Abstract
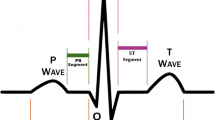
Heart is responsible for circulation of the blood throughout the human body. The conduction of the heart is nonlinear in nature and hence needs appropriate utilisation of technological advancements. The activity of the heart is assessed through an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal that consists of three different types of waves viz. P-wave, QRS-wave (also called QRS complex), and T-wave. But these waves are non-stationary, and hence, investigation of effective tools is essential for their accurate analysis. In this paper, the spectrogram technique is proposed to be used for feature extraction to analyse different segments of heartbeats (energy change) through colour contrasts of various frequency components with respect to time unlike the existing techniques where it was not possible. The features are extracted after the pre-processing accomplished using a digital bandpass filter (DBPF). The extracted features are further proposed to be optimised using the spider monkey optimisation technique due to its acclaimed effectiveness in solving the real-world optimisation problems. The robustness of the proposed methodology is established in fulfilling the ever-increasing demand of modern health care.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- MECG:
-
Maternal ECG
- fECG:
-
Foetal ECG
- Se:
-
Sensitivity
- PP:
-
Positive predictivity
- IFIR:
-
Interpolated finite impulse response
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- DR:
-
Detection rate
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- ANS:
-
Autonomic nervous system
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural networks
- KNN:
-
K-nearest neighbour
- Acc:
-
Accuracy
- SSA:
-
Salp swarm algorithm
- ICA:
-
Independent component analysis
- DER:
-
Detection error rate
- SMO:
-
Spider monkey optimisation
- MIT:
-
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- BIH:
-
Beth Israel Hospital
- EC:
-
Entropy criterion
- ISC:
-
Improved So and Chan
- RLE:
-
Run-length encoding
- SampEn:
-
Sample entropy
- ANCs:
-
Adaptive noise cancellers
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- WT:
-
Wavelet transform
- SA:
-
Sino-atrial
- AV:
-
Atrio-ventricular
- PLI:
-
Power line interference
- BLW:
-
Base line wander
- EMG:
-
Electromyogram
References
Cardiac conduction system. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/anatomyvideos/000021.htm. Accessed on 07 May 2021
A. Sheetal, H. Singh, A. Kaur, QRS detection of ECG signal using hybrid derivative and MaMeMi filter by effectively eliminating the baseline wander. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 98(1), 1–9 (2019)
I. Kaur, R. Rajni, A. Marwaha, ECG signal analysis and arrhythmia detection using wavelet transform. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B. 97(4), 499–507 (2016)
V. Gupta, A. Kanungo, P. Kumar, A.K. Sharma, A. Gupta, Auto-regressive time frequency analysis (ARTFA) of electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 13(6), 133–138 (2018)
S.O. Rajankar, S.N. Talbar, An electrocardiogram signal compression techniques: a comprehensive review. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 98(1), 59–74 (2019)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal et al., Detection of R-peaks using fractional Fourier transform and principal component analysis. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 13, 961–972 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03484-3
W. Xingyuan, M. Juan, Wavelet-based hybrid ECG compression technique. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 59(3), 301–308 (2009)
V. Gupta et al., Electrocardiogram signal pattern recognition using PCA and ICA on different databases for improved health management. Int. J. Appl. Pattern Recognit. 7(1), 41–63 (2022)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal et al., FrWT-PPCA-based R-peak detection for improved management of healthcare system. IETE J. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2021.1982412
K. Bensafia, A. Mansour, A.O. Boudraa et al., Blind separation of ECG signals from noisy signals affected by electrosurgical artifacts. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 104, 191–204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01674-1
M. Engin, ECG-late potential extraction using averaged singular—values of third-order cumulant (TOC) based bispectrum. Analog Integr. Circuits. Signal Process 33, 301–303 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020722030618
S. Zourob, K. Hayatleh, S. Barker et al., Increasing signal to noise ratio and minimising artefacts in biomedical instrumentation systems. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process. 95, 403–408 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1150-4
M. Chakraborty, D. Ghosh, Quantitative assessment of arrhythmia using non-linear approach: a non-invasive prognostic tool. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-017-0307-3
B. Halder, S. Mitra, M. Mitra, Classification of complete myocardial infarction using rule-based rough set method and rough set explorer system. IETE J. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2019.1588175
S.S. Mehta, N.S. Lingayat, Development of SVM based ECG pattern recognition technique. IETE J. Res. 54(1), 5–11 (2008)
