Abstract
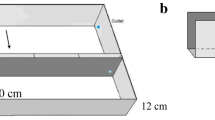
Olive oil milling, widely practiced in Mediterranean countries, including Palestine, yields the so-called olive mill waste water (OMWW) or Zebar (Zibar). The waste contains minerals and organic materials (including phenols and polyphenols) which undergo continuous oxidation and cause environmental hazards if not well managed. This work basically aims at purifying surface waters, intentionally pre-contaminated with OMWW organic contaminants. Fate of other mineral ions present in the contaminated water is also investigated. ZnO nanoparticles, deposited as films onto glass reactor bottom (165 cm2 area), are described as catalyst for photodegradation of the organic contaminants, in a continuous flow reaction mode (gravity fed, typically at flow rate 3.5 mL/min). Two types of ZnO materials, namely commercial ZnO onto glass (C–ZnO/Glass) and synthetic ZnO supported onto clay and deposited on glass (Syn–ZnO/Clay/Glass), have been examined. The Syn–ZnO/Clay/Glass catalyst is slightly more efficient in removing organic contaminants (~ 43%), compared to the C–ZnO/Glass (41%) in 30 h. Different reaction parameters have been investigated, such as waste dilution factor, exposure duration, pH and catalyst recovery and reuse.









Similar content being viewed by others
Referenc es
Akhtar MJ, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahmad J, Alrokayan SA (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomed 7:845–857. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S29129
Al-Abri M, Al-Ghafri B, Bora T, Dobretsov S, Dutta J, Castelletto S, Rosa L, Boretti A (2019) Chlorination disadvantages and alternative routes for biofouling control in reverse osmosis desalination. npj Clean Water 2(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-018-0024-8
Aldaqqa N (2014) ZnO/Montmorillonite nanoparticles as a photodegradation catalyst and adsorbent for tetracycline in water: Synergic effect in supported system. An-Najah National University, Palestine, Faculty of Graduate Studies
Barbera AC, Maucieri C, Cavallaro V, Ioppolo A, Spagna G (2013) Effects of spreading olive mill wastewater on soil properties and crops, a review. Agricultural Water Management, 119, 43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.12.009
Bhatkhande SD, Pangarkar GV, Beenackers AA (2002) Photocatalytic degradation for environmental applications, a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77(1):102–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.532
Duarte K, Justino C, Panteleitchouk T, Zrineh A, Freitas A, Duarte A, Rocha-Santos TAP (2014) Removal of phenolic compounds in olive mill wastewater by silica–alginate–fungi biocomposites. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(3):589–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0268-2
Elhag M, Bahrawi JA, Galal HK, Aldhebiani A, Al-Ghamdi AAM (2017