Abstract
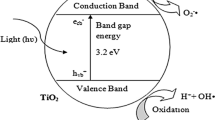
The design and development of visible light photocatalysts for wastewater remediation applications have received considerable attention due to their ability to operate under low energy, renewable and clean. The application of ZnO nanostructures as a photocatalyst in various photodegradation applications has shown to be of continued interest. However, ZnO possessed several setbacks, including their large bandgap, which require high energy for the excitation of the electrons. To overcome these limitations, doping ZnO photocatalysts has been confirmed to enhance their photocatalytic performance by narrowing their large bandgap, thus opening up numerous possibilities. Doped ZnO nanostructures have found extensive use in pollution control applications as visible light photocatalysts. The doping with metal or non-metal elements, metal oxides, and inclusion with other semiconductors to form a hybrid heterojunction photocatalyst are among the strategies employed. This mini review summarizes recent progress in the strategies employed in the preparation of doped ZnO photocatalysts for the degradation of various organic pollutants, including synthetic dye molecules and emerging contaminants. Their application in antibacterial performance is also briefly explained. Additionally, the degradation mechanism of selected pollutants is also discussed. Finally, the advantages of using doped ZnO photocatalyst for pollution remediation are discussed. Considering the issue of water security, this review is timely to address the impending problem that the world is facing. Hopefully, this article can assist readers in gaining a better understanding of doped ZnO photocatalysts.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AOP:
-
Advanced oxidation process
- APS:
-
Ammonium persulfate
- BG:
-
Brilliant green
- CIP:
-
Ciprofloxacin
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- CR:
-
Congo red
- DB38:
-
Direct black 38
- EBT:
-
Eriochrome Black T
- GO:
-
Graphene oxide
- GRL:
-
Maxilon blue
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- MG:
-
Malachite green
- MO:
-
Methyl orange
- OFL:
-
Ofloxacin
- OG:
-
Orange G
- OTC:
-
Oxytetracycline
- PTh:
-
Polythiophene
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RR:
-
Reactive red
- rGO:
-
Reduced graphene oxide
- RhB:
-
Rhodamine B
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- TC:
-
Tetracycline
References
Abideen ZU, Shah AH, Teng F et al (2021) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO microtubes with an efficient photocatalytic activity. Micro Nano Lett 16:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1049/mna2.12024
Aftab S, Shabir T, Shah A et al (2022) Highly efficient visible light active doped ZnO photocatalysts for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with dyes and pathogens of emerging concern. Nanomaterials 12:486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030486
Ahammed KR, Ashaduzzaman M, Paul SC et al (2020) Microwave assisted synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles in a noble approach: utilization for antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. SN Appl Sci 2:955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2762-8
Ahmad I, Akhtar MS, Ahmed E, Ahmad M (2020) Highly efficient visible light driven photocatalytic activity of graphene and CNTs based Mg doped ZnO photocatalysts: a comparative study. Sep Purif Technol 245:116892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116892
Aida MS, Alonizan NH, Hussein MA et al (2021) Facile synthesis and antibacterial activity of bioplastic membrane containing in doped ZnO/cellulose acetate nanocomposite. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02171-2
Alahmadi N, Amin MS, Mohamed RM (2020) Superficial visible-light-responsive Pt@ZnO nanorods photocatalysts for effective remediation of ciprofloxacin in water. J Nanoparticle Res 22:230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04968-7
Al-Ariki S, Yahya NAA, Al-A’nsi SA et al (2021) Synthesis and comparative study on the structural and optical properties of ZnO doped with Ni and Ag nanopowders fabricated by sol gel technique. Sci Rep 11:11948. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91439-1
Alatawi NM, Ben SL, Soltane L et al (2021) Enhanced solar photocatalytic performance of Cu-doped nanosized ZnO. Polyhedron 197:115022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2021.115022
Alhanash AM, Al-Namshah KS, Mohamed SK, Hamdy MS (2019) One-pot synthesis of the visible light sensitive C-doped ZnO@g-C3N4 for high photocatalytic activity through Z-scheme mechanism. Optik (stuttg) 186:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.04.084
Alkaim AF, Alrobayi EM, Algubili AM, Aljeboree AM (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of sonochemical/hydration–dehydration prepared ZnO rod-like architecture nano/microstructures assisted by a biotemplate. Environ Technol 38:2119–2129. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1246615
Al-Namshah KS, Shkir M, Ibrahim FA, Hamdy MS (2022) Auto combustion synthesis and characterization of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles with boosted photocatalytic performance. Phys B Condens Matter 625:413459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.413459