H.M. Rai, A. Trivedi, S. Shukla, ECG signal processing for abnormalities detection using multi-resolution wavelet transform and artificial neural network classifier. Measurement 46, 3238–3246 (2013)
V. Gupta, G. Singh, A. Gupta and A. Singh, Occupancy grid mapping using artificial neural networks. 2010 International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control and Robotics, 247–250 Orissa, 2010 https://doi.org/10.1109/IECR.2010.5720161
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal, Chaos theory: an emerging tool for arrhythmia detection. Sens. Imaging 21(10), 1–22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11220-020-0272-9
V. Gupta, and M. Mittal, A novel method of cardiac arrhythmia detection in electrocardiogram signal. IJMEI (2019) https://www.inderscience.com/info/ingeneral/forthcoming.php?jcode=ijmei
A. NguomkamNegou, J. Kengne, A minimal three-term chaotic flow with coexisting routes to chaos, multiple solutions, and its analog circuit realisation. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01436-8
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, QRS complex detection using STFT, chaos analysis, and PCA in standard and real-time ECG databases. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B. 100(5), 489–497 (2019)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, Electrocardiogram signals interpretation using chaos theory. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 9, 2392–2397 (2018)
N. Abdul Jaleel, P. Vijaya Kumar, Implementation of an efficient FPGA architecture for capsule endoscopy processor core using hyper analytic wavelet-based image compression technique. Int. J. Data Anal. Tech. Strateg 12(3), 262–286 (2020)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, R-Peak detection in ECG signal using yule-walker and principal component analysis. IETE J. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2019.1575292
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, Principal component analysis & factor analysis as an enhanced tool of pattern recognition. Int. J. Elec. Electr. Eng. Telecoms 1(2), 73–7844 (2015)
G. Singh, V.Gupta, N.S. Rekhi, Power line interference noise removal from ECG signal using adaptive filter LMS algorithms. BEATs, NIT Jalandhar, India (2010)
B.T. Krishna, Electrocardiogram signal and linear time-frequency transforms. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B. 95, 377–382 (2014)
P. Kora, K.S.R. Krishna, ECG based heart arrhythmia detection using wavelet coherence and bat algorithm. Sens. Imag., 17 (2016).
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal et al., An efficient AR modeling based electrocardiogram signal analysis for health informatics. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics (IJMEI) 14(1), 74–89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMEI.2022.119314
M. Das, S. Ari, Analysis of ECG signal denoising method based on S-transform. IRBM 34(6), 362–370 (2013)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, KNN and PCA classifier with autoregressive modelling during different ECG signal interpretation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 125, 18–24 (2018)
K. Karda, N. Dubey, A. Kanungo, V. Gupta, Automation of noise sampling in deep reinforcement learning. Int. J. Appl. Pattern Recognit. 7(1), 15–23 (2022)
T.A.A. Ali, Z. Xiao, J. Sun, S. Mirjalili, V. Havyarimana, H. Jiang, Optimal design of IIR wideband digital differentiators and integrators using salp swarm algorithm. Knowl. Based Syst. 182, 104834 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.07.005
C. Nayak, S.K. Saha, R. Kar, D. Mandal, An efficient QRS complex detection using optimally designed digital differentiator. Circuits System Signal Process. 38(5), 716–749 (2018)
S. Chandra, A. Sharma, G.K. Singh, Computationally efficient cosine modulated filter bank design for ECG signal compression. IRBM (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2019.06.002
W.H. Jung, S.G. Lee, An arrhythmia classification method in utilising the weighted KNN and the fitness rule. IRBM (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2017.04.002
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, Respiratory signal analysis using PCA, FFT and ARTFA. In: Proc. of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Power and Energy Systems (ICEPES), India, 221–225 December 2016
V. Gupta, and M. Mittal, ECG signal analysis: past, present and future. In: Proc. 8th IEEE Power India International Conference (PIICON), India, 1–6 December 2018
E.J.S. Luz, W.R. Schwartz, G.C. Chávez, D. Menotti, ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: a survey. J. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 127, 144–164 (2016)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal, R-peak detection based chaos analysis of ECG signal. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01556-1
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, A comparison of ECG signal pre-processing using FrFT, FrWT and IPCA for improved analysis. IRBM 40(3), 145–156 (2019)
Z. Zidelmal, QRS detection based on wavelet coefficients. Comp. Met. Prog. Biomed. 107(3), 490–496 (2012)
S.S. Mehta, N.S. Lingayat, SVM based QRS detection in electrocardiogram using signal entropy. IETE J. Res. 54(3), 231–240 (2008)
