Abstract
Background
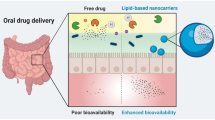
The biopharmaceuticals market has grown rapidly in recent years owing to the low toxicity and high therapeutic efficacy of peptide and protein drugs. However, due to their low stability, biopharmaceuticals have to be administrated via invasive routes, and there is an unmet need for alternative routes. The most familiar and preferred alternative route of administration is the oral route; however, peptide and protein drugs are readily affected by the harsh gastrointestinal environment, resulting in low oral bioavailability. Lipid-based drug delivery systems (LDDSs) for oral administration protect the incorporated drugs and enhance their absorption in the GI tract. However, only lipophilic substances can be stably incorporated in LDDSs, and hydrophilic peptides and proteins require lipidation via, e.g., hydrophobic ion pairing (HIP).
Area covered
This review discusses the issues that hamper the oral administration of peptides and proteins and introduces HIP and LDDSs as strategies to overcome these. The principle of HIP complexation, the parameters to be considered for complexation, and the various counterions used are described. As for LDDSs, the advantages of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDSs), which are suitable for oral peptide and protein delivery, and in vivo study results are described.
Expert opinion
HIP complexes are prepared based on an understanding of the characteristics of drugs and counterions. HIP complexes of peptides and proteins in the oil phase of SEDDSs are protected from the GI environment and therefore, improved absorption is expected. Although their fundamental mechanisms remain unclear and require further study, HIP-incorporated SEDDSs provide a potential strategy for oral peptide and protein delivery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, Samiei M, Kouhi M, Nejati-Koshki K (2013) Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 8(1):1–9
Al-Hilal TA, Alam F, Byun Y (2013) Oral drug delivery systems using chemical conjugates or physical complexes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(6):845–864
Allahyari M, Mohit E (2016) Peptide/protein vaccine delivery system based on PLGA particles. Hum Vaccin Immunother 12(3):806–828
Bashyal S, Seo J-E, Choi YW, Lee S (2021) Bile acid transporter-mediated oral absorption of insulin via hydrophobic ion-pairing approach. J Controll Release. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.060
Beloqui A, Solinís MÁ, Rodríguez-Gascón A, Almeida AJ, Préat V (2016) Nanostructured lipid carriers: promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med 12(1):143–161
Bernkop-Schnürch A, Jalil A (2018) Do drug release studies from SEDDS make any sense? J Control Release 271:55–59
Blasi P (2019) Poly (lactic acid)/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based microparticles: an overview. J Pharm Investig 49(4):337–346
Bonengel S, Jelkmann M, Abdulkarim M, Gumbleton M, Reinstadler V, Oberacher H, Prüfert F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2018) Impact of different hydrophobic ion pairs of octreotide on its oral bioavailability in pigs. J Control Release 273:21–29
Brayden DJ, Maher S (2021) Transient permeation enhancer®(TPE®) technology for oral delivery of octreotide: a technological evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2021.1942838
Brayden DJ, Hill T, Fairlie D, Maher S, Mrsny R (2020) Systemic delivery of peptides by the oral route: formulation and medicinal chemistry approaches. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 157:2–36
Brown TD, Whitehead KA, Mitragotri S (2019) Materials for oral delivery of proteins and peptides. Nat Rev Mater 5:127–148
Bruno BJ, Miller GD, Lim CS (2013) Basics and recent advances in peptide and protein drug delivery. Ther Deliv 4(11):1443–1467
Bulbake U, Doppalapudi S, Kommineni N, Khan W (2017) Liposomal formulations in clinical use: an updated review. Pharmaceutics 9(2):12
Burton PS, Conradi RA, Hilgers AR (1991) (B) Mechanisms of peptide and protein absorption:(2) Transcellular mechanism of peptide and protein absorption: passive aspects. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 7(3):365–385
Calceti P, Salmaso S, Walker G, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2004) Development and in vivo evaluation of an oral insulin–PEG delivery system. Eur J Pharm Sci 22(4):315–323
