Abstract
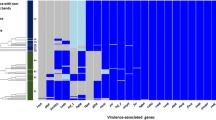
Pasteurella multocida causes endemic diseases of economic importance in livestock. A number of capsular serotypes of P. multocida bacteria are associated with different clinical diseases in the host species. Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) are at the interface of bacterium and host which are likely to play an important roles in host specificity and disease. The prime objective of the present study was to comparatively analyze seven P. multocida strains obtained from sheep, buffaloes, rabbit and pigs succumbed to different clinical conditions by ompA gene sequence analysis in conjunction with the capsular type. The ompA genes of various capsular serotypes from host species origins were amplified and sequenced. Further, sequence, phylogenetic and structural analyses were carried out. Analysis revealed that length of CDs region in different serogroups of P. multocida varied from ~ 1050 to 1077 bp, being highest in serogroups B (1077 bp) and lowest in serogroups A of rabbit strain (1050 bp). Nucleotide length was same in all sheep serogroup A strains (1059 bp). Protein domain analysis of OmpA showed signal peptide, N-terminal ompA domain and C-terminal ligand binding domain. The phylogenetic analysis showed two major clusters of the bovine and porcine/ sheep/rabbit/human strains, which was further divided in to different sub clusters such as subcluster I = NIVEDIPm sheep strains serogroup A, subcluster II = NIVEDIPm rabbit strains serogroup A, subcluster III = NIVEDIPm pig strains serogroup A, subcluster IV = NIVEDIPm pig strains serogroup D, subcluster V = NIVEDIPm bovine strains serogroup B. This study concluded that the clustering of P. multocida based on ompA proteins was associated with capsular serogroup and host species.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
ompA gene sequence of strains (NIVEDIPm 2, 17, 19, 29, 34, 40, 41) was deposited in NCBI database (GenBank), and accession number was assigned MW065783, MW065784, MW065785, MW065786, MW065787, MW065788 and MW065789, respectively.
References
Shivachandra SB, Viswas KN, Kumar AA (2011) A review of hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and buffalo. Anim Health Res Rev 12(1):67–82
Peng Z, Wang X, Zhou R, Chen H, Wilson BA, Wu B (2019) Pasteurella multocida: genotypes and genomics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 83(4):e00014-19
Wilson BA, Ho M (2013) Pasteurella multocida: from zoonosis to cellular microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 26(3):631–655
Carter GR (1990) Diagnosis of hemorrhagic septicemia. Veterinary diagnostic bacteriology, a manual of laboratory procedures for selected diseases of livestock. Anim Prod Health Rome, FAO, 81
Heddleston KL, Gallagher JE, Rebers PA (1972) Fowl cholera: gel diffusion precipitin test for serotyping Pasteurella multocida from avian species. Avian Dis 925–936.
Harper M, John M, Turni C, Edmunds M, St Michael F, Adler B, Blackall PJ, Cox AD, Boyce JD (2015) Development of a rapid multiplex PCR assay to genotype Pasteurella multocida strains by use of the lipopolysaccharide outer core biosynthesis locus. J Clin Microbiol 53(2):477–485
Shivachandra SB, Yogisharadhya R, Ahuja A, Bhanuprakash V (2012) Expression and purification of recombinant type IV fimbrial subunit protein of Pasteurella multocida serogroup B: 2 in Escherichia coli. Res Vet Sci 93(3):1128–1131
Prajapati A, Yogisharadhya R, Mohanty NN, Mendem SK, Nizamuddin A, Chanda MM, Shivachandra SB (2022) Comparative genome analysis of Pasteurella multocida serogroup B: 2 strains causing haemorrhagic septicaemia (HS) in bovines. Gene 826:146452
Davies RL, MacCorquodale R, Caffrey B (2003) Diversity of avian Pasteurella multocida strains based on capsular PCR typing and variation of the OmpA and OmpH outer membrane proteins. Vet Microbiol 91(2–3):169–182
Verma S, Salwan R, Katoch S, Verma L, Chahota R, Dhar P, Sharma M (2016) The relationship between capsular type and OmpA of Pasteurella multocida is associated with the outcome of disease. Microb Pathog 101:68–75
Hatfaludi T, Al-Hasani K, Boyce JD, Adler B (2010) Outer membrane proteins of Pasteurella multocida. Vet Microbiol 144:1–17