Alshammari AS, Chi L, Chen X et al (2015) Visible-light photocatalysis on C-doped ZnO derived from polymer-assisted pyrolysis. RSC Adv 5:27690–27698. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA17227B
Altıntıg E, Altundag H, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017) Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using magnetic loaded activated carbon as novel adsorbent. Chem Eng Res Des 122:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.03.035
Anku WW, Agorku ES, Oppong SO-B, Karikari AY (2020) MWCNTs attached neodymium doped-ZnO photocatalysts for efficient removal of dyes from wastewater. SN Appl Sci 2:972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2805-1
Arya S, Mahajan P, Mahajan S et al (2021) Review—influence of processing parameters to control morphology and optical properties of sol-gel synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 10:023002. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/abe095
Baruah S, Dutta J (2009) Hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanostructures. Sci Technol Adv Mater 10:013001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/10/1/013001
Bembibre A, Benamara M, Hjiri M et al (2022) Visible-light driven sonophotocatalytic removal of tetracycline using Ca-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 427:132006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132006
Bharti DB, Bharati AV (2017) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using a hydrothermal method and a study its optical activity. Luminescence 32:317–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3180
Borysiewicz MA (2019) ZnO as a functional material, a review. Crystals 9:1–29
Bouarroudj T, Aoudjit L, Djahida L et al (2021) Photodegradation of tartrazine dye favored by natural sunlight on pure and (Ce, Ag) co-doped ZnO catalysts. Water Sci Technol 83:2118–2134. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.106
Chandrappa KG, Venkatesha TV (2012) Electrochemical synthesis and photocatalytic property of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nano-Micro Lett 4:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03353686
Chankaew C, Tapala W, Grudpan K, Rujiwatra A (2019) Microwave synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using longan seeds biowaste and their efficiencies in photocatalytic decolorization of organic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17548–17554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05099-w
Chankhanittha T, Komchoo N, Senasu T et al (2021) Silver decorated ZnO photocatalyst for effective removal of reactive red azo dye and ofloxacin antibiotic under solar light irradiation. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 626:127034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127034
Chaudhary S, Umar A, Bhasin KK, Baskoutas S (2018) Chemical sensing applications of ZnO nanomaterials. Materials (basel) 11:1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020287
Chauhan A, Verma R, Kumari S et al (2020) Photocatalytic dye degradation and antimicrobial activities of Pure and Ag-doped ZnO using Cannabis sativa leaf extract. Sci Rep 10:7881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64419-0
Chen X, Wu Z, Liu D, Gao Z (2017) Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1904-4
Chen X, Xu X, Cui J et al (2020) Visible-light driven degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride and 2,4-dichlorophenol by film-like N-carbon@N-ZnO catalyst with three-dimensional interconnected nanofibrous structure. J Hazard Mater 392:122331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122331
Chidambaram S, Ganesan MK, Sivakumar M et al (2021) Au integrated 2D ZnO heterostructures as robust visible light photocatalysts. Chemosphere 280:130594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130594
Chowdhury FI, Dick C, Meng L et al (2017) Cellulose nanocrystals as host matrix and waveguide materials for recyclable luminescent solar concentrators. RSC Adv 7:32436–32441. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04344A
da Silva E, de Moraes M, Brito W et al (2020) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by the sol-gel protein route: a viable and efficient method for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and ibuprofen. J Braz Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20200050
Djurišić AB, Chen X, Leung YH, Man Ching Ng A (2012) ZnO nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:6526. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm15548f
Elangovan SV, Chandramohan V, Sivakumar N, Senthil TS (2016) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles at different molarity concentrations for photocatalytic applications. Desalin Water Treat 57:9671–9678. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1035340
Faisal M, Harraz FA, Jalalah M et al (2020) Polythiophene doped ZnO nanostructures synthesized by modified sol-gel and oxidative polymerization for efficient photodegradation of methylene blue and gemifloxacin antibiotic. Mater Today Commun 24:101048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101048
Fan L, Zhang H, Gao M et al (2020) Cellulose nanocrystals/silver nanoparticles: in-situ preparation and application in PVA films. Holzforschung 74:523–528. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2018-0251
