Abstract
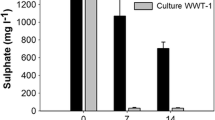
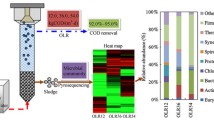
Microbial shift and predominance profile of a mesophilic upflow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) reactor treating lignocellulose-rich wastewater [i.e., paper industry effluent with 665 mg SO4−2/L and COD/SO4 = 2–8] was investigated using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology in accordance with a mass balance determination on sulfur and organic compounds. Since paper producing industries generate wastewaters with high organic and sulfate concentrations, coexistence of microbial-especially of sulfur-reducing and methane-producing-communities and their interactions have been also searched out considering the impact on biogas yield (~ 0.16 L CH4/g CODremoved) and sulfate reduction (up to 82%). Analysis of the microbiomes by Illumina sequencing showed that Desulfovibrio spp. were the detected sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) coexisting with methane-producing archaea (MPA). Despite no evident inhibition of relatively high sulfate on biogas generation, predominance of Euryarchaeota decreased by nearly half and taxonomic classification revealed a shift of microbial population from aceticlastic (Methanosaeta) to hydrogenotrophic (Methanolinea) methanogens as operation continued probably due to their general tendency to dominate in stressed condition. Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria (involving major SRB genera in the delta subclass) phyla had the highest ratios of relative abundances demonstrating the crucial role of their coexistence during the removal of the pollutants in lignocellulosic wastewaters.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated in this study are original. Raw sequence data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed I, Zia MA, Afzal H et al (2021) Socio-economic and environmental impacts of biomass valorisation: a strategic drive for sustainable bioeconomy. Sustainability 13:4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084200
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American water works association/water environment federation, Washington D.C., USA
Bajpai P (2017) Anaerobic technology in pulp and paper industry. in: part of the springerbriefs in applied sciences and technology book series, Singapore. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4130-3
Bakraoui M, Karouach F, Ouhammou B et al (2020) Biogas production from recycled paper mill wastewater by UASB digester: Optimal and mesophilic conditions. Biotechnol Rep 25:e00402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00402
Brahmacharimayum B, Mohanty MP, Ghosh PK (2019) Theoretical and practical aspects of biological sulfate reduction: a review. Global NEST J 21:222–244. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002577
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:4044–4064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057
Chen JL, Ortiz R, Steele TWJ et al (2014) Toxicants inhibiting anaerobic digestion: a review. Biotechnol Adv 32:1523–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.005
Chinnaraj S, Venkoba Rao G (2006) Implementation of an UASB anaerobic digester at bagasse based pulp and paper industry. Biomass Bioenerg 30:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2005.10.007
Chou H-H, Huang J-S, Chen W-G et al (2008) Competitive reaction kinetics of sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic bacteria in anaerobic filters. Bioresour Technol 99:8061–8067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.044
Dar SA, Kleerebezem R, Stams AJ et al (2008) Competition and coexistence of sulfate-reducing bacteria, acetogens and methanogens in a lab-scale anaerobic bioreactor as affected by changing substrate to sulfate ratio. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1391-8
De Vrieze J, Pinto AJ, Sloan WT et al (2018) The active microbial community more accurately reflects the anaerobic digestion process: 16S rRNA (gene) sequencing as a predictive tool. Microbiome 6:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0449-9
Dubey RS, Upadhyay SN (2004) Microbiologically influenced corrosion. In: Pandey A (ed) Concise encyclopedia of bioresource technology. Food Products Press
Ekstrand E-M (2019) Anaerobic digestion in the kraft pulp and paper industry: challenges and possibilities for implementation, Edition 1:1, Department of thematic studies – environmental change, faculty of arts and sciences, Printed by: LiU-Tryck, Linköping.
