Abstract
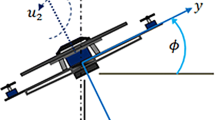
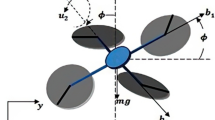
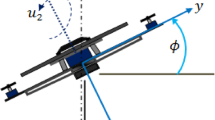
This paper presents a new neuro-fuzzy bee colony optimization method to find the optimal distribution of the membership functions (MFs) in the design of neuro-fuzzy controllers for complex nonlinear systems. The paper proposes an intelligent controller based on adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and bee colony optimization (BCO) algorithm to govern the behavior of a three-degree-of-freedom quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle. The quadrotor was chosen due to its simple mechanical structure; nevertheless, these types of aircraft are highly nonlinear. Intelligent control such as fuzzy logic is a suitable choice for controlling nonlinear systems. The ANFIS controller is used to reproduce the desired trajectory of the quadrotor in 2D vertical plane, and the BCO algorithm aims to dynamically find the optimal distribution of the MFs at the input and output ends of the ANFIS in order to reduce learning errors and improve the quality of the controller. To evaluate the performance of the proposed BCO-tuned ANFIS controller, a comparison between the proposed ANFIS-BCO controller and other controller’s performance such as ANFIS and proportional-integral-derivative controllers is illustrated using the same system. The comparison of results shows that the proposed ANFIS-BCO method outperforms the other methods already developed in the same study.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Mostafa, M.S. Ahmad, A. Mustapha, Adjustable autonomy: a systematic literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 51, 149–186 (2017)
C. Paucar, L. Morales, K. Pinto, M. Sánchez, R. Rodríguez, M. Gutierrez, L. Palacios, Use of drones for surveillance and reconnaissance of military areas. In: International Conference of Research Applied to Defense and Security. Springer, 119–132 (2018)
A. Bujak, M. Smolarek, A. Gebczynska, Applying military telematic solutions for logistics purposes. in 11th Int. Conf. Transport Systems Telematics 248–256 (2011).
L.A. Haidari, S.T. Brown, M. Ferguson, E. Bancroft, M. Spiker, A. Wilcox, R. Ambikapathi, V. Sampath, D.L. Connor, B.Y. Lee, The economic and 432 operational value of using drones to transport vaccines. Vaccine 34, 4062–4067 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.022
E.N. Barmpounakis, E.I. Vlahogianni, J.C. Golias, Unmanned aerial systems for transportation engineering: current practice and future challenges. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 5, 111–122 (2016)
P. Reinartz, M. Lachaise, E. Schmeer, T. Krauss, H. Runge, Traffic monitoring with serial images from airborne cameras. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 61, 149–158 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2006.09.009
European Aviation Safety Agency, ‘‘Prototype” Commission Regulation on Unmanned Aircraft Operations (2016).
S. Siebert, J. Teizer, Mobile 3D mapping for surveying earthwork projects using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) system. Autom. Constr. 41, 1–14 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2014.01.004
J. Valente, J.D. Cerro, A. Barrientos, D. Sanz, Aerial coverage optimization in precision agriculture management: a musical harmony inspired approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 99, 153–159 (2013)
P.K. Freeman, R.S. Freeland, Politics & technology: U.S. polices restricting unmanned aerial systems in agriculture. Food Policy 49, 302–311 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2014.09.008
D. Lenhart, S. Hinz, J. Leitloff, U. Stilla, Automatic traffic monitoring based on aerial image sequences. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 18, 400–405 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054661808030061
A. Puri, K. Valavanis, M. Kontitsis, Statistical profile generation for traffic monitoring using real-time UAV based video data. Mediterr. Conf. Control Autom. 1–6(2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/MED.2007.4433658
K. Kanistras, G. Martins, M.J. Rutherford, K.P. Valavanis, Survey of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for traffic monitoring. In: Handbook of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Springer, pp. 2643–2666 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICUAS.2013.6564694
J.Y.J. Chow, Dynamic UAV-based traffic monitoring under uncertainty as a stochastic arc-inventory routing policy. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 5(3), 167–185 (2016)
S. Srinivasan, H. Latchman, J. Shea, Airborne traffic surveillance systems: video surveillance of highway traffic. Proc. ACM 2nd Int. Work. Video Surveill. Sens. Networks, 131–135.