Ferreira SH, Morais M, Nunes D et al (2021) High UV and sunlight photocatalytic performance of porous ZnO nanostructures synthesized by a facile and fast microwave hydrothermal method. Materials (basel) 14:2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092385
Franco P, Sacco O, De Marco I et al (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of eriochrome black-T Azo dye using Eu-doped ZnO prepared by supercritical antisolvent precipitation route: a preliminary investigation. Top Catal 63:1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01279-y
Gaffuri P, Dedova T, Appert E et al (2022) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of chemically deposited ZnO nanowires using doping and annealing strategies for water remediation. Appl Surf Sci 582:152323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152323
Georgekutty R, Seery MK, Pillai SC (2008) A Highly efficient Ag-ZnO photocatalyst: synthesis, properties, and mechanism. J Phys Chem C 112:13563–13570. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp802729a
Gerbreders V, Krasovska M, Sledevskis E et al (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanostructures with controllable morphology change. CrystEngComm 22:1346–1358. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CE01556F
Gholami M, Jonidi-Jafari A, Farzadkia M et al (2021) Photocatalytic removal of bentazon by copper doped zinc oxide nanorods: reaction pathways and toxicity studies. J Environ Manage 294:112962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112962
Girija Shankar E, Aishwarya M, Khan A et al (2021) Efficient solar light photocatalytic degradation of commercial pharmaceutical drug and dye using rGO-PANI assisted c-ZnO heterojunction nanocomposites. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.206
Goktas A, Modanlı S, Tumbul A, Kilic A (2022) Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO, ZnO:Co, and ZnO/ZnO: Co nano rod-like homojunction thin films: role of crystallite/grain size and microstrain in photocatalytic performance. J Alloys Compd 893:162334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162334
Herrmann J-M (1999) Heterogeneous photocatalysis: fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal Today 53:115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00107-8
Hu Y, Lee T, Chang P, Su P (2015) High power Co3O4/ZnO p–n type piezoelectric transducer. Thin Solid Films 584:112–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2014.12.041
Ibrahim I, Tsubota T, Hassan MA, Andou Y (2021) Surface functionalization of biochar from oil palm empty fruit bunch through hydrothermal process. Processes 9:149. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010149
Jain A, Sagar P, Mehra RM (2006) Band gap widening and narrowing in moderately and heavily doped n-ZnO films. Solid State Electron 50:1420–1424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2006.07.001
Jalili-Jahani N, Rabbani F, Fatehi A, Musavi Haghighi T (2021) Rapid one-pot synthesis of Ag-decorated ZnO nanoflowers for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and product analysis by LC/APCI-MS and direct probe ESI-MS. Adv Powder Technol 32:3075–3089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.06.022
Kabir R, Saifullah MAK, Ahmed AZ et al (2020) Synthesis of N-doped ZnO nanocomposites for sunlight photocatalytic degradation of textile dye pollutants. J Compos Sci 4:49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020049
Karthik KV, Raghu AV, Reddy KR et al (2022) Green synthesis of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles and its application for the photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic pollutants. Chemosphere 287:132081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132081
Khalfallah B, Riahi I, Chaabouni F (2021) Effect of Cu doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin films grown by RF magnetron sputtering: application to solar photocatalysis. Opt Quantum Electron 53:238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-02861-8
Kovács Z, Molnár C, Štangar UL et al (2021) Optimization method of the solvothermal parameters using box-Behnken experimental design—the case study of ZnO structural and catalytic tailoring. Nanomaterials 11:1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051334
Kumaran V, Reshmawhahini VR, Gomathipriya P (2021) Effect of Cu dopant on ZnO photocatalyst in the degradation of navy blue textile dye from synthetic wastewater. Chem Eng Technol 44:942–947. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.202000458
Kumari V, Mittal A, Jindal J et al (2019) S-, N- and C-doped ZnO as semiconductor photocatalysts: a review. Front Mater Sci 13:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-019-0453-4
Lau GE, Che Abdullah CA, Wan Ahmad WAN et al (2020) Eco-friendly photocatalysts for degradation of dyes. Catalysts 10:1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10101129
Lavand AB, Malghe YS (2015) Synthesis, characterization, and visible light photocatalytic activity of nanosized carbon doped zinc oxide. Int J Photochem 2015:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/790153
Leng B, Zhang X, Chen S et al (2021) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic degradation and antibacterial activity by GaN:ZnO solid solution nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Technol 94:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.04.014