Celik-Tekeli M, Celebi N, Tekeli MY, Aktas Y (2021) Evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of exendin-4’s new oral self-nanoemulsifying system in rats. Eur J Pharm Sci 158:105644
Chamieh J, Tarrat AD, Doudou C, Jannin V, Demarne F, Cottet H (2019) Peptide release from SEDDS containing hydrophobic ion pair therapeutic peptides measured by Taylor dispersion analysis. Int J Pharm 559:228–234
Chavda VP, Shah D (2017) Self-emulsifying delivery systems: one step ahead in improving solubility of poorly soluble drugs. Nanostructures for cancer therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 653–718
Choi S, Kim SW (2003) Controlled release of insulin from injectable biodegradable triblock copolymer depot in ZDF rats. Pharm Res 20(12):2008–2010
Dai W-G, Dong LC (2007) Characterization of physiochemical and biological properties of an insulin/lauryl sulfate complex formed by hydrophobic ion pairing. Int J Pharm 336(1):58–66
Das S, Ng WK, Tan RB (2012) Are nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) better than solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): development, characterizations and comparative evaluations of clotrimazole-loaded SLNs and NLCs? Eur J Pharm Sci 47(1):139–151
de la Cruz-Moreno MP, Montejo C, Aguilar-Ros A, Dewe W, Beck B, Stappaerts J, Tack J, Augustijns P (2017) Exploring drug solubility in fasted human intestinal fluid aspirates: impact of inter-individual variability, sampling site and dilution. Int J Pharm 528(1–2):471–484
Dumont C, Bourgeois S, Fessi H, Jannin V (2018) Lipid-based nanosuspensions for oral delivery of peptides, a critical review. Int J Pharm 541(1–2):117–135
Dumont C, Bourgeois S, Fessi H, Dugas P-Y, Jannin V (2019) In-vitro evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles: ability to encapsulate, release and ensure effective protection of peptides in the gastrointestinal tract. Int J Pharm 565:409–418
Dumont C, Beloqui A, Miolane C, Bourgeois S, Préat V, Fessi H, Jannin V (2020) Solid lipid nanocarriers diffuse effectively through mucus and enter intestinal cells–but where is my peptide? Int J Pharm 586:119581
Eleraky NE, Swarnakar NK, Mohamed DF, Attia MA, Pauletti GM (2020) Permeation-enhancing nanoparticle formulation to enable oral absorption of enoxaparin. AAPS PharmSciTech 21(3):88
Evaluate (2020) Evaluate pharma world preview 2020, outlook to 2026. https://www.evaluate.com/thought-leadership/pharma/evaluatepharma-world-preview-2020-outlook-2026. Accessed 16 Mar 2021
Fallingborg J (1999) Intraluminal pH of the human gastrointestinal tract. Dan Med Bull 46(3):183
Fan T, Chen C, Guo H, Xu J, Zhang J, Zhu X, Yang Y, Zhou Z, Li L, Huang Y (2014) Design and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles modified with peptide ligand for oral delivery of protein drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 88(2):518–528
Fosgerau K, Hoffmann T (2015) Peptide therapeutics: current status and future directions. Drug Discov Today 20(1):122–128
Friedl H, Dünnhaupt S, Hintzen F, Waldner C, Parikh S, Pearson JP, Wilcox MD, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2013) Development and evaluation of a novel mucus diffusion test system approved by self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci 102(12):4406–4413
Gallarate M, Battaglia L, Peira E, Trotta M (2011) Peptide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared through coacervation technique. Int J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/132435
Gamboa JM, Leong KW (2013) In vitro and in vivo models for the study of oral delivery of nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(6):800–810
Gradauer K, Barthelmes J, Vonach C, Almer G, Mangge H, Teubl B, Roblegg E, Dünnhaupt S, Fröhlich E, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2013) Liposomes coated with thiolated chitosan enhance oral peptide delivery to rats. J Control Release 172(3):872–878
Grant RL, Yao C, Gabaldon D, Acosta D (1992) Evaluation of surfactant cytotoxicity potential by primary cultures of ocular tissues: I. Characterization of rabbit corneal epithelial cells and initial injury and delayed toxicity studies. Toxicology 76(2):153–176
Greenfield NJ (2006) Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc 1(6):2876–2890
