Abstract
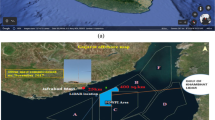
The accuracy in analysis of wind speed is very critical to assess wind potential at any site. Wind power potential has been estimated using statistical distribution methods at numerous places around the world. The main aim of this article is to analyse wind potential and to compare between metaheuristic optimization algorithms and numerical approaches utilising the wind data at various places in India measured from masts and remote sensing technologies. The Weibull distribution fitness test is calculated using real-time wind data from various locations. The optimal Weibull parameters are estimated using numerical methods such as empirical method of Justus, maximum likelihood method, graphical method, modified maximum likelihood method and Wind Atlas Analysis and Application Program (WAsP). Furthermore, to assess Weibull distribution function for different sites (onshore, nearshore and offshore) in India, the social spider optimization is compared to particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. To examine the accuracy of various approaches, further goodness-of-fit method is estimated. The mean power density is maximum for offshore, followed by nearshore and onshore site with 452.32 W/m2, 431.53 W/m2, and 283 W/m2, respectively, at 120 m height. WAsP approach outperforms other numerical approaches used in this work. When compared to the genetic algorithm, the social spider optimization and particle swarm optimization were shown to be more efficient. The suggested method is more accurate than the numerical approaches utilised for wind potential assessment, according to the results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- EMJ:
-
Empirical method of Justas
- MLM:
-
Maximum likelihood method
- GM:
-
Graphical method
- MMLM:
-
Modified maximum likelihood method
- EPFM:
-
Energy pattern factor method
- WAsP:
-
Wind atlas analysis and application program
- GAO:
-
Genetic algorithm optimization
- EEM:
-
Energy equivalent method
- GWOA:
-
Grey wolf optimizer algorithm
- MOM:
-
Method of moment
- ABCOA:
-
Artificial bee colony optimization algorithm
- r1, r2:
-
Random numbers
- Xl ,best, i :
-
Best population of l variable and i iteration
- MVO:
-
Multiverse optimization
- X′l , n , i :
-
Population update for l variable, n population, and i iteration
- BOA:
-
Bat optimization algorithm
- MFO:
-
Moth flame optimizations
- LSE:
-
Least square estimation
- SSO:
-
Social spider optimization
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- ESA:
-
Evolutionary statistical approach
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- MBE:
-
Mean bas error
- NRMSE:
-
Normalized root mean square error
- LiDAR:
-
Light detection and ranging
- SODAR:
-
Sound detection and ranging
- Xl ,worst, i :
-
Worst population of l variable and i iteration
- c1, c2:
-
Acceleration coefficients
- Xl , n , i :
-
Existing population
References
Ahmed AS (2018) Wind resource assessment and economics of electric generation at four locations in Sinai Peninsula. Egypt J Clean Prod 183:1170–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.182
Alberto L-C, Cuevas E, Fausto F, Zaldivar D, Pérez M (2018) Social spider optimization algorithm: modifications, applications, and perspectives. Hindawi Math Probl Eng 2018:29. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6843923
Ashtine M, Bello R, Higuchi K (2016) Assessment of wind energy potential over Ontario and Great Lakes using the NARR data: 1980–2012. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 56:272–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.019
Bahrami A, Teimourian A, Okoye CO, Shiri H (2019) Technical and economic analysis of wind energy potential in Uzbekistan. J Clean Prod 223:801–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.140
Boopathi K, Kushwaha R, Balaraman K, Bastin J, Kanagavel P, Reddy Prasad DM (2021) Assessment of wind power potential in the coastal region of Tamil Nadu, India. Ocean Eng 219:108356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108356
Carneiro TC, Melo SP, Carvalho PCM, Plínio A, de S. Braga. (2016) Particle swarm optimization method for estimation of Weibull parameters: a case study for the Brazilian northeast region. Renew Energy 86:751–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.08.060
Chandel SS, Ramasamy P, Murthy KSR (2014) Wind power potential assessment of 12 locations in western Himalayan region of India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:530–545
Chang TP (2011) Wind energy assessment incorporating particle swarm optimization method. Energy Convers Manag 52(3):1630–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.10.024
Chaurasiya PK, Ahmed S, Warudkar V (2018) Comparative analysis of Weibull parameters for wind data measured from met-mast and remote sensing techniques. Renew Energy 115:1153–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.08.014