Li D, Huang J-F, Cao L-Y et al (2014) Microwave hydrothermal synthesis of K+ doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic properties under visible-light. Mater Lett 118:17–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.12.052
Li H, Zhang L, Lu H et al (2020) Macro-/nanoporous Al-doped ZnO/cellulose composites based on tunable cellulose fiber sizes for enhancing photocatalytic properties. Carbohydr Polym 250:116873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116873
Limón-Rocha I, Guzmán-González CA, Anaya-Esparza LM et al (2022) Effect of the precursor on the synthesis of ZnO and its photocatalytic activity. Inorganics 10:16. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10020016
Lin JY, He XL, Huang SH (2019) Fabrication and field emission characteristics of surface-conduction electron-emission with ZnO nanorods based on planar-gate. AIP Adv. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5113918
Liu B, Zeng HC (2003) Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods in the diameter regime of 50 nm. J Am Chem Soc 125:4430–4431. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0299452
Luo S, Chen R, Xiang L, Wang J (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of (001) facet highly exposed ZnO plates: a new insight into the effect of citrate. Crystals 9:552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9110552
Maeda K, Takata T, Hara M et al (2005) GaN:ZnO solid solution as a photocatalyst for visible-light-driven overall water splitting. J Am Chem Soc 127:8286–8287. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0518777
Majumder S, Chatterjee S, Basnet P, Mukherjee J (2020) ZnO based nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradation of aqueous pharmaceutical waste solutions–a contemporary review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100386
Mallikarjunaswamy C, Lakshmi Ranganatha V, Ramu R et al (2020) Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: application to photodegradation, antibacterial and antioxidant. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:1004–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02612-2
Mezni A, Ben Saber N, Ibrahim MM et al (2020) Pt–ZnO/M (M = Fe Co, Ni or Cu): a new promising hybrid-doped noble metal/semiconductor photocatalysts. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:4627–4636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01588-5
Mirzaeifard Z, Shariatinia Z, Jourshabani M, Rezaei Darvishi SM (2020) ZnO photocatalyst revisited: effective photocatalytic degradation of emerging contaminants using S-doped ZnO nanoparticles under visible light radiation. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:15894–15911. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c03192
Mohammad Redha Z, Abdulla Yusuf H, Burhan S, Ahmed I (2021) Facile synthesis of ZnO nanospheres by co-precipitation method for photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes: optimization via response surface methodology. Int J Energy Environ Eng 12:453–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-020-00380-y
Mohd Adnan MA, Julkapli NM, Abd Hamid SB (2016) Review on ZnO hybrid photocatalyst: impact on photocatalytic activities of water pollutant degradation. Rev Inorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1515/revic-2015-0015
Nadeem MS, Munawar T, Mukhtar F et al (2021) Enhancement in the photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanoparticles by structural variations and energy bandgap tuning through Fe and Co co-doping. Ceram Int 47:11109–11121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.234
Nahar S, Zain M, Kadhum A et al (2017) Advances in photocatalytic CO2 reduction with water: a review. Materials (basel) 10:629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060629
Neena D, Humayun M, Zuo W et al (2020) Hierarchical hetero-architectures of in-situ g-C3N4-coupled Fe-doped ZnO micro-flowers with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activities. Appl Surf Sci 506:145017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145017
Nguyen THA, Le VT, Doan V-D et al (2022) Green synthesis of Nb-doped ZnO nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotic under visible light. Mater Lett 308:131129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131129
Noman MT, Petru M, Militký J et al (2019) One-pot sonochemical synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications modelling and optimization. Materials (basel) 13:14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010014
Noukelag SK, Razanamahandry LC, Ntwampe SKO et al (2021) Industrial dye removal using bio-synthesized Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles environ nanotechnology. Monit Manag 16:100463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100463
Oliveira AG, de Lara Andrade J, Montanha MC et al (2019) Decontamination and disinfection of wastewater by photocatalysis under UV/visible light using nano-catalysts based on Ca-doped ZnO. J Environ Manage 240:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.124
Oliveira AG, de Lara Andrade J, Montanha MC et al (2021) Wastewater treatment using Mg-doped ZnO nano-semiconductors: a study of their potential use in environmental remediation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 407:113078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.113078