Griesser J, Hetényi G, Moser M, Demarne F, Jannin V, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Hydrophobic ion pairing: key to highly payloaded self-emulsifying peptide drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm 520(1–2):267–274
Griesser J, Hetényi G, Kadas H, Demarne F, Jannin V, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2018) Self-emulsifying peptide drug delivery systems: how to make them highly mucus permeating. Int J Pharm 538(1–2):159–166
Grimsley GR, Scholtz JM, Pace CN (2009) A summary of the measured pK values of the ionizable groups in folded proteins. Protein Sci 18(1):247–251
Gupta V, Hwang BH, Doshi N, Mitragotri S (2013) A permeation enhancer for increasing transport of therapeutic macromolecules across the intestine. J Control Release 172(2):541–549
Harde H, Das M, Jain S (2011) Solid lipid nanoparticles: an oral bioavailability enhancer vehicle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 8(11):1407–1424
Hauptstein S, Prüfert F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2015) Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems as novel approach for pDNA drug delivery. Int J Pharm 487(1–2):25–31
Hauss DJ (2007) Oral lipid-based formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59(7):667–676
Hauss DJ, Fogal SE, Ficorilli JV, Price CA, Roy T, Jayaraj AA, Keirns JJ (1998) Lipid-based delivery systems for improving the bioavailability and lymphatic transport of a poorly water-soluble LTB4 inhibitor. J Pharm Sci 87(2):164–169
Heade J, Maher S, Bleiel SB, Brayden DJ (2018) Labrasol® and salts of medium-chain fatty acids can be combined in low concentrations to increase the permeability of a macromolecule marker across isolated rat intestinal mucosae. J Pharm Sci 107(6):1648–1655
Hegg P-O (1979) Precipitation of egg white proteins below their isoelectric points by sodium dodecyl sulphate and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct 579(1):73–87
Hetényi G, Griesser J, Moser M, Demarne F, Jannin V, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Comparison of the protective effect of self-emulsifying peptide drug delivery systems towards intestinal proteases and glutathione. Int J Pharm 523(1):357–365
Hintzen F, Perera G, Hauptstein S, Müller C, Laffleur F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2014) In vivo evaluation of an oral self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) for leuprorelin. Int J Pharm 472(1–2):20–26
Ijaz M, Bonengel S, Zupančič O, Yaqoob M, Hartl M, Hussain S, Huck CW, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2016) Development of oral self nano-emulsifying delivery system (s) of lanreotide with improved stability against presystemic thiol-disulfide exchange reactions. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13(7):923–929
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L (2006) Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomed 1(3):297
Ismail R, Phan TNQ, Laffleur F, Csoka I, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2020) Hydrophobic ion pairing of a GLP-1 analogue for incorporating into lipid nanocarriers designed for oral delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.04.025
Jackson M, Mantsch HH (1995) The use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy in the determination of protein structure. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 30(2):95–120
Karamanidou T, Karidi K, Bourganis V, Kontonikola K, Kammona O, Kiparissides C (2015) Effective incorporation of insulin in mucus permeating self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 97:223–229
Karamanidou T, Bourganis V, Kammona O, Kiparissides C (2016) Lipid-based nanocarriers for the oral administration of biopharmaceutics. Nanomedicine 11(22):3009–3032
Kim H-J, Yoon KA, Hahn M, Park E-S, Chi S-C (2000) Preparation and in vitro evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems containing idebenone. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 26(5):523–529
Kohli K, Chopra S, Dhar D, Arora S, Khar RK (2010) Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: an approach to enhance oral bioavailability. Drug Discov Today 15(21–22):958–965
Kollipara S, Gandhi RK (2014) Pharmacokinetic aspects and in vitro–in vivo correlation potential for lipid-based formulations. Acta Pharm Sin B 4(5):333–349
Kozuch DJ, Ristroph K, Prud’homme RK, Debenedetti PG (2020) Insights into hydrophobic ion pairing from molecular simulation and experiment. ACS Nano 14(5):6097–6106