Chaurasiya PK, Warudkar V, Ahmed S (2019) Wind energy development and policy in India: a review. Energy Strategy Rev 24:342–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.04.010
Clerc M (2006) Particle swarm optimization. ISTE, London
Cuevas E, Cienfuegos M, Zaldívar D, Perez-Cisneros M (2013) A swarm optimization algorithm inspired in the behavior of the social-Spider. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.05.041
Dollaor J, Chiewchanwattana S, Sunat K, Muangkote N (2016) The application of social-spider optimization for parameter improvement in the Lukasiewicz structure. In: International conference on knowledge and smart technology KST Thailand, pp 27–32
Dong Y, Wang J, Jiang H, Shi X (2013) Intelligent optimized wind resource assessment and wind turbines selection in Huitengxile of Inner Mongolia, China. Appl Energy 109:239–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.04.028
Enevoldsen P, Valentine SV (2016) Do onshore and offshore wind farm development patterns differ? Energy Sustain Dev 35:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2016.10.002
Farivar F, Elin M, Nima S (2017) Wind energy potential and economic assessment of four locations in Sistan and Balouchestan province in Iran. Renew Energy 109:646–667
Gao X, Yang H, Lu L (2014) Study on offshore wind power potential and wind farm optimization in Hong Kong. Appl Energy 130:519–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.02.070
Gautam A, Warudkar V, Bhagoria J (2022) A comparative analysis of wind characteristics for distinct terrains of India. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 52(PA):102089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102089
Gungor A, Gokcek M, Uçar H, Arabacı E, Akyüz A (2020) Analysis of wind energy potential and Weibull parameter estimation methods: a case study from Turkey. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(2):1011–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02566-2
Guo X, Zhang X, Du S, Li C, Siu YL, Rong Y et al (2020) The impact of onshore wind power projects on ecological corridors and landscape connectivity in Shanxi, China. J Clean Prod 254:120075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120075
GWEC (2019) Gobal wind energy report 2019. https://Gwec.Net/Wp-Content/Uploads/2020/08/Annual-Wind-Report_2019_digital_final_2r.Pdf Accessed 9 Mar 2021
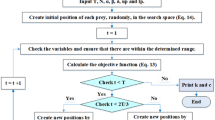
Haiyan J, JianzhouWang JW, Geng W (2017) Comparison of numerical methods and metaheuristic optimization algorithms for estimating parameters for wind energy potential assessment in low wind regions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:1199–1217
Hatim OM, Elkhachine H, Benabdelouahab F, Khamlichi A (2020) Comparative study of five different methods of adjustment by the Weibull model to determine the most accurate method of analyzing annual variations of wind energy in Tetouan-Morocco. Procedia Eng 46:698–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.03.099
Holland JH. “An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence.” MIT Press 1975.
Kang D, Ko K, Huh J (2018) Comparative study of different methods for estimating Weibull parameters: a case study on Jeju Island, South Korea. Energies 11:356. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020356
Kasra M (2016) Assessing different parameters estimation methods of Weibull distribution to compute wind power density. Energy Convers Manage 108:322–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.11.015
Katinas V, Marˇciukaitis M, Geceviˇcius G, Markeviˇcius A (2017) Statistical analysis of wind characteristics based on Weibull methods for estimation of power generation in Lithuania. Renew Energy 113:190–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.05.071
Khorramnia R, Akbarizadeh M-R, Jahromi MK, Khorrami SK, Kavusifard F (2015) A new unscented transform for considering wind turbine uncertainty in ED problem based on SSO algorithm. J Intell Fuzzy Syst Appl Eng Technol 29(4):1479–1491
Kumar MBH, Balasubramaniyan S, Padmanaban S, Holm-Nielsen JB (2019) Wind energy potential assessment by Weibull parameter estimation using multiverse optimization method: a case study of Tirumala region in India. Energies 12(1):2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112158
Li Y, Wu XP, Li QS, Tee KF (2018) Assessment of onshore wind energy potential under different geographical climate conditions in China. Energy 152:498–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.172
Li Yi, Huang X, Tee KF, Li Q, Xiao Peng W (2020) Comparative study of onshore and offshore wind characteristics and wind energy potentials: a case study for Southeast Coastal region of China. Sustain Energy Technol Assess. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100711