Ong CB, Ng LY, Mohammad AW (2018) A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:536–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.020
Ou R, Zeng Z, Ning X et al (2022) Improved photocatalytic performance of N-doped ZnO/graphene/ZnO sandwich composites. Appl Surf Sci 577:151856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151856
Peter CN, Anku WW, Sharma R et al (2019) N-doped ZnO/graphene oxide: a photostable photocatalyst for improved mineralization and photodegradation of organic dye under visible light. Ionics (kiel) 25:327–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2571-x
Qamar MA, Javed M, Shahid S et al (2021) Designing of highly active g-C3N4/Co@ZnO ternary nanocomposites for the disinfection of pathogens and degradation of the organic pollutants from wastewater under visible light. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105534
Qi K, Xing X, Zada A et al (2020) Transition metal doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial performances: experimental and DFT studies. Ceram Int 46:1494–1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.116
Qiu R, Zhang D, Mo Y et al (2008) Photocatalytic activity of polymer-modified ZnO under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 156:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.114
Ramasamy B, Jeyadharmarajan J, Chinnaiyan P (2021) Novel organic assisted Ag-ZnO photocatalyst for atenolol and acetaminophen photocatalytic degradation under visible radiation: performance and reaction mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13532-2
Ramírez AE, Montero-Muñoz M, López LL et al (2021) Significantly enhancement of sunlight photocatalytic performance of ZnO by doping with transition metal oxides. Sci Rep 11:2804. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78568-9
Reis RYN, Lima AEB, Costa MJS et al (2020) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic performance of ZnO films doped with N2 by a facile electrochemical method. Surf Interfac 21:100675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100675
Ribeiro V, Marcelo A, da Silva K et al (2017) New ZnO@Cardanol porphyrin composite nanomaterials with enhanced photocatalytic capability under solar light irradiation. Materials (basel) 10:1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101114
Russo M, Iervolino G, Vaiano V (2021) W-Doped ZnO photocatalyst for the degradation of glyphosate in aqueous solution. Catalysts 11:234. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020234
Sabry RS, Aziz WJ, Rahmah MI (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ag and Fe 2 O 3 co-doped ZnO nanostructure under visible light irradiation. Mater Technol 35:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2019.1681717
Sacco O, Franco P, De Marco I et al (2022) Photocatalytic activity of Eu-doped ZnO prepared by supercritical antisolvent precipitation route: when defects become virtues. J Mater Sci Technol 112:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.09.054
Sahu K, Choudhary S, Singh J et al (2018) Facile wet chemical synthesis of ZnO nanosheets: effects of counter ions on the morphological, structural, optical and photocatalytic properties. Ceram Int 44:23094–23101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.09.116
Saleh TA, Sarı A, Tuzen M (2017a) Effective adsorption of antimony(III) from aqueous solutions by polyamide-graphene composite as a novel adsorbent. Chem Eng J 307:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.070
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017b) Magnetic activated carbon loaded with tungsten oxide nanoparticles for aluminum removal from waters. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2853–2860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.038
Sansenya T, Masri N, Chankhanittha T et al (2022) Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO photocatalyst for detoxification of anionic azo dyes and antibiotic. J Phys Chem Solids 160:110353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110353
Shah NS, Iqbal J, Sayed M et al (2022) Enhanced solar light photocatalytic performance of Fe-ZnO in the presence of H2O2, S2O82−, and HSO5− for degradation of chlorpyrifos from agricultural wastes: toxicities investigation. Chemosphere 287:132331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132331
Shandilya P, Sudhaik A, Raizada P et al (2020) Synthesis of Eu3+−doped ZnO/Bi2O3 heterojunction photocatalyst on graphene oxide sheets for visible light-assisted degradation of 2,4-dimethyl phenol and bacteria killing. Solid State Sci 102:106164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106164
Shanmugam N, Meena A, Suthakaran S (2021) Enhanced solar-light-driven photocatalytic activity of surfactant-assisted Sn4+-doped ZnO. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:6438–6453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05361-3
Shenoy S, Ahmed S, Lo IMC et al (2021) Rapid sonochemical synthesis of copper doped ZnO grafted on graphene as a multi-component hierarchically structured visible-light-driven photocatalyst. Mater Res Bull 140:111290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111290
Sher M, Javed M, Shahid S et al (2021a) The controlled synthesis of g-C 3 N 4 /Cd-doped ZnO nanocomposites as potential photocatalysts for the disinfection and degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. RSC Adv 11:2025–2039. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA08573A
