mansour, Electronically tunable Doherty power amplifier for multi-mode multi-band base stations. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 61(4), 1229–1240 (2013)
G. Lv, W. Chen, X. Liu, F.M. Ghannouchi, Z. Feng, A fully integrated C-band GaN MMIC Doherty power amplifier with high efficiency and compact size for 5G application. IEEE Access 7, 71665–71674 (2019)
A. Agah, H.-T. Dabag, B. Hanafi, P.M. Asbeck, J.F. Buckwalter, L.E. Larson, Active millimeter-wave phase-shift Doherty power amplifier in 45-nm SOI CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 48(10), 2338–2350 (2013)
E. Kaymaksut, P. Reynaert, Transformer-based uneven Doherty power amplifier in 90 nm CMOS for WLAN applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(7), 1659–1671 (2012)
I. Aoki, S.D. Kee, D.B. Rutledge, A. Hajimiri, Fully integrated CMOS power amplifier design using the distributed active-transformer architecture. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 37(3), 371–383 (2002)
E. Kaymaksut, D. Zhao, P. Reynaert, Transformer-based Doherty power amplifiers for mm-wave applications in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 63(4), 1186–1192 (2015)
H. Chireix, High power outphasing modulation. Proc. Inst. Radio Eng. 23(11), 1370–1392 (1935)
A. Miller, J. Novik, Principles of operation of the Ampliphase transmitter. Broadcast News 104, 44–47 (1959)
D. Musson et al., Ampliphase... for economical super-power AM transmitters. Broadcast News 119, 24–29 (1964)
D. Cox, Linear amplification with nonlinear components. IEEE Trans. Commun. 22(12), 1942–1945 (1974)
A. Grebennikov, RF and Microwave Power Amplifier Design (McGraw-Hill Education, New York, 2004)
M.P. Van Der Heijden, M. Acar, J.S. Vromans, D.A. Calvillo-Cortes, A 19W high-efficiency wide-band CMOS-GaN class-E Chireix RF outphasing power amplifier, in 2011 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IEEE, 2011), pp. 1–4
W. Tai, H. Xu, A. Ravi, H. Lakdawala, O. Bochobza-Degani, L.R. Carley, Y. Palaskas, A transformer-combined 31.5 dbm outphasing power amplifier in 45 nm LP CMOS with dynamic power control for back-off power efficiency enhancement. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(7), 1646–1658 (2012)
P. Madoglio, A. Ravi, H. Xu, K. Chandrashekar, M. Verhelst, S. Pellerano, L. Cuellar, M. Aguirre, M. Sajadieh, O. Degani et al., A 20 dbm 2.4 GHz digital outphasing transmitter for WLAN application in 32 nm CMOS, in 2012 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (IEEE, 2012), pp. 168–170
J. Qureshi, R. Liu, A. De Graauw, M. Van der Heijden, J. Gajadharsing, L. De Vreede, A highly efficient Chireix amplifier using adaptive power combining, in 2008 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE, 2008), pp. 759–762
P.P.A. Godoy, Techniques for high-efficiency outphasing power amplifiers. PhD Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2011)
T.W. Barton, D.J. Perreault, Theory and implementation of RF-input outphasing power amplification. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 63(12), 4273–4283 (2015)
N. Faraji, T.W. Barton, An RF-input Chireix outphasing power amplifier, in 2016 IEEE Topical Conference on Power Amplifiers for Wireless and Radio Applications (PAWR) (IEEE, 2016), pp. 11–14
D. Zhao, S. Kulkarni, P. Reynaert, A 60 GHz outphasing transmitter in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(12), 3172–3183 (2012)
C.M. Andersson, D. Gustafsson, J.C. Cahuana, R. Hellberg, C. Fager, A 1–3 GHz digitally controlled dual-RF input power-amplifier design based on a Doherty–Outphasing continuum analysis. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(10), 3743–3752 (2013)
A.R. Qureshi, M. Acar, J. Qureshi, R. Wesson, L.C. de Vreede, A 112 W GaN dual input Doherty–Outphasing power amplifier, in 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS) (IEEE, 2016), pp. 1–4
H. Jang, R. Wilson, T. Canning, D. Seebacher, C. Schuberth, B. Arigong, F. Trang, S. Ward, RF input self-outphasing Doherty–Chireix combined amplifier. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 64(12), 4518–4534 (2016)