Enitan AM, Adeyemo J, Swalaha FM et al (2017) Optimization of biogas generation using anaerobic digestion models and computational intelligence approaches. Rev Chem Eng 33:309–335. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2015-0057
Faisal S, Thakur N, Jalalah M et al (2021) Facilitated lignocellulosic biomass digestibility in anaerobic digestion for biomethane production: microbial communities’ structure and interactions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 96:1798–1817. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6747
Fakhri H, Arabaci DN, Unlu ID et al (2021) Addition of Trichocladium canadense to an anaerobic membrane bioreactor: Evaluation of the microbial composition and reactor performance. Biofouling 37:711–723. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2021.1949002
Gao M, Guo B, Zhang L et al (2020) Biomethane recovery from source-diverted household blackwater: Impacts from feed sulfate. Process Saf Environ Prot 136:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.01.010
Guo J, Peng Y, Ni B-J et al (2015) Dissecting microbial community structure and methane producing pathways of a full-scale anaerobic reactor digesting activated sludge from wastewater treatment by metagenomic sequencing. Microb Cell Fact 14:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0218-4
Han C, Kotsyurbenko O, Chertkov O et al (2012) Complete genome sequence of the sulfur compounds oxidizing chemolithoautotroph Sulfuricurvum kujiense type strain (YK-1(T)). Stand Genomic Sci 6:94–103. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.2456004
Jing Z, Hu Y, Niu Q et al (2013) UASB performance and electron competition between methane producing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria in treating sulfate-rich wastewater containing ethanol and acetate. Bioresour Technol 137:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.137
Kamali M, Gameiro T, Costa MEV et al (2016) Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastes – an overview of the developments and improvement opportunities. Chem Eng J 298:162–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.119
Khanal SK, Huang J-C (2005) Effect of high influent sulfate on anaerobic wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 77:3037–3046. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25045923. Assessed 02 September 2021
Kushkevych I, Vítězová M, Vítěz T et al (2017) Production of biogas: relationship between methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms. Open Life Sci 12:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2017-0009
Lackner N, Wagner AO, Illmer P (2020) Effect of sulfate addition on carbon flow and microbial community composition during thermophilic digestion of cellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:4605–4615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10546-7
Liu X, Li M, Castelle CJ et al (2018) Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 6:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0488-2
Lopes SIC, Capela MI, Lens PNL (2010) Sulfate reduction during the acidification of sucrose at pH 5 under thermophilic (55°C) conditions. II: Effect of sulfide and COD/SO42- ratio. Bioresour Technol 101:4278–4284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.010
Luo G, Fotidis IA, Angelidaki I (2016) Comparative analysis of taxonomic, functional, and metabolic patterns of microbiomes from 14 full-scale biogas reactors by metagenomic sequencing and radioisotopic analysis. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0465-6
Maillacheruvu KY, Parkin GF (1996) Kinetics of growth, substrate utilization and sulfide toxicity for propionate, acetate, and hydrogen utilizers in anaerobic systems. Water Environ Res 68:1099–1106. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25044818
Mei X, Wang Z, Miao Y et al (2018) A pilot-scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor under short hydraulic retention time for municipal wastewater treatment: performance and microbial community identification. J Water Reuse Desal 8:58–67. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2017.164
Meyer T, Edwards EA (2014) Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastewater and sludge. Water Res 65:321–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.022
Moestedt J, Påledal SN, Schnürer A (2013) The effect of substrate and operational parameters on the abundance of sulphate-reducing bacteria in industrial anaerobic biogas digesters. Bioresour Technol 132:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.043
Moon C, Singh R, Veeravalli SS et al (2015) Effect of COD:SO42- ratio, HRT and linoleic acid concentration on mesophilic sulfate reduction: Reactor performance and microbial population dynamics. Water 7:2275–2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7052275
O’Flaherty V, Collins G, Mahony T (2010) Anaerobic digestion of agricultural residues. In: Mitchell R, Gu J-D (eds) Environmental microbiology. Wiley
