Abstract
India achieved the goal of a circular economy towards regenerative, value-creating development and growth for long-term prosperity. But at the same time, due to the recent unprecedented urbanization and industrialization, wastes and pollutants generated from these activities are enormous, which causes water, air and soil pollution. For example, brine sludge is one of the large quantities of waste from the chlor-alkali industry. This paper reviews different environmental impacts of waste minimization of brine sludge from the chlor-alkali industry with current treatment and utilization technologies. Various materials developed like paver blocks, bricks, non-toxic radiation shielding materials, cement-free materials, etc., using brine sludge as resource material, which can be helpful for broad application spectrum. Conventional softening, Ion exchange, and membrane technologies are available to remove solute from brine sludge. For the salt content in brine sludge, resins' uses are most economical and immensely practical. Due to high-quality recovery with power generation and environmentally friendly brine treatment, membrane-based technologies like membrane distillation, forward osmosis, and electrodialysis can be preferred. In the future perspective, recent membrane technologies like pressure-retarded osmosis and reverse electrodialysis are used to generate power from the salinity gradient between waste brine and freshwater.
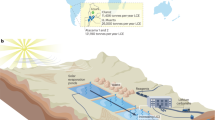
Graphical abstract






(Copyright © 2014 under the Creative Commons Attribution License)











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alahmad M (2010) Prediction of performance of seawater reverse osmosis units. Desalination 261(1–2):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.018)
Alkali Manufacturers Association of India (AMAI) (2020). http://ama-india.org/industry-data/caustic-soda/
Amritphale SS, Verma S, Khan MA,Anshul A, Das S (2015) A novel process for chemically designed multi-functional advanced materials, using geopolymerized brine sludge, Patent No. 0185NF20152015
Amritphale SS, Verma S, Das S (2016) Utilization of brine sludge and fly ash together, for making, non-toxic, homogeneous, radiation shielding glass by an energy-efficient process. Patent No. 0059NF2016
Amritphale SS, Anshul A, Verma S, Khan MA, Das S (2018a) Advanced non-toxic radiation shielding materials from tailored brine sludge and a process for the preparation thereof. US Patent 10,214,453
Amritphale SS, Verma S, Das S (2018b) Functionalized brine sludge material and a process for the preparation thereof. US Patent 9,890,081 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 13
Amritphale SS, Verma S, Khan MA, Das S (2018c) Chemically designed multifunctional advanced material fromgeopolymerized brine sludge and process for preparation
Ariono D, Purwasasmita M, Wenten IG (2016) Brine effluents: characteristics, environmental impacts, and their handling. J Eng Technol Sci 48(4):367–387. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2016.48.4.1)
Basu S, Mukhopadhyay SK, Gangopadhyay A, Dastidar SG (2013) Characteristic change of effluent from a chlor-alkali industry of india due to process modification. Int Res J Environ Sci 2(2):44–47
Busto Y, Cabrera X, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2011) Potential of thermal treatment for decontamination of mercury containing wastes from chlor-alkali industry. J Hazard Mater 186:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.099
Campbell JL, Lorenz A, Witkin KL, Hays T, Loidl J, Cohen-Fix O (2006) Yeast nuclear envelope subdomains with distinct abilities to resist membrane expansion. Mol Biol Cell 17(4):1768–1778. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0839
Cartier S, Theoleyre MA, Decloux M (1997) Treatment of sugar decolorizing resin regeneration waste using nanofiltration. Desalination 113:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0011-9164(97)00110-0
CPCB (2000) Environmental standards for ambient air, automobiles, fuel industries and noise, Central Pollution Control Board, MoEF
CPCB (2013) Report on 'review of environmental standards of caustic soda industry (membrane cell) and COINDS on Caustic Soda. https://doi.org/10.12999/awwa.b501.13
Davenport DM, Deshmukh A, Werber JR, Elimelech M (2018) High-pressure reverse osmosis for energy-efficient hypersaline brine desalination: current status, design considerations, and research needs. Environ Sci Technol Lett 5(8):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00274
Drioli E, Curcio E, Di Profio G (2005) State of the art and recent progresses in membrane ontactors. Chem Eng Res Des 83:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1205/cherd.04203
Fouad MMK, Zaki AMA, Monem NA et al (2002) Industrial wastewater treatment inchlor-alkali plant case study. J Eng Appl Sci 49(3):597–611
Garg M, Pundir A (2014) Utilization of brine sludge in nonstructural building components: a sustainable approach. J Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/389316
Giwa A, Dufour V, Al Marzooqi F, Al Kaabi M, Hasan SW (2017) Brine management methods: recent innovations and current status. Desalination 407:1–23