Kurpiers M, Wolf JD, Spleis H, Steinbring C, Jörgensen AM, Matuszczak B, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2020) Lysine-based biodegradable surfactants: increasing the lipophilicity of insulin by hydrophobic ion paring. J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2020.07.024
Lam HT, Le N-MN, Phan TNQ, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2021) Mucolytic self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) containing a hydrophobic ion-pair of proteinase. Eur J Pharm Sci 162:105658
Lau JL, Dunn MK (2018) Therapeutic peptides: historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorg Med Chem 26(10):2700–2707
Leichner C, Menzel C, Laffleur F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Development and in vitro characterization of a papain loaded mucolytic self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Int J Pharm 530(1–2):346–353
Leonaviciute G, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2015) Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems in oral (poly) peptide drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 12(11):1703–1716
Leonaviciute G, Zupančič O, Prüfert F, Rohrer J, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2016) Impact of lipases on the protective effect of SEDDS for incorporated peptide drugs towards intestinal peptidases. Int J Pharm 508(1–2):102–108
Leonaviciute G, Adamovic NT, Lam HT, Rohrer J, Partenhauser A, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): proof-of-concept how to make them mucoadhesive. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 112:51–57
Li X, Chen D, Le C, Zhu C, Gan Y, Hovgaard L, Yang M (2011) Novel mucus-penetrating liposomes as a potential oral drug delivery system: preparation, in vitro characterization, and enhanced cellular uptake. Int J Nanomed 6:3151
Li P, Nielsen HM, Müllertz A (2012) Oral delivery of peptides and proteins using lipid-based drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 9(10):1289–1304
Li P, Nielsen HM, Fano M, Müllertz A (2013) Preparation and characterization of insulin–surfactant complexes for loading into lipid-based drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci 102(8):2689–2698
Li P, Tan A, Prestidge CA, Nielsen HM, Müllertz A (2014) Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for oral insulin delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluations of enteric coating and drug loading. Int J Pharm 477(1–2):390–398
Li M, Kaminskas LM, Marasini N (2021) Recent advances in nano/microparticle-based oral vaccines. J Pharm Investig. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00537-9
Lipka E, Crison J, Amidon GL (1996) Transmembrane transport of peptide type compounds: prospects for oral delivery. J Control Release 39(2–3):121–129
Liu J, Werner U, Funke M, Besenius M, Saaby L, Fanø M, Mu H, Müllertz A (2019a) SEDDS for intestinal absorption of insulin: Application of Caco-2 and Caco-2/HT29 co-culture monolayers and intra-jejunal instillation in rats. Int J Pharm 560:377–384
Liu J, Xu Y, Liu Z, Ren H, Meng Z, Liu K, Liu Z, Yong J, Wang Y, Li X (2019b) A modified hydrophobic ion-pairing complex strategy for long-term peptide delivery with high drug encapsulation and reduced burst release from PLGA microspheres. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 144:217–229
Loo RO, Dales N, Andrews P (1994) Surfactant effects on protein structure examined by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Protein Sci 3(11):1975–1983
Lu HD, Rummaneethorn P, Ristroph KD, Prud’homme RK (2018) Hydrophobic ion pairing of peptide antibiotics for processing into controlled release nanocarrier formulations. Mol Pharm 15(1):216–225
Ma E-L, Ma H, Liu Z, Zheng C-X, Duan M-X (2006) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel oral insulin formulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27(10):1382–1388
Maher S, Geoghegan C, Brayden DJ (2021) Intestinal permeation enhancers to improve oral bioavailability of macromolecules: reasons for low efficacy in humans. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 18(2):273–300
Mahmood A, Prüfert F, Efiana NA, Ashraf MI, Hermann M, Hussain S, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2016) Cell-penetrating self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for oral gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13(11):1503–1512