Omil F, Lens P, Visser A et al (1998) Long-term competition between sulfate reducing and methanogenic bacteria in UASB reactors treating volatile fatty acids. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:676–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19980320)57:6%3c676::AID-BIT5%3e3.3.CO;2-8
O’Reilly C, Colleran E (2006) Effect of influent COD/SO42- ratios on mesophilic anaerobic reactor biomass populations: Physico-chemical and microbiological properties. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00066.x
Ozturk I (2007) Anaerobic treatment and its applications. Turkish Water Foundation Press
Pabbathi NPP, Velidandi A, Tavarna T et al (2021) Role of metagenomics in prospecting novel endoglucanases, accentuating functional metagenomics approach in second-generation biofuel production: a review. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01186-y
Patel K, Patel N, Vaghamshi N et al (2021) Trends and strategies in the effluent treatment of pulp and paper industries: a review highlighting reactor options. Curr Res Microb Sci 2:100077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100077
Paulo LM, Stams AJM, Sousa DZ (2015) Methanogens, sulphate and heavy metals: a complex system. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:537–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9387-1
Pekyavas G, Yangin-Gomec C (2019) Response of Anammox bacteria to elevated nitrogen and organic matter in pre-digested chicken waste at a long-term operated UASB reactor initially seeded by methanogenic granules. Bioresour Technol Rep 7:100222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100222
Pokój T, Klimiuk E, Bułkowska K et al (2020) Effect of individual components of lignocellulosic biomass on methane production and methanogen community structure. Waste Biomass Valor 11:1421–1433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0434-3
Sarti A, Zaiat M (2011) Anaerobic treatment of sulfate-rich wastewater in an anaerobic sequential batch reactor (AnSBR) using butanol as the carbon source. J Environ Manage 92:1537–1541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.01.009
Sato Y, Hamai T, Hori T et al (2019) Desulfosporosinus spp. were the most predominant sulfate reducing bacteria in pilot- and laboratory-scale passive bioreactors for acid mine drainage treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:7783–7793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10063-2
Senés-Guerrero C, Colón-Contreras FA, Reynoso-Lobo JF et al (2019) Biogas-producing microbial composition of an anaerobic digester and associated bovine residues. MicrobiologyOpen 8:e00854. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.854
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewaters. Archae Press
van Lier JB, van der Zee FP, Frijters CTMJ et al (2015) Celebrating 40 years anaerobic sludge bed reactors for industrial wastewater treatment. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:681–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9375-5
Warren YA, Citron DM, Merriam CV et al (2005) Biochemical differentiation and comparison of Desulfovibrio species and other phenotypically similar genera. J Clin Microbiol 43:4041–4045. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.43.8.4041-4045.2005
Westerholm M, Schnürer A (2019) Microbial responses to different operating practices for biogas production systems, In: Jeyakumar RB (ed). Anaerobic Digestion. IntechOpen. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/65614
Yang SL, Tang YQ, Gou M et al (2015) Effect of sulfate addition on methane production and sulfate reduction in a mesophilic acetate-fed anaerobic reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3269–3277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6235-0
Yangin-Gomec C, Yarsur E, Ozcan OY (2021) Energy recovery during anaerobic treatment of lignocellulosic wastewater with dynamic modeling and simulation results. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01757-7
Yarsur E (2021) Biogas recovery during anaerobic treatment of lignocellulose-rich pollutants with high sulfate content: an investigation via innovative applications. Dissertation, Istanbul Technical University
Funding
This work was supported by Department of Scientific Research Projects of ITU (Grant Number MYL-2019-42365).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Cigdem Yangin-Gomec and Eda Yarsur. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Cigdem Yangin-Gomec and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Josef Trögl.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yangin-Gomec, C., Yarsur, E. Coexistence of sulfate-reducing and methane-producing populations in upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor treating lignocellulosic effluent with material balance. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 6609–6622 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04719-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04719-2