Glasser FP (1997) Fundamental aspects of cement solidification and stabilisation. J Hazard Mater 52(2–3):151–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3894(96)01805-5
Grazaino D, Hyrn JN, Daniels EJ (1996a) The economics of salt cake recycling. Metals and Material Society, CA, Argonne National Laboratory
Graziano D, Hryn JN, Daniels EJ (1996b) The economics of salt cake recycling. In: Hale W (ed) Light metals. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Warrendale, p 1255
Gupta A, Rajurkar P (2001) Waste minimization in a chlor-alkali plant. Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai
Hashem FS, Metwally MK, Mostafa S, Mohammad AL (2019) Utilization of brine sludge resulted from chlorine alkali industry. https://doi.org/10.17628/ecb.2019.8.132-136
Kamsonlian S, Suresh S, Ramanaiah V, Majumder CB, Chand S, Kumar A (2012a) Bio-sorptivebehaviour of mango leaf powder and rice husk for arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:565–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0054-6
Kamsonlian S, Suresh S, Majumder CB, Chand S (2012b) Biosorption of arsenic from contaminated water onto solid psidiumguajava leaf surface: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, and desorption study. Bioremed J 16(2):97–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2012.665962
Kumar R, Ahmad R (2011) Biosorption of hazardous crystal violet dye from aqueous solution onto treated ginger waste. Desalination 265:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.040
Lee KL, Baker RW, Lonsdale HK (1981) Membranes for power generation by pressure-retarded osmosis. J Membr Sci 8:141–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0376-7388(00)82088-8
Lien LA (1999) Spent brine reclamation. US Patent 6,004,464
Lima AT, Ottosen LM, Ribeiro AB (2012) Assessing fly ash treatment: remediation and stabilization of heavy metals. J Environ Manag 95:110–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.009
Low M (2019) Report on Innovations in automation and advanced chemical softening for R.O. systems maximize membrane brine concentration and recovery in water technology
Manual (2010) TechnicalE.I.A.Guidance Manual for common effluent treatment plants, MoEF
Manual (2017) Good practices manual, green house gases emission reduction on chlor-alkali sector. This manual is the property of Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India
Masilela E, Lerotholi L, Seodigeng T, Rotto H (2018) Dissolution kinetics of industrial brine sludge waste. J Air Waste Manag 66:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2017.1280097
Mcadam EJ, Pawlett M, Judd SJ (2010) Fate and impact of organics in an immersed membrane bioreactor applied to brine denitrification and ion exchange regeneration. Water Res 44:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.048
Mishra BB (1986) Role of blue-green algae in bio-degradation of chlor-alkali industrial wastes (soil) with special reference to rice cultivation. Ph.D. Thesis, Berhampur University, Orissa, India
Mishra SR, Misra BN (1984) Studies on the solid waste extracts from a chlor-alkali industry. I. Morphological behaviour of rice seedlings grown in waste extracts. Environ Pollut 35:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-1471(84)90127-2
Mishra BB, Nanda DR, Misra BN (1985a) Reclamation with blue-green algae: changes in nucleic acids, proteins and nitrogen content of algae exposed to solid waste of a chlor-alkali factory. Environ Pollut 37:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-1471(85)90001-7
Mishra BB, Nanda DR, Misra BN (1985b) Reclamation with blue-green algae: mercury uptake by algae cultured in solid waste of a chlor-alkali factory and its effect on growth and pigmentation. J Environ Biol 6(4):223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-1471(85)90001-7
Misra KA, Sahu A, Kanwar S, Sarma D, Panigrahi AK (2013) Mercury pollution in and around a chlor-alkali industry: a review. Int Q J Environ Sci Spec Issue, iii: 349–366
Nanda DR, Mishra BB, Misra BN (1985) Toxic effects of solid waste extract of a chlor-alkali factory on pigment concentration of a crop plant. PhaseolousAureusRoxb J Environ Biol 7(2):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-1471(85)90001-7
Panda KK, Lenka M, Panda BB (1989) Allium micronucleus assay to assess bioavailability, bioconcentration and genotoxicity of mercury from solid waste deposits of a chlor-alkali plant and antagonism of L. Cysteine Sci Total Environ 79:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(89)90050-8
Pingle V, Saraswat S (2018) Experimental study of use of brine sludge in cement concrete. Int J Sci Res Dev 6(9):30–33
Post JW, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2008) Energy recovery from controlled mixing salt and fresh water with a reverse electrodialysis system. Environ Sci Technol 42:5785–5790. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8004317
Pramanik BK, Shu L, Jegatheesan V (2017) A review of the management and treatment of brine solutions. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 3:625
Purwasasmita M, Nabu EBP, Khoiruddin A, Wenten IG (2015) Non-dispersive chemical deacidificationof crude palm oil in hollow fiber membrane contactor. J Eng Technol Sci 47:426–446. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2015.47.4.6