Liu F-J, Chen P-H, Kuo S-S, Su D-C, Chang T-P, Yu Y-H et al (2011) Wind characterization analysis incorporating genetic algorithm: a case study in Taiwan Strait. Energy 36(5):2611–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.02.001
Moazzami M, Moradi J, Shahinzadeh H, Gharehpetian GB, Mogoei H (2018) Optimal economic operation of microgrids integrating wind farms and advanced rail energy storage system. Int J Renew Energy Res 8:1155–1164
Mostafaeipour A, Sadeghi S, Jahangiri M, Nematollahi O, Rezaeian SA (2020) Investigation of accurate location planning for wind farm establishment: a case study. J Eng Des Technol 18(4):821–45. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-08-2019-0208
Natarajan N, Vasudevan M, Rehman S (2021) Evaluation of suitability of wind speed probability distribution models: a case study from Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14315-5
NIWE (2019) India’s wind potential atlas at 120 m Agl. NIWE Website. In, 77. https://niwe.res.in/assets/Docu/India’s_Wind_Potential_Atlas_at_120m_agl.pdf. Accessed 30 Nov 2021
Patidar H, Shende V, Baredar P, Soni A (2022) Comparative study of offshore wind energy potential assessment using different Weibull parameters estimation methods. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19109-x
Petrović A, Đurišić Z (2021) Genetic algorithm based optimized model for the selection of wind turbine for any site-specific wind conditions. Energy 2(236):121476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121476
Pishgar-Komleh SH, Keyhani A, Sefeedpari P (2015) Wind speed and power density analysis based on Weibull and Rayleigh distributions (a case study: Firouzkooh county of Iran). Renew Sustain Energy Rev 42:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.028
Rueda-Bayona JG, Guzmán A, Eras JJC, Silva-Casarín R, Bastidas-Arteaga E, Horrillo-Caraballo J (2019) Renewables energies in Colombia and the opportunity for the offshore wind technology. J Clean Prod 220:529–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.174
Saeed MA, Ahmed Z, Yang J, Zhang W (2020) An optimal approach of wind power assessment using Chebyshev metric for determining the Weibull distribution parameters. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 37:100612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2019.100612
Shafiqur R, Narayanan N, Mangottiri V, Alhems L (2019) Assessment of wind energy potential across varying topographical features of Tamil Nadu, India. Energy Explor Exploit. https://doi.org/10.1177/0144598719875276
Shaltout ML, Mostafa MA, Metwalli SM (2021) Enhancement of wind energy resources assessment using multi-objective genetic algorithm: a case study at Gabal Al-Zayt wind farm in Egypt. Int J Green Energy 18(14):322–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2021.1904949
Sharma PK, Warudkar V, Ahmed S (2019) Application of lidar and measure correlate predict method in offshore wind resource assessments. J Clean Prod 215:534–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.267
Sharma PK, Warudkar V, Ahmed S (2020) Application of a new method to develop a CFD model to analyze wind characteristics for a complex terrain. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 37:100580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2019.100580
Shoaib M, Rehman SU, Siddiqui I, Rehman S, Khan S, Ibrahim Z (2020) Comparison of Weibull and Gaussian mixture models for wind speed data analysis. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 11(1):10–16. https://doi.org/10.46660/ojs.v11i1.405
Tiam Kapen P, Jeutho Gouajio M, Yemélé D (2020) Analysis and efficient comparison of ten numerical methods in estimating Weibull parameters for wind energy potential: application to the city of Bafoussam, Cameroon. Renew Energy 159:1188–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.185
Zhou Y, Zhao R, Luo Q, Wen C (2017) Sensor deployment scheme based on social spider optimization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Neural Process Lett 48:71–94
Acknowledgements
The researchers are thankful to the assistance offered by the faculties of NIT Bhopal for providing the support to facilitate this study.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP contributed to conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft, review and editing, software. VS helped in visualization, software, validation, resources. PB contributed to review, supervision. AS contributed to review and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Shahid Hussain.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patidar, H., Shende, V., Baredar, P. et al. Comparative analysis of wind potential and characteristics using metaheuristic optimization algorithms at different places in India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 13819–13834 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04678-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04678-8