Mahmood A, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2018) SEDDS: a game changing approach for the oral administration of hydrophilic macromolecular drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 142:91–101
McCartney F, Jannin V, Chevrier S, Boulghobra H, Hristov DR, Ritter N, Miolane C, Chavant Y, Demarne F, Brayden DJ (2019) Labrasol® is an efficacious intestinal permeation enhancer across rat intestine: ex vivo and in vivo rat studies. J Control Release 310:115–126
McMurtry CM, Riddell RP, Taddio A, Racine N, Asmundson GJ, Noel M, Chambers CT, Shah V (2015) Far from" just a poke": common painful needle procedures and the development of needle fear. Clin J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000272
Menzel C, Holzeisen T, Laffleur F, Zaichik S, Abdulkarim M, Gumbleton M, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2018) In vivo evaluation of an oral self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for exenatide. J Control Release 277:165–172
Meyer JD, Manning MC (1998) Hydrophobic ion pairing: altering the solubility properties of biomolecules. Pharm Res 15(2):188–193
Meyer JD, Matsuura JE, Ruth JA, Shefter E, Patel ST, Bausch J, McGonigle E, Manning MC (1994) Selective precipitation of interleukin-4 using hydrophobic ion pairing: a method for improved analysis of proteins formulated with large excesses of human serum albumin. Pharm Res 11(10):1492–1495
Meyer JD, Matsuura JE, Kendrick BS, Evans ES, Evans GJ, Manning MC (1995) Solution behavior of α-chymotrypsin dissolved in nonpolar organic solvents via hydrophobic ion pairing. Biopolym: Orig Res Biomol 35(5):451–456
Meyer JD, Kendrick BS, Matsuura JE, Ruth JA, Bryan PN, Manning MC (1996) Generation of soluble and active subtilisin and α-chymotrypsin in organic solvents via hydrophobic ion pairing. Int J Pept Protein Res 47(3):177–181
Mitragotri S, Burke PA, Langer R (2014) Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(9):655–672
Mohanraj VJ, Barnes TJ, Prestidge CA (2010) Silica nanoparticle coated liposomes: a new type of hybrid nanocapsule for proteins. Int J Pharm 392(1–2):285–293
Moriguchi I, Hirono S, Liu Q, Nakagome I, Matsushita Y (1992) Simple method of calculating octanol/water partition coefficient. Chem Pharm Bull 40(1):127–130
Morishita M, Peppas NA (2006) Is the oral route possible for peptide and protein drug delivery? Drug Discov Today 11(19–20):905–910
Moroz E, Matoori S, Leroux J-C (2016) Oral delivery of macromolecular drugs: where we are after almost 100 years of attempts. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 101:108–121
Müller RH, Radtke M, Wissing SA (2002) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:S131–S155
Nazir I, Asim MH, Dizdarević A, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2019) Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: impact of stability of hydrophobic ion pairs on drug release. Int J Pharm 561:197–205
Neves AR, Queiroz JF, Lima SAC, Figueiredo F, Fernandes R, Reis S (2016) Cellular uptake and transcytosis of lipid-based nanoparticles across the intestinal barrier: relevance for oral drug delivery. J Colloid Interface Sci 463:258–265
Nigade PM, Patil SL, Tiwari SS (2012) Self emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS): a review. Int J Pharm Biol Sci 2(2):42–52
Nikolakakis I, Partheniadis I (2017) Self-emulsifying granules and pellets: composition and formation mechanisms for instant or controlled release. Pharmaceutics 9(4):50
Novák P, Havlíček V (2016) Protein extraction and precipitation. Proteomic profiling and analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 51–62
Park M-J, Balakrishnan P, Yang S-G (2013) Polymeric nanocapsules with SEDDS oil-core for the controlled and enhanced oral absorption of cyclosporine. Int J Pharm 441(1–2):757–764
Patel A, Gaudana R, Mitra AK (2014) A novel approach for antibody nanocarriers development through hydrophobic ion-pairing complexation. J Microencapsul 31(6):542–550
Phan TNQ, Le-Vinh B, Efiana NA, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2019a) Oral self-emulsifying delivery systems for systemic administration of therapeutic proteins: science fiction? J Drug Target 27(9):1017–1024
Phan TNQ, Shahzadi I, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2019b) Hydrophobic ion-pairs and lipid-based nanocarrier systems: the perfect match for delivery of BCS class 3 drugs. J Control Release 304:146–155