Ramon GZ, Feinberg BJ, Hoek EMV (2011) Membrane-based production of salinity-gradient power. Energy Environ Sci 4:4423–4434. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee01913a
Ravizky A, Nadav N (2007) Salt production by the evaporation of SWRO brine in eilat: a success story. Desalination 205:374–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.03.559
Rengifo F, Garbo B, Quach A, Ela WP, Sáez AE (2005) Stabilization of arsenic-bearing iron hydroxide solid wastes in polymeric matrices
Report (1986) Final report on Process engineering and economic evaluations of diaphragm and membrane chloride cell technologies, Agronne National Laboratory, IL, USA, DoE
Reza K, Teo YS, Iman J, Saeid M, Davood MH, Abadi F (2020) An overview on the treatment and management of the desalination brine solution Open access peer-reviewed chapter April 27th 2020; Published: June 12th 2020
Sahu A (1987) Toxicological effects of a pesticide on a blue-green alga: III. Effect of PMA. On a blue-green alga, Westiellopsisprolifica, Janet and its ecological implications. Ph.D. Thesis, Berhampur University, India
Sahu A, Shaw BP, Panigrahi AK, Misra BN (1987) Effect of phenyl mercuric acetate on the atpase activity of Westiellopsisprolifia, Janet. Microbios Lett 33:45–50
Shukla PM, Patel JA, Joshi DS, Joshi PP (2015) Recovery of barium sulphate from brine sludge. Int Waste Res Technol Center IJEP 35(4):312–315
Suresh S, Sundaramoorthy S (2015) Green chemical engineering: an introduction to catalysis, kinetics and chemical processes. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group (ISBN: 9781466558830), pp 1–530
Tamim Y (2005) Environmental issues of desalination. J Contemp Water Res Educ 132:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1936-704X.2005.mp132001003
Turek M (2003) Seawater desalination and salt production in a hybrid membrane-thermal process. Desalination 153:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0011-9164(02)01123-2
Unnikrishnan H, Rakesh A (2014) Single stage brine filtration system inchlor-alkali industries. Int J Eng Trends Technol 9:5. https://doi.org/10.14445/22315381/ijett-v9p249
Veldhuis MJW, Fuhr F, Boon JP, Ten Hallers-Tjabbers CC (2006) Treatment of ballast water; how to test a system with a modular concept. Environ Technol 27:909–992. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332708618701
Verma S, Amritphale SS, Khan MA, Anshul A, Das S (2017a) Development of advanced geopolymerized brine sludge based composites. J Polym Environ 5(4):999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0877-1
Verma S, Amritphale SS, Das S (2017b) Development of functionalized nanoprecursor gel useful for making flexible and moldable radiation shielding material. J Mater Eng Perform J Mater Eng Perform 26(3):1018–1025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2532-y
Verma S, Sanghi S, Amritphale SS (2018a) Development of advanced, non-toxic, X-ray radiation shielding glass possessing barium, boron substituted kornerupine crystallites in the glassy matrix. J Inorgan Organomet Polym Mater 28:35–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0697-3
Verma S, Amritphale SS, Khan MA (2018b) Utilization of brine sludge and fly ash waste, as complementary resource for making non toxic geopolymeric material. Iran J Sci Technol 43(1–3):66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-018-0191-3
Verma S, Sanghi SK, Srivastava AK (2019) Development of advanced hybrid, nano-sized, brine sludge impregnated MWCNT composite material useful for broad application spectrum. Appl Innov Res 1:66–73
Verma S, Mili M, Bajpai H, Hashmi SAR, Srivastava AK (2020) Advanced lead free, multi-constituent-based composite materials for shielding against diagnostic X-rays. Plast Rubber Compos. https://doi.org/10.1080/14658011.2020.1831264
Wenten IG, Khoiruddin A, Aryanti PTP, Hakim AN (2016) Scale-up strategies for membrane-based desalination processes: a review. J Membr Sci Res 2:42–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.12.011
Whitescarver OD, Kwan JT, Chan MK, Hoyer DP (1990) Process for using sludge from geothermal brine to make concrete and concrete composition. US Patent 4,900,360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(90)90043-b
Yadav VG, Yadav GD, Patankar SC (2020) The production of fuels and chemicals in the new world: critical analysis of the choice between crude oil and biomass vis-à-vis sustainability and the environment. Clean Technol Environ Policy 22:1757–1774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01945-5
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CSIR (Grant No. MLP 0213) given to SV Authors are also thankful to the Director, CSIR-AMPRI, Bhopal, for providing necessary institutional facilities and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Shahid Hussain.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Suresh, S., Mili, M. et al. Future process options for brine sludge management from the chlor-alkali industry. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 9291–9310 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04433-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04433-z