I. Hakala, D.K. Choi, L. Gharavi, N. Kajakine, J. Koskela, R. Kaunisto, A 2.14 GHz Chireix outphasing transmitter. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 53(6), 2129–2138 (2005)
L.R. Kahn, Single-sideband transmission by envelope elimination and restoration. Proc. IRE 40(7), 803–806 (1952)
F.H. Raab, B.E. Sigmon, R.G. Myers, R.M. Jackson, L-band transmitter using Kahn EER technique. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 46(12), 2220–2225 (1998)
F.H. Raab, Intermodulation distortion in Kahn-technique transmitters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 44(12), 2273–2278 (1996)
A.A. Saleh, D.C. Cox, Improving the power-added efficiency of FET amplifiers operating with varying-envelope signals. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 31(1), 51–56 (1983)
B. Geller, F. Assal, R. Gupta, P. Cline, A technique for the maintenance of FET power amplifier efficiency under Backoff, in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE, 1989), pp. 949–952
F. Wang, A. Ojo, D. Kimball, P. Asbeck, L. Larson, Envelope tracking power amplifier with pre-distortion linearization for WLAN 802.11 g, in 2004 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37535), vol. 3 (IEEE, 2004), pp. 1543–1546
J. Choi, D. Kim, D. Kang, B. Kim, A polar transmitter with CMOS programmable hysteretic-controlled hybrid switching supply modulator for multistandard applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 57(7), 1675–1686 (2009)
D. Kang, D. Kim, J. Choi, J. Kim, Y. Cho, B. Kim, A multimode/multiband power amplifier with a boosted supply modulator. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 58(10), 2598–2608 (2010)
J. Kim, J. Kim, J. Moon, J. Son, I. Kim, S. Jee, B. Kim, Saturated power amplifier optimized for efficiency using self-generated harmonic current and voltage. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 59(8), 2049–2058 (2011)
Y. Li, J. Lopez, C. Schecht, R. Wu, D.Y. Lie, Design of high efficiency monolithic power amplifier with envelope-tracking and transistor resizing for broadband wireless applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(9), 2007–2018 (2012)
M. Rodriguez, Y. Zhang, D. Maksimović, High frequency PWM buck converters using GaN-on-SiC HEMTs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(5), 2462–2473 (2013)
Y. Zhang, M. Rodriguez, D. Maksimović, High frequency integrated gate drivers for half-bridge GaN power stage, in 2014 IEEE 15th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 1–9
R. Wu, Y.-T. Liu, J. Lopez, C. Schecht, Y. Li, D.Y. Lie, High efficiency silicon based envelope tracking power amplifier design with envelope shaping for broadband wireless applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 48(9), 2030–2040 (2013)
C. Florian, T. Cappello, R.P. Paganelli, D. Niessen, F. Filicori, Envelope tracking of an RF high power amplifier with an 8-level digitally controlled GaN-on-Si supply modulator. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 63(8), 2589–2602 (2015)
J.J. Yan, P. Theilmann, D.F. Kimball, A high efficiency 780 MHz GaN envelope tracking power amplifier, in 2012 IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium (CSICS) (IEEE, 2012), pp. 1–4
V. Camarchia, M. Pirola, R. Quaglia, S. Jee, Y. Cho, B. Kim, The Doherty power amplifier: review of recent solutions and trends. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 63(2), 559–571 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors are immensely grateful to Wolfspeed, a CREE company, for providing HEMTs mathematical models.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saurabh, K., Singh, S. Architectures for Efficiency Enhancement in Power Amplifiers. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 105, 385–396 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-023-00951-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-023-00951-7