Phan TNQ, Ismail R, Le-Vinh B, Zaichik S, Laffleur F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2020) The effect of counterions in hydrophobic ion pairs on oral bioavailability of exenatide. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00637
Pinkerton NM, Grandeury A, Fisch A, Brozio JR, Riebesehl BU, Prud’homme RK (2013) Formation of stable nanocarriers by in situ ion pairing during block-copolymer-directed rapid precipitation. Mol Pharm 10(1):319–328
Plaza-Oliver M, Santander-Ortega MJ, Lozano MV (2021) Current approaches in lipid-based nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00908-7
Pouton CW (1997) Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 25(1):47–58
Qiao J, Ji D, Sun S, Zhang G, Liu X, Sun B, Guan Q (2018) Oral bioavailability and lymphatic transport of pueraria flavone-loaded self-emulsifying drug-delivery systems containing sodium taurocholate in rats. Pharmaceutics 10(3):147
Rao SVR, Shao J (2008) Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs: I. Formul Dev Int J Pharm 362(1–2):2–9
Ristroph KD, Prud’homme RK (2019) Hydrophobic ion pairing: encapsulating small molecules, peptides, and proteins into nanocarriers. Nanoscale Adv 1(11):4207–4237
Ristroph K, Salim M, Clulow AJ, Boyd BJ, Prud’homme RK (2021) Chemistry and geometry of counterions used in hydrophobic ion pairing control internal liquid crystal phase behavior and thereby drug release. Mol Pharm 18(4):1666–1676
Rubas W, Cromwell M, Shahrokh Z, Villagran J, Nguyen T-N, Wellton M, Nguyen T-H, Mrsny R (1996) Flux measurements across Caco-2 monolayers may predict transport in human large intestinal tissue. J Pharm Sci 85(2):165–169
Sakloetsakun D, Dünnhaupt S, Barthelmes J, Perera G, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2013) Combining two technologies: multifunctional polymers and self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral insulin administration. Int J Biol Macromol 61:363–372
Samiei N, Shafaati A, Zarghi A, Moghimi H, Foroutan S (2014) Enhancement and in vitro evaluation of amifostine permeation through artificial membrane (PAMPA) via ion pairing approach and mechanistic selection of its optimal counter ion. Eur J Pharm Sci 51:218–223
Samiei N, Foroutan SM, Razipour F, Zarghi A, Shafaati A (2017) An investigation into the ability of alendronate ion pairs to increase oral absorption. Int J Pharm 527(1–2):184–190
Sarmento B, Martins S, Ferreira D, Souto EB (2007) Oral insulin delivery by means of solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 2(4):743
Sha X, Yan G, Wu Y, Li J, Fang X (2005) Effect of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems containing Labrasol on tight junctions in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci 24(5):477–486
Shahzadi I, Dizdarević A, Efiana NA, Matuszczak B, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2018) Trypsin decorated self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): key to enhanced mucus permeation. J Colloid Interface Sci 531:253–260
Shahzadi I, Asim MH, Dizdarević A, Wolf JD, Kurpiers M, Matuszczak B, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2019) Arginine-based cationic surfactants: Biodegradable auxiliary agents for the formation of hydrophobic ion pairs with hydrophilic macromolecular drugs. J Colloid Interface Sci 552:287–294
Shahzadi I, Nazir I, Phan TNQ, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2020) About the impact of superassociation of hydrophobic ion pairs on membrane permeability. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 151:1–8
Sharma G, Wilson K, Van der Walle C, Sattar N, Petrie J, Kumar MR (2010) Microemulsions for oral delivery of insulin: design, development and evaluation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 76(2):159–169
Shrestha N, Bouttefeux O, Vanvarenberg K, Lundquist P, Cunarro J, Tovar S, Khodus G, Andersson E, Keita ÅV, Dieguez CG (2018) The stimulation of GLP-1 secretion and delivery of GLP-1 agonists via nanostructured lipid carriers. Nanoscale 10(2):603–613
Sim T, Lim C, Hoang NH, Joo H, Lee JW, Kim D-W, Lee ES, Youn YS, Kim JO, Oh KT (2016) Nanomedicines for oral administration based on diverse nanoplatform. J Pharm Investig 46(4):351–362
Sun S, Cui F, Kawashima Y, Liang N, Zhang L, Shi K, Yu Y (2008) A novel insulin-sodium oleate complex for oral administration: preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 18(4):239–243