S.S. Mehta, D.A. Shete, N.S. Lingayat, V.S. Chouhan, K-means algorithm for the detection and delineation of QRS-complexes in electrocardiogram. IRBM 31, 48–54 (2010)
S.S. Mehta, N.S. Lingayat, SVM-based algorithm for recognition of QRS complexes in electrocardiogram. IRBM 29, 310–317 (2008)
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, Arrhythmia detection in ECG signal using fractional wavelet transform with principal component analysis. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. B. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-020-00488-z
S. Mian Qaisar, S.F. Hussain, An effective arrhythmia classification via ECG signal subsampling and mutual information based subbands statistical features selection. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03275-w
U. Qidwai, J. Chaudhry, S. Jabbar et al., Using casual reasoning for anomaly detection among ECG live data streams in ubiquitous healthcare monitoring systems. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 10, 4085–4097 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1091-x
A. Khamparia, B. Pandey, A novel integrated principal component analysis and support vector machines-based diagnostic system for detection of chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Data Anal. Tech. Strateg. 12(2), 99–113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJDATS.2020.106641
G. Gnana Subha, S. SujaPriyadharsini, An efficient algorithm based on combined encoding techniques for compression of ECG data from multiple leads. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 108, 2137–2147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06513-9
M.J. Al-Dujaili, M.T. Mezeel, Novel approach for reinforcement the extraction of ECG signal for twin fetuses based on modified BSS. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 119, 2431–2450 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08337-y
G. Premalatha, V.T. Bai, Wireless IoT and cyber-physical system for health monitoring using honey badger optimized least-squares support-vector machine. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09500-9
V. Gupta, M. Mittal, V. Mittal, A novel FrWT based arrhythmia detection in ECG signal using YWARA and PCA. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09403-1
W. Xingyuan, M. Juan, Wavelet-based hybrid ECG compression technique. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 59(3), 301–308 (2009)
G. Tsirimokou, C. Psychalinos, Ultra-low voltage fractional-order differentiator and integrator topologies: an application for handling noisy ECGs. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process 81, 393–405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0391-0
Y.S. Alshebly, M. Nafea, Isolation of fetal ECG signals from abdominal ECG using wavelet analysis. IRBM 41(5), 252–260 (2020)
S. Rekik, N. Ellouze, Enhanced and optimal algorithm for QRS detection. IRBM 38(1), 56–61 (2017)
X. Gu, J. Hu, L. Zhang, J. Ding, F. Yan, An improved method with high anti-interference ability for R Peak detection in wearable devices. IRBM 41(3), 172–183 (2020)
S. Chandra, A. Sharma, G.K. Singh, Computationally efficient cosine modulated filter bank design for ECG signal compression. IRBM 41(1), 2–17 (2020)
S.S. Mehta and N.S. Lingayat. ECG pattern classification using support vector machine. Advances in Pattern Recognition, pp. 295–298 (2006).
S.S. Mehta and N.S. Lingayat biomedical signal processing using SVM, IET-UK International Conference on Information and Communication Technology in Electrical Sciences (ICTES 2007)
P. Marwaha, R.K. Sunkaria, Cardiac variability time-series analysis by sample entropy and multiscale entropy. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics 7(1), 1–14 (2015)
D. Amar, S. Abboud, P-wave morphology in focal atrial tachycardia using a 3D numerical model of the heart. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics 8(3), 263–274 (2016)
M.N. Salman, P.T. Rao, M.Z.U. Rahman, Cardiac signal enhancement using normalised variable step algorithm for remote healthcare monitoring systems. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics 9(2), 145–161 (2017)
H.S. Niranjana Murthy, M. Meenakshi, Novel and efficient algorithms for early detection of myocardial ischemia. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics 9(4), 351–372 (2017)
S.S. Mehta, N.S. Lingayat, Combined entropy based method for detection of QRS complexes in 12-lead electrocardiogram using SVM. Comput. Biol. Med. 38(1), 138–145 (2008)
K. Rawal, B.S. Saini, I. Saini, Effect of age and postural related changes on cardiac autonomic function in the pre-menopausal and post-menopausal women. Int. J. Med. Eng. Informatics 9(4), 299–315 (2017)
S.S. Mehta, N.S. Lingayat, Application of support vector machine for the detection of P- and T-waves in 12-lead electrocardiogram. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 93(1), 46–60 (2009)
M. Mortezaee, Z. Mortezaie, V. Abolghasemi, An improved SSA-based technique for EMG removal from ECG. IRBM 40, 62–68 (2019)
H.M. Rai, A. Trivedi, K. Chatterjee, S. Shukla, R-Peak detection using daubechies wavelet and ecg signal classification using radial basis function neural network. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B. 95(1), 63–71 (2014)