A. Wada, T. Yamashita, M. Maruyama, T. Arai, H. Adachi, H. Tsuji, A surveillance system using small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) related technologies. NEC Tech. J. 8(1), 68–72 (2015)
R.L. Finn, D. Wright, Unmanned aircraft systems: Surveillance, ethics and privacy in civil applications. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 28, 184–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clsr.2012.01.005
L. Ma, M.C. Li, Y.F. Wang, L.H. Tong, L. Cheng, Using high-resolution imagery acquired with an autonomous unmanned aerial vehicle for urban construction and planning. Proc. 2013 Int. Conf. Remote Sensing, Environ. Transp. Eng. (Rsete 2013) 31, 200–203 (2013).
R.J. Dobson, C. Brooks, C. Roussi, T. Colling, Developing an unpaved road assessment system for practical deployment with high-resolution opticaldata collection using a helicopter UAV. in International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS). IEEE, 235–243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICUAS.2013.6564695
V.A. Knyaz, A.G. Chibunichev, Photogrammetric techniques for road surface analysis. in ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. Prague, Czech Republic, 515–520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XLI-B5-515-2016
N.V. Hoffer, C. Coopmans, A.M. Jensen, Y. Chen, A survey and categorization of small low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle system identification. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 74, 129–145 (2014)
C. Kanellakis, G. Nikolakopoulos, Survey on computer vision for UAVs: current developments and trends. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 87, 141–168 (2017)
A.C. Watts, V.G. Ambrosia, E.A. Hinkley, Unmanned aircraft systems in remote sensing and scientific research: classification and considerations of use. Remote Sens. 4, 1671–1692 (2012)
C. Di Franco, G. Buttazzo, Coverage path planning for UAVs photogrammetry with energy and resolution constraints. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 83, 445–462 (2016)
O. Artemenko, O.J. Dominic, O. Andryeyev, A. Mitschele-Thiel, Energy-aware trajectory planning for the localization of mobile devices using an unmanned aerial vehicle. in Proceedings of the 2016 25th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), Waikoloa, HI, USA,1–4 August 2016; pp. 1–9 (2016).
T.M. Cabreira, C. Di Franco, P.R. Ferreira Jr., G.C. Buttazzo, Energy-aware spiral coverage path planning for UAV photogrammetric applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3, 3662–3668 (2018)
P. Vincent, I. Rubin, A framework and analysis for cooperative search using UAV swarms. in Proceedings of the A Framework and Analysis for Cooperative Search Using UAV Swarms, Nicosia, Cyprus, 14–17 March2004; pp. 79–86 (2004)
A. Xu, C. Viriyasuthee, I. Rekleitis, Optimal complete terrain coverage using an unmanned aerial vehicle. in Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 2513–2519 (2011).
A. Xu, C. Viriyasuthee, I. Rekleitis, Efficient complete coverage of a known arbitrary environment with applications to aerial operations. Auton. Robots 36, 365–381 (2014)
C. Caraveo, F. Valdez, O. Castillo, Optimization of fuzzy controller design using a new bee colony algorithm with fuzzy dynamic parameter adaptation. Appl. Soft Comput. 43, 131–142 (2012)
O. Castillo, L. Amador-Angulo, A generalized type-2 fuzzy logic approach for dynamic parameter adaptation in bee colony optimization applied to fuzzy controller design. Inform. Sci. 460, 476–496 (2018)
L.C. Gonçalves, M.F. Santos, R.J.F. de Sa, J.L. da Silva, H.B. Rezende, et al., Development of a PI controller through an ant colony optimization algorithm applied to a SMAR® didactic level plant. in 19th International Carpathian Control Conference (ICCC), IEEE (2018).
