Abstract
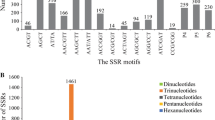
The walnut (Juglans regia) has been extensively characterized for expressed sequence tags (EST) sequences and currently 6169492 ESTs are available in National Center for Biotechnology Information. Although this is a valuable resource for marker development, the redundancy in sequences makes the mining out of unique candidates for designing markers cumbersome. Keeping this in view, the present study was undertaken with the aim to remove the data redundancy in walnut ESTs and then to develop simple sequence repeats (SSRs) markers. The EST sequences were assembled into a non-redundant set of 85 contigs and 1584 singletons (total sequences 1699), indicating 16.55% reduction in data redundancy. These 1699 sequences were then used to mine out SSR motifs. 132 EST-SSRs were detected, with dinucleotide repeats being predominant (70.45%), followed by trinucleotide repeats (27.27%) and very less frequent hexanucleotides (2.27%). These markers were validated by designing primer pairs. 15 of these designed primers were tested on a group of 37 walnut genotypes. Out of which 7 markers gave robust amplification, generating polymorphism. These findings indicate the usefulness of EST-SSRs in genome analysis. This study further emphasizes the importance of assembly of the vast amounts of data submitted in public databases. Our results have generated a set of non redundant walnut ESTs which is of prime importance for development of marker systems without any repetition or overlapping.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pollegioni P, Major A, Bartoli S, Ducci F, Proiett I, Malvolti ME (2008) Application of microsatellite and dominant molecular markers for the discrimination of species and interspecific hybrids in genus Juglans. Acta Hortic 705:191–197
Khan WM, Khan IA, Ahmad H, Ali H, Ghafoor S, Afzal M, Khan FA, Shah M, Afridi SG (2010) Estmation of genetic diversity in walnut. Pak J Bot 42(3):1791–1796
Mitchell SE, Kresovich CA, Jester CA, Hernandez CJ, Szewc MAK (1997) Application of multiplex PCR and fluorescence-based, semi-automated sizing technology for genotyping plant genetic resources. Crop Sci 37:617–624
Phippen WB, Kresovich S, Candelas FG, McFerson JR (1997) Molecular characterization can discriminate and partition variation among gene bank holdings: a case study with phenotypically similar interspecific comparisons. Mol Ecol 5:99–110
Dangl GS, Mendum ML, Prins BH, Walker MA, Meredith CP, Simon CJ (2001) Simple sequence repeat analysis of a clonally propagated species: a tool for managing a grape germplasm collection. Genome 44:432–438
Doyle JJ, Doyle JJ (1987) A rapid DNA isolaton procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Masoudi-Nejad A, Koichiro T, Shuichi K, Yuki M, Masanori S, Masumi I (2006) EGassembler: online bioinformatics service for large-scale processing, clustering and assembling ESTs and genomic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:459–462
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Temnykh S, Clerk G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch SR (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer 3 on the www for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 365–386
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Kaur R, Shilpa VE, Kumar K (2015) Development, characterization and transferability of peach genic SSRs to some Rosaceae species. Adv Res 3(2):165–180
Vaidya E, Kaur R, Kumar K, Sharma N (2015) Exploitation of Malus ESTs for development of SSR markers after in silico analysis. J Appl Bot Food Qual 88:164–169
Zhang R, Zhu AD, Wang XJ, Yu J, Zhang HR, Gao JS (2010) Development of Juglans regia SSR markers by data mining of the EST database. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:646–653
Ahmad NS (2013) Genetic analysis of plant morphology in bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Y. S. Parmar University Of Horticulture and Forestry, Nauni, Solan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest among them.
Additional information
Significance statement The developed 98 EST-SSR markers have a high rate of PCR amplification and can be used in walnut breeding and genetic studies. The use of these markers would reduce the cost and therefore facilitate cultivar identification, genetic distance assessments, gene mapping and possible marker-assisted selection.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shailja, S., Kaur, R., Shilpa, C. et al. Exploitation of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Expressed Sequence Tags for Development of SSR Markers After In Silico Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 89, 267–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-017-0941-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-017-0941-1