Sun S, Liang N, Kawashima Y, Xia D, Cui F (2011) Hydrophobic ion pairing of an insulin-sodium deoxycholate complex for oral delivery of insulin. Int J Nanomed 6:3049
Swaminathan J, Ehrhardt C (2012) Liposomal delivery of proteins and peptides. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 9(12):1489–1503
Tanford C (1963) The interpretation of hydrogen ion titration curves of proteins. Advances in protein chemistry, vol 17. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 69–165
Toorisaka E, Hashida M, Kamiya N, Ono H, Kokazu Y, Goto M (2005) An enteric-coated dry emulsion formulation for oral insulin delivery. J Control Release 107(1):91–96
Torres-Lugo M, Peppas NA (1999) Molecular design and in vitro studies of novel pH-sensitive hydrogels for the oral delivery of calcitonin. Macromolecules 32(20):6646–6651
Vaishya RD, Mandal A, Gokulgandhi M, Patel S, Mitra AK (2015) Reversible hydrophobic ion-paring complex strategy to minimize acylation of octreotide during long-term delivery from PLGA microparticles. Int J Pharm 489(1–2):237–245
Wang J, Wu D, Shen W-C (2002) Structure-activity relationship of reversibly lipidized peptides: studies of fatty acid-desmopressin conjugates. Pharm Res 19(5):609–614
Wibel R, Friedl JD, Zaichik S, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2020) Hydrophobic ion pairing (HIP) of (poly) peptide drugs: benefits and drawbacks of different preparation methods. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.04.004
Xie L, Wehling RL, Ciftci O, Zhang Y (2017) Formation of complexes between tannic acid with bovine serum albumin, egg ovalbumin and bovine beta-lactoglobulin. Food Res Int 102:195–202
Yang L, Cui F, Shi K, Cun D, Wang R (2009) Design of high payload PLGA nanoparticles containing melittin/sodium dodecyl sulfate complex by the hydrophobic ion-pairing technique. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 35(8):959–968
Yoo HS, Choi HK, Park TG (2001) Protein–fatty acid complex for enhanced loading and stability within biodegradable nanoparticles. J Pharm Sci 90(2):194–201
Yuan H, Jiang S-P, Du Y-Z, Miao J, Zhang X-G, Hu F-Q (2009) Strategic approaches for improving entrapment of hydrophilic peptide drugs by lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 70(2):248–253
Zhang N, Ping Q, Huang G, Xu W, Cheng Y, Han X (2006) Lectin-modified solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers for oral administration of insulin. Int J Pharm 327(1–2):153–159
Zhou XH (1994) Overcoming enzymatic and absorption barriers to non-parenterally administered protein and peptide drugs. J Control Release 29(3):239–252
Zupančič O, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Lipophilic peptide character–what oral barriers fear the most. J Control Release 255:242–257
Zupančič O, Grieβinger JA, Rohrer J, de Sousa IP, Danninger L, Partenhauser A, Sündermann NE, Laffleur F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2016a) Development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for oral enoxaparin administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 109:113–121
Zupančič O, Leonaviciute G, Lam HT, Partenhauser A, Podričnik S, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2016b) Development and in vitro evaluation of an oral SEDDS for desmopressin. Drug Deliv 23(6):2074–2083
Zupančič O, Rohrer J, Thanh Lam H, Grießinger JA, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2017) Development and in vitro characterization of self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for oral opioid peptide delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 43(10):1694–1702
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Sciences, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2016R1D1A1B01015369), and the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1A6A1A03011325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (G. Noh, T. Keum, S. Bashyal, J.-E. Seo, L. Shrawani, J. H. Kim, and S. Lee) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noh, G., Keum, T., Bashyal, S. et al. Recent progress in hydrophobic ion-pairing and lipid-based drug delivery systems for enhanced oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Investig. 52, 75–93 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00549-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00549-5