Sher M, Javed M, Shahid S et al (2021b) Designing of highly active g-C3N4/Sn doped ZnO heterostructure as a photocatalyst for the disinfection and degradation of the organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 418:113393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113393
Srinivasan N, Anbuchezhiyan M, Harish S, Ponnusamy S (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of C doped ZnO nanoparticles coupled with BiVO4 and their photocatalytic performance under the visible light irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 494:771–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.093
Srinivasan alias Arunsankar N, Anbuchezhiyan M, Padmaja S (2021) Enhanced photocatalytic mineralization efficiency of anionic element doped ZnO by improving separation of excitons. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:12631–12647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05899-2
Suganya Josephine GA, Jayaprakash K, Meenakshi G et al (2021) Photocatalytically active ZnO flaky nanoflowers for environmental remediation under solar light irradiation: effect of morphology on photocatalytic activity. Bull Mater Sci 44:247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02531-1
Sun L, Shao Q, Zhang Y et al (2020) N self-doped ZnO derived from microwave hydrothermal synthesized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 toward enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Coll Interfac Sci 565:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.107
Suresh S, Karthikeyan S (2016) Optical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of magnetically separable Fe3O4-doped ZnO and pristine ZnO nanospheres. J Iran Chem Soc 13:2049–2057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0922-y
Suresh M, Sivasamy A (2020) Fabrication of graphene nanosheets decorated by nitrogen-doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Methylene Blue dye. J Mol Liq 317:114112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114112
Ta QTH, Namgung G, Noh J-S (2019) Facile synthesis of porous metal-doped ZnO/g-C3N4 composites for highly efficient photocatalysts. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 368:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.09.049
Theerthagiri J, Salla S, Senthil RA et al (2019) A review on ZnO nanostructured materials: energy, environmental and biological applications. Nanotechnology 30:392001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab268a
Toloman D, Popa A, Stan M et al (2021) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of different organic pollutants using Cu doped ZnO-MWCNT nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 866:159010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159010
Tu VA, Tuan VA (2018) A facile and fast solution chemistry synthesis of porous ZnO nanoparticles for high efficiency photodegradation of tartrazine. Vietnam J Chem 56:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/vjch.201800016
Ujjan ZA, Bhatti MA, Shah AA et al (2022) Simultaneous doping of sulfur and chloride ions into ZnO nanorods for improved photocatalytic properties towards degradation of methylene blue. Ceram Int 48:5535–5545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.098
Umar M, Abdul H (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. In: Organic pollutants-monitoring, risk and treatment. InTech
Uribe-López MC, Hidalgo-López MC, López-González R et al (2021) Photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles and the role of the synthesis method on their physical and chemical properties. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 404:112866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112866
Vallejo W, Cantillo A, Díaz-Uribe C (2020a) Methylene blue photodegradation under visible irradiation on Ag-Doped ZnO thin films. Int J Photoenergy 2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1627498
Vallejo W, Cantillo A, Salazar B et al (2020b) Comparative study of ZnO thin films doped with transition metals (Cu and Co) for methylene blue photodegradation under visible irradiation. Catalysts 10:528. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050528
Venkatesh N, Aravindan S, Ramki K et al (2021) Sunlight-driven enhanced photocatalytic activity of bandgap narrowing Sn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:16792–16803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11763-3
Wahab R, Ansari SG, Kim YS et al (2009) The role of pH variation on the growth of zinc oxide nanostructures. Appl Surf Sci 255:4891–4896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.12.037
Wahba MA, Yakout SM, Khaled R (2021) Interface engineered efficient visible light photocatalytic activity of MWCNTs/Co doped ZnO nanocomposites: Morphological, optical, electrical and magnetic properties. Opt Mater (amst) 115:111039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111039
Wang M, Ren F, Zhou J et al (2015) N Doping to ZnO nanorods for photoelectrochemical water splitting under visible light: engineered impurity distribution and terraced band structure. Sci Rep 5:12925. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12925