Nielsen DW, Ricker N, Barbieri NL, Allen HK, Nolan LK, Logue CM (2020) Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of extra intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. BMC Res Notes 13(1):1–7
Vougidou C, Sandalakis V, Psaroulaki A, Siarkou V, Petridou E, Ekateriniadou L (2015) Distribution of the ompA-types among ruminant and swine pneumonic strains of Pasteurella multocida exhibiting various cap-locus and toxA patterns. Microbiol Res 174:1–8
Prajapati A, Chanda MM, Yogisharadhya R, Parveen A, Ummer J, Dhayalan A, Mohanty NN, Shivachandra SB (2020) Comparative genetic diversity analysis based on virulence and repetitive genes profiling of circulating Pasteurella multocida isolates from animal hosts. Infect Genet Evol 85:104564
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Gupta S, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Bailey TL, Noble WS (2007) Quantifying similarity between motifs. Genome Biol 8(2):1–9
Bailey TL, Gribskov M (1998) Combining evidence using p-values: application to sequence homology searches. Bioinform 14(1):48–54
Wilkie IW, Harper M, Boyce JD, Adler B (2012) Pasteurella multocida: diseases and pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 361:1–22
Katoch S, Sharma M, Patil RD, Kumar S, Verma S (2014) In vitro and in vivo pathogenicity studies of Pasteurella multocida strains harbouring different ompA. Vet Res Commun 38(3):183–191
Koebnik R, Locher KP, Van Gelder P (2000) Structure and function of bacterial outer membrane proteins: barrels in a nutshell. Mol Microbiol 37(2):239–253
Yogisharadhya R, Mohanty NN, Chacko N, Mondal M, Chanda MM, Shivachandra SB (2019) Sequence and structural analysis of OmpW protein of Pasteurella multocida strains reveal evolutionary conservation among members of Pasteurellaceae along with its homologues. Gene Rep 14:36–44
Touw DS, Patel DR, Van Den Berg B (2010) The crystal structure of OprG from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a potential channel for transport of hydrophobic molecules across the outer membrane. PLoS ONE 5(11):e15016
TeerasakNE LR, Pannoi S, Anuntasomboon P, Thongkamkoon P, Thamchaipenet A (2017) OmpA protein sequence-based typing and virulence-associated gene profiles of Pasteurella multocida isolates associated with bovine hemorrhagic septicemia and porcine pneumonic pasteurellosis in Thailand. BMC Vet Res 13:243
Neary JM, Yi K, Karalus RJ, Murphy TF (2001) Antibodies to loop 6 of the P2 porin protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenza are bactericidal against multiple strains. Infect Immun 69:773–778
Leeanan R, Pannoi S, Anuntasomboon P, Thongkamkoon P, Thamchaipenet A (2017) OmpA protein sequence-based typing and virulence-associated gene profiles of Pasteurella multocida isolates associated with bovine haemorrhagic septicaemia and porcine pneumonic pasteurellosis in Thailand. BMC Vet Res 13(1):1–13
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi, and ICAR-National Institute of Veterinary Epidemiology and Disease Informatics (NIVEDI), Bengaluru, Karnataka, India, for providing the necessary facilities and financial assistance to carry out the research on P. multocida. This study was a part of doctoral research carried out by AP under the institute funded project (Code: IXX12176) on ‘Epidemiology of Haemorrahgic septicaemia (HS) in India’ granted to SBS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significance Statement
Comparatively analyzed seven P. multocida isolates obtained from sheep, buffaloes, rabbit and pigs succumbed to different clinical conditions by ompA gene sequence-based phylogenetic analysis in conjunction with the capsular types which indicated two distinct clusters.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prajapati, A., Yogisharadhya, R., Chanda, M.M. et al. Phylogenetic Analysis Based on OmpA Protein Sequences of Diverse Pasteurella multocida Strains Originated from Different Animal Host Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 94, 439–447 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-023-01543-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-023-01543-7