Bandpass filter. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Band-pass_filter. Accessed on 07 April 2021
Spectrogram graph. https://www.roomeqwizard.com/help/help_en-GB/html/graph_spectrogram.html. Accessed on 23 June 2020
V. Agrawal, R. Rastogi, D.C. Tiwari, Spider monkey optimization: a survey. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-017-0685-6
Spectrogram. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectrogram. Accessed on 23 June 2020
V.Gupta, M.Mittal, V.Mittal, and A. Gupta, ECG signal analysis using CWT, spectrogram and autoregressive technique. Iran J. Comput. Sci. Accepted (in press)
V. Gupta and M. Mittal, Respiratory signal analysis using PCA, FFT and ARTFA. 2016 International Conference on Electrical Power and Energy Systems (ICEPES), Bhopal, 221–225 2016 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEPES.2016.7915934
V. Gupta, G. Singh, M. Mittal and S. K. Pahuja, Fourier transform of untransformable signals using pattern recognition technique. 2010 Second International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Jakarta, 6–9 2010 https://doi.org/10.1109/ACT.2010.11
G. Singh, V. Gupta, S. Pundir, S. Sharma, An interesting difference between fourier transform & laplace transform. AMR 403–408, 114–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.403-408.114
J.C. Bansal, H. Sharma, S.S. Jadon, M. Clerc, Spider monkey optimisation algorithm for numerical optimisation. Memet. Comput. 6(1), 31–47 (2014)
H. Sharma, G. Hazrati, J.C. Bansal, Spider monkey optimization algorithm. In: Evolutionary and Swarm Intelligence Algorithms. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 779, ed. by J. Bansal, P. Singh, N. Pal (Springer, Cham, 2019), https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91341-4_4
J.C. Bansal, H. Sharma, S.S. Jadon, M. Clerc, Spider monkey optimisation algorithm for numerical optimisation. Memetic Comput. 6(1), 31–47 (2014)
C. Nayak, S.K. Saha, R. Kar, D. Mandal, Optimal SSA based wideband digital differentiator design for cardiac QRS complex detection application. Int. J. Numer. Model 32(2), 1–25 (2018)
A.K. Dohare, V. Kumar, R. Kumar, An efficient new method for the detection of QRS in electrocardiogram. Comput. Electr. Eng. 40(5), 1717–1730 (2014)
A. Ghaffari, M.R. Homaeinezhad, M. Akraminia, M. Atarod, M. Daevaeiha, A robust wavelet-based multilead electrocardiogram delineation algorithm. Med. Eng. Phys 31(10), 1219–1227 (2009)
D. Pandit, L. Zhang, C. Liu, S. Chattopadhyay, N. Aslam, C.P. Lim, A lightweight QRS detector for single lead ECG signals using a max-min difference algorithm. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 144, 61–75 (2017)
M. Rakshit, S. Das, An efficient wavelet-based automated R-Peaks detection method using Hilbert transform. Biocybernetics Biomed. Eng. 37(3), 566–577 (2017)
S. Yazdani, J.M. Vesin, Extraction of QRS fiducial points from the ECG using adaptive mathematical morphology. Dig. Sig. Proc. 56, 100–109 (2016)
B. Biswal, ECG signal analysis using modified S-transform. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 4(2), 68–72 (2017)
F. Bouaziz, D. Boutana, M. Benidir, Multiresolution wavelet-based QRS complex detection algorithm suited to several abnormal morphologies. IET Signal Proc. 8(7), 774–782 (2014)
D.C. Rufas, J. Carrabina, Simple real-time QRS detector with the MaMeMi filter. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 21, 137–145 (2015)
J. Pan, W.J. Tompkins, A real-time qrs detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 32, 230–236 (1985)
P. Ray, K.K. Mandal, B.K. Mohanty, Analysis of electrocardiogram signal using computational intelligence technique. Appl. Artif. Intell. Tech. Eng. SIGMA 1, 519–532 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1819-1
V. Gupta, N.K. Saxena, A. Kanungo et al., PCA as an effective tool for the detection of R-peaks in an ECG signal processing. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-022-01650-0
P. Kumar, S. Shilpi, A. Kanungo et al., A novel ultra wideband antenna design and parameter tuning using hybrid optimization strategy. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 122, 1129–1152 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08942-x
J.C. Bansal, S. Singh, A better exploration strategy in grey wolf optimizer. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 12, 1099–1118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02153-1
J. Mayilsamy, D.P. Rangasamy, Load balancing in software-defined networks using spider monkey optimization algorithm for the internet of things. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 116, 23–43 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07703-6
J. Swanevelder, Cardiac physiology. In: Fundementals of Anaesthesis, ed. by C. Mowatt T. Lin, T. Smith, & C. Pinnock (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2016) pp. 282–314 https://doi.org/10.1017/9781139626798.018
Funding
The authors have not obtained any type of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, V., Mittal, M., Mittal, V. et al. ECG Signal Analysis based on the Spectrogram and Spider Monkey Optimisation Technique. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 104, 153–164 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-022-00831-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-022-00831-6