Wang M, Jin Z, Liu M et al (2017) Nanoplate-assembled hierarchical cake-like ZnO microstructures: solvothermal synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv 7:32528–32535. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03849F
Wang S, Chen Z, Zhao Y et al (2021a) High photocatalytic activity over starfish-like La-doped ZnO/SiO2 photocatalyst for malachite green degradation under visible light. J Rare Earths 39:772–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2020.04.009
Wang Y, Yang C, Liu Y et al (2021b) Solvothermal synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and p-nitrophenol. Water 13:3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223224
Xuan MCT, Tran TN, Botto C et al (2021) Zinc-containing precursor dependence of hydrothermal method for the synthesis of N-doped ZnO photocatalysts. Chem Eng Commun 208:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1694917
Young SJ, Liu YH, Chien JT (2018) Improving field electron emission properties of ZnO nanosheets with Ag nanoparticles adsorbed by photochemical method. ACS Omega 3:8135–8140. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01041
Yusoff N, Ho L-N, Ong S-A et al (2017) Enhanced photodegradation of phenol by ZnO nanoparticles synthesized through sol-gel method. Sains Malaysiana 46:2507–2514. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2017-4612-28
Zawawi RM, Zheng ALT (2020) Zinc oxide/vancomycin-based electrochemical chiral sensor for the recognition of penicillamine enantiomers. Int J Electrochem Sci. https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.04.39
Zhang H, Chen W, Li Y, Song Z (2018) Gas sensing performances of ZnO hierarchical structures for detecting dissolved gases in transformer oil : a mini review. Front Chem 6(508):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00508
Zhang J, Luo K, Zhao K et al (2021a) A synergistic boost of photo-activity of ZnO for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by Ag decoration and Fe doping. Mater Lett 286:129250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129250
Zhang Y, Zhao G, Gan L et al (2021b) S-doped carbon nanosheets supported ZnO with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance for pollutants degradation. J Clean Prod 319:128803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128803
Zhao L, Chen Y, Zhang Z et al (2018) Coplanar-gate ZnO nanowire field emitter arrays with enhanced gate-control performance using a ring-shaped cathode. Sci Rep 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30279-y
Zheng ALT, Andou Y (2021) Detection and remediation of bisphenol A (BPA) using graphene-based materials: mini-review. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03512-x
Zheng ALT, Andou Y, Zawawi RM (2017) Effects of deposition parameters on the electrochemical behaviour of ZnO thin film. J Adv Chem Sci 3:521–524
Zheng ALT, Phromsatit T, Boonyuen S, Andou Y (2020) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles /porphyrin/reduced graphene oxide hydrogel as dye adsorbent for wastewater treatment. FlatChem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flatc.2020.100174
Zheng ALT, Boonyuen S, Li GY et al (2021a) Design of reduced graphene hydrogel with alkylamine surface functionalization through immersion/agitation method and its adsorption mechanism. J Mol Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131008
Zheng ALT, Boonyuen S, Ohno T, Andou Y (2021b) Accessing effects of aliphatic dicarboxylic acid towards the physical and chemical changes in low temperature hydrothermally reduced graphene hydrogel. J Porous Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01072-6
Zheng ALT, Boonyuen S, Ohno T, Andou Y (2021c) Hydrothermally reduced graphene hydrogel intercalated with divalent ions for dye adsorption studies. Processes 9:169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010169
Zheng ALT, Farrag HN, Sabidi S et al (2021) Accessing the anti-microbial activity of cyclic peptide immobilized on reduced graphene oxide. Mater Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021d.130621
Zheng ALT, Sabidi S, Ohno T et al (2022a) Cu2O/TiO2 decorated on cellulose nanofiber/reduced graphene hydrogel for enhanced photocatalytic activity and its antibacterial applications. Chemosphere 286:131731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131731
Zheng ALT, Ohno T, Andou Y (2022b) Recent progress in photocatalytic efficiency of hybrid three-dimensional (3d) graphene architectures for pollution remediation. Top Catal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-022-01610-9
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the assistance of Assoc Prof Dr Supakorn Boonyuen for the advice rendered during the revision stage. The first author would like to thank the Graduate School of Life Science and Systems Engineering, Kyushu Institute of Technology for the post-doctoral fellowship awarded to him.
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ALTZ, CACA and ELTC carried out the literature search and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. YA critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, A.L.T., Abdullah, C.A.C., Chung, E.L.T. et al. Recent progress in visible light-doped ZnO photocatalyst for pollution control. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 5753–5772 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04354-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04354-x