A.S. Oshaba, E.S. Ali, S.M. Abd Elazim, Speed control of SRM supplied by photovoltaic system via ant colony optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 28, 365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2068-8
M. Rahman, Z.C. Ong, W.T. Chong et al., Wind turbine tower modeling and vibration control under different types of loads using ant colony optimized PID controller. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 707 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3190-6
Y. Mokhtari, D. Rekioua, High performance of maximum power point tracking using ant colony algorithm in wind turbine. Renew. Energy 126, 1055–1063 (2018)
M.E. Karar, M.A. El-Brawany, Fully tuned RBF neural network controller for ultrasound hyperthermia cancer tumour therapy. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/0954898X.2018.1539260
R. Singh, L.B. Prasad, Optimal trajectory tracking of robotic manipulator using ant colony optimization. in 5th IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (UPCON), Gorakhpur, India, 2018, pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/UPCON.2018.8597087
T.K. Priyambodo, A.E. Putra, A. Dharmawan, Optimizing control based on ant colony logic for Quadrotor stabilization. in IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology (ICARES), Bali, 2015, 1–4 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICARES.2015.7429820
A. Jacknoon, M.A. Abido, Ant Colony based LQR and PID tuned parameters for controlling Inverted Pendulum. in International Conference on Communication, Control, Computing and Electronics Engineering (ICCCCEE), Khartoum, 2017, pp. 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCCEE.2017.7867652
M.P. Aghababa, Optimal design of fractional-order PID controller for five bar linkage robot using a new particle swarm optimization algorithm. Soft Comput 20, 4055 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1741-2
A. Thamallah, A. Sakly, F. M’Sahli, A new constrained PSO for fuzzy predictive control of Quadruple Tank process. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed 136, 93–104 (2019)
J. Nanda, S. Mishra, L.C. Saikia, Maiden application of bacterial foraging-based optimization technique in multiarea automatic generation control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 24, 602–609 (2009)
E.S. Ali, S.M. Abd-Elazim, Bacteria foraging optimization algorithm based load frequency controller for interconnected power system. Int. J. Elec. Power Energy Syst. 33, 633–638 (2011)
L. Liu, L. Shan, J. Yan, C. Liu, Y. Dai, An improved BFO algorithm for optimising the PID parameters of servo system. Chin. Control Decis. Conf. (CCDC) Shenyang 2018, 3831–3836 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCDC.2018.8407788
H. Metered, W. Abbas, A. Emam, Optimized proportional integral derivative controller of vehicle active suspension system using genetic algorithm. SAE Technical Paper, pp. 01–1399 (2018).
Z. Li, M. Pourmehrab, L. Elefteriadou, S. Ranka, Intersection control optimization for autonomous vehicles using genetic algorithm. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 144, 04018074 (2018)
Z. Civelek, Optimization of fuzzy logic (Takagi-Sugeno) blade pitch angle controller in wind turbines by genetic algorithm. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2019.04.010
J.S.R. Jang, ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3), 665–685 (1993)
N. Walia, H. Singh, A. Sharma, ANFIS: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-a survey. Int J Comput Appl 123, 32–38 (2015)
D. Karaboga, E. Kaya, Adaptive network based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) training approaches: a comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9610-2
D. Karaboga, An Idea based on Honey Bee Swarm for Numerical Optimization (Technical Report-Tr06, October, 2005), Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty Computer Engineering Department, Kayseri/Türkiye (2005).
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selma, B., Chouraqui, S., Selma, B. et al. Design an Optimal ANFIS Controller using Bee Colony Optimization for Trajectory Tracking of a Quadrotor UAV. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 103, 1505–1519 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-022-00747-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-022-00747-1