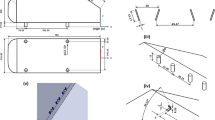
Abstract
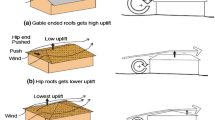
This work focuses on the evaluation of interference factors and the study of the variation of wind effects on low-rise pitched roof structures with one side kept open to the wind environment under various interference conditions induced by changing the spacing in full blockage configurations. Since no provisions are available in the wind standards for use in designing such structures, the numerical simulations are performed using Ansys CFX fluid flow solver through a standard k − ε turbulence model. Such type of study requires the use of either wind tunnel pressure measurements, or the numerical simulation of the wind environment virtually on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) domain. In this study, the CFD simulations have been carried out for four different spacing conditions and seven different wind incidence angles varied at the interval of 30° to obtain the wind pressure coefficients (Cp). Using the obtained results, the interference difference (ID) and the interference factor (IF) for each of the considered configurations were determined. The variations of IF along the roof direction were also analyzed. Also, the drag and lift force coefficients were calculated, and their variations were studied. It was found that the increase in spacing and the change in wind incidence angles affected the interference parameters. The wind flow pattern around and inside the structure varied for different wind incidence angles. The formation of eddies at various stagnation regions affected the drag and lift forces acting on the structure.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.A. Blackmore, Load reduction on flat roofs—the effect of edge profile. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 29(1), 89–98 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(88)90148-1
H.J. Gerhardt, C. Kramer, Effect of building geometry on roof wind loading. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 43(1), 1765–1773 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(92)90589-3
D. Meecham, The improved performance of hip roofs in extreme winds—A case study. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 43(1), 1717–1726 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(92)90583-V
K. C. Mehta, M. L. Levitan, R. E. Iverson, and J. R. McDonald, “Roof corner pressures measured in the field on a low building,” J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn., pp. 181–192 (1992).
J. A. Amin, A. K. Ahuja, “Experimental study of wind-induced pressures on buildings of various geometries,” 2011. [Online]. Available: www.ijest-ng.com
R. Paul, S.K. Dalui, Wind effects on ‘Z’ plan-shaped tall building: a case study. Int. J. Adv. Struct. Eng. 8(3), 319–335 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40091-016-0134-9
M. Mallick, A. Kumar, K.C. Patra, Experimental Investigation on the Wind-Induced Pressures on C-Shaped Buildings. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 23(8), 3535–3546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-1929-6
B. Bhattacharyya, S.K. Dalui, A.K. Ahuja, Wind Induced Pressure on ‘E’ Plan Shaped Tall Buildings. Jordan J. Civil Eng. 8(2), 120 (2014)
S. Chakraborty, K. Dalui, A.K. Ahuja, Experimental Investigation of Surface Pressure on ‘+’ Plan Shape Tall Building. Jordan J. Civil Eng. 8(3), 251 (2014)
S. Mukherjee, S. Chakraborty, S. K. Dalui, A. K. Ahuja, Wind induced pressure on ‘Y’ plan shape tall building. Wind Struct. Int. J. 19(5), 523–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2014.19.5.523.
A. K. Bairagi, A. Mukherjee, “Wind pressure and velocity pattern around ‘N’ plan shape tall building—A case study. Asian J. Civil Eng. 18(8), 1241–1258, (2017) [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319620553
P. Sanyal, S. K. Dalui, Effects of internal angle between limbs of ‘Y’ plan shaped tall building under wind load. J. Build. Eng. 33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101843.
P. Sanyal, S.K. Dalui, Effects of side ratio for ‘Y’ plan shaped tall building under wind load. Build. Simul. 14(4), 1221–1236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12273-020-0731-1
N. Gaur, R. Raj, Aerodynamic mitigation by corner modification on square model under wind loads employing CFD and wind tunnel. Ain Shams Eng. J. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.06.007
A. Kumar, R. Raj, Study of Pressure Distribution on an Irregular Octagonal Plan Oval-Shape Building Using CFD. Civil Eng. J. 7(10) (2021). https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2021-03091760.
J. Singh, A.K. Roy, Effects of roof slope and wind direction on wind pressure distribution on the roof of a square plan pyramidal low-rise building using CFD simulation. Int. J. Adv. Struct. Eng. 11(2), 231–254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40091-019-0227-3
J. Singh, A. K. Roy, CFD simulation of the wind field around pyramidal roofed single-story buildings. SN Appl. Sci. 1(11) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1476-2.
J. Singh, A.K. Roy, Wind pressure coefficients on pyramidal roof of square plan low rise double storey building. Comput. Eng. Phys. Model. 2(1), 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.22115/cepm.2019.144599.1043
J. Singh, A.K. Roy, Wind loads on roof of low-rise buildings. Disaster Adv. 14(5), 83–98 (2021)
P. Zhou, B. Tang, P. Liu, G. Zheng, Study on Wind Load Distribution on the Surface of Dome Structure Based on CFD Numerical Simulation. J. Phys. Conf. Seri. 1176(5). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1176/5/052056.
A. Verma, A.K. Ahuja, Wind pressure distribution on rectangular plan buildings with multiple domes. Int. J. Eng. Techn. Res. (IJETR) 3(7), 129–133 (2015)
A. Verma, A. K. Ahuja, Wind Pressure Distribution on Low-Rise buildings with Cylindrical Roofs. In Implementing Innovative Ideas in Structural Engineering and Project Management, 2015, pp. 1211–1216
S. Ahmad, K. Kumar, Interference effects on wind loads on low-rise hip roof buildings. Eng. Struct. 23(12), 1577–1589 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(01)00057-8
N. Gaur, R. Raj, P.K. Goyal, Interference effect on corner-configured structures with variable geometry and blockage configurations under wind loads using CFD. Asian J. Civil Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-021-00400-0
S. K. Nagar, R. Raj, N. Dev, Experimental study of wind-induced pressures on tall buildings of different shapes. Wind Struct. 31(5), 441–453 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12989/was.2020.31.5.441.
S. K. Nagar, R. Raj, N. Dev, Proximity effects between two plus-plan shaped high-rise buildings on mean and RMS pressure coefficients. Sci. Iran. (2021). https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2021.55928.4484.
S. Pal, R. Raj, Evaluation of Wind Induced Interference Effects on Shape Remodeled Tall Buildings. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(11), 11425–11445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05923-x
T. Stathopoulos, Adverse wind loads on low buildings due to buffeting. J. Struct. Eng. 110(10), 2374–2392 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:10(2374)
K. Shruti, S. Rajesh, G.R. Sabareesh, P.N. Rao, Study of interference effects on Chimneys. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1276(1), 012033 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1276/1/012033
IS 875 (Part 3), “Design Loads (Other than Earthquake) for Buildings and Structures-Code of Practice Part 3 Wind Loads (Third Revision).” 2015.
“Ansys Engineering Simulation Software.” 2021.
J.D. Holmes, Wind Loading of Structures, 3rd edn. (Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, 2017)
ANSYS Meshing User’s Guide, Release 13.0. Canonsburg: ANSYS, Inc., 2010.
A.C. Khanduri, T. Stathopoulos, C. Bédard, Wind-induced interference effects on buildings—a review of the state-of-the-art. Eng. Struct. 20(7), 617–630 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(97)00066-7
Funding
Authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Delhi Technological University, Delhi, India, for providing funding to conduct the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, A., Jha, A.K. & Raj, R. Wind-Induced Interference Effects on Low-Rise Pitched Roof Structure Based on CFD Simulations. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 103, 1271–1285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-022-00675-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-022-00675-9