Abstract
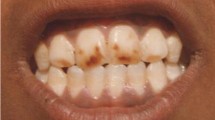
Industrial fluorosis and its effects on serum biochemistry and haemogram were investigated in cattle inhabiting fluoride (F) contaminated areas due to aluminium and fertilizer units situated at Eloor industrial belt of Ernakulam district of Kerala, India. A total of 119 cattle above 3-year-old examined clinically for evidence of osteo-dental and non-skeletal fluorosis. Out of these 55 (46.22 %) animals showed clinical signs of lameness, dental lesions, bony exostoses, reproductive problems and gastro-intestinal disorders. The F level in the biological samples including plasma, urine, milk and bone of the industrial fluorosed cattle were significantly higher (P < 0.01) than the control animals. F content (ppm) in the environmental samples, forage, sludge and drinking water was also high (1.328 ± 0.294 to 251.700 ± 23.113) in the study areas. Biochemical analysis of serum revealed significant decrease (P < 0.01) of serum calcium, albumin, total protein content but increased value of serum alkaline phosphatase and inorganic phosphorus was seen in the affected animals. Total erythrocyte count, haemoglobin and packed cell volume were significantly (P < 0.01) decreased in such animals. Differential leucocyte count showed neutrophilia, lymphocytopenia, monocytophenia and eosinophilia. No significant changes were noticed in the total erythrocyte count, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular haemoglobin and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration. Changes in the serum biochemistry and haemogram could be used for diagnosis of fluorosis in bovines where clinical signs of osteo-dental fluorosis are not evident or poorly discernible.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choubisa SL, Choubisa DK, Joshi SC, Choubisa L (1997) Fluorosis in some tribal villages of Dungarpur district of Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 30(4):223–228
Choubisa SL (2001) Endemic fluorosis in southern Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 34(2):61–70
Choubisa SL (2012) Fluoride in drinking water and its toxicosis in tribals of Rajasthan, India. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B 82(2):325–330. doi:10.1007/s40011-012-0047-8
Choubisa SL (1999) Some observations on endemic fluorosis in domestic animals of southern Rajasthan (India). Vet Res Commun 23(7):457–465
Choubisa SL (2007) Fluoridated ground water and its toxic effects on domestic animals residing in rural areas of Rajasthan (India). Int J Environ Stud 64(2):151–159
Choubisa SL (2013) Fluorotoxicosis in diverse species of domestic animals inhabiting areas with high fluoride in drinking waters of Rajasthan, India. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B 83(3):317–321. doi:10.1007/s40011-012-0138-6
Choubisa SL (2013) Fluoride toxicosis in immature herbivorous domestic animals living in low fluoride water endemic areas of Rajasthan, India: an observational survey. Fluoride 46(1):19–24
Choubisa SL (2012) Status of fluorosis in animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B 82(3):331–339. doi:10.1007/s40011-012-0026-0
Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Mirzaei M, Moghaddam AH (2012) Protective effect of quercetin against sodium fluoride induced oxidative stress in rat’s heart. Food Funct 3(4):437–441
Choubisa SL, Choubisa L, Choubisa DK (2001) Endemic fluorosis in Rajasthan. Indian J Environ Health 43(4):177–189
Swarup D, Dwivedi SK (2002) Environmental pollution and effects of lead and fluoride and animal health. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Patra RC, Dwivedi SK, Bhardwaj B, Swarup D (2000) Industrial fluorosis in cattle and buffalo around Udaipur, India. Sci Total Environ 253:145–150
Swarup D, Dwivedi SK, Ray SK (1998) Fluoride intoxication in bovines due to industrial pollution. Indian J Anim Sci 68(7):605–608
Kumar PS, Aravindakshan CM, Gopakumar N, Chandrasekharan AM (2001) Fluorine toxicity and its effect on cattle in Eloor industrial area. J Vet Pharm Toxicol 1(1&2):73
Lorgue G, Lechnet J, Rivviere A (1996) Clinical veterinary toxicology, 1st edn. Blackwell Science Ltd, London, pp 19–24
Horwitz W (1980) Official methods of analysis of the association of analytical chemists, 13th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC, pp 40–41
Piper CS (1966) Soil and plant analysis. Hans Publishers, Bombay, p 367
Orion Research Analytical Methods Guide (1978) Orion research analytical methods guide, 9th edn. Orion Research, Cambridge
Singer L, Armstrond WD (1968) Determination of fluoride in bone with fluoride electrode. Anal Chem 40:613–614
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1989) Statistical methods, 8th edn. Lowa State University Press, Ames
Choubisa SL, Modasiya V, Bahura CK, Sheikhc Z (2012) Toxicity of fluoride in cattle of the Indian Thar desert, Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 45:371–376
Shupe JL, Miner ML, Greenwood DA, Harris LE, Stoddard GE (1963) The effect of fluorine on dairy cattle. II. Clinical and pathologic effects. Am J Vet Res 24:300–306
Roberts SJ (1971) Veterinary obstetrics and genital diseases, 2nd edn. CBS Publishers and Distributors, Delhi 453
Venkateshwarlu M, Reddy VSC, Sharma GP, Reddy VS, Yadagiri B, Reddy CE (1994) Calcium and phosphorus levels in cyclic and true anestrous buffaloes in fluorosis endemic areas. Indian J Anim Reprod 15:134–137
Udall DH, Keller KP (1952) A report of flurosis cattle in the Columbia River Valley. Cornell Vet 42:159–184
WHO Expert Committee Report on Oral Health Status and Fluoride Use (1994) WHO Technical Report Series 846, WHO, Geneva, pp 1–37
Hoogstratten B, Leone NS, Shupe JL, Greenwood DA, Lieberman J (1965) Effects of fluorides on the haemopoietic system, liver and thyroid gland in cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc 192:26–32
Wheeler SM, Fell LR (1983) Fluorides in cattle nutrition. Nutr Abstr Rev 53:741–766
Vandermissen A, Blaude MN, Bloden S, Ansay M (1993) Urinary fluoride variations in cattle in Wallonie: an indicator of atmospheric pollution. Ann de Med Vet 137:435–442
Kaur R, Sing D, Makhni SS (1978) Long term effects of fluoride administration an experimental study II. Effect on serum proteins. Fluoride 11:25–32
Choubisa SL (2014) Bovine calves as ideal bio-indicators for fluoridated drinking water and endemic osteo-dental fluorosis. Environ Monit Assess 186(7):4493–4498
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. S. Chandra Sekar Nair and Dr. N. Gopa Kumar for their co-operation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senthil Kumar, P., Aravindakshan, C.M. Industrial Fluorosis and Its Effects on Serum Biochemistry and Haemogram in Cattle of Kerala, India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 85, 867–872 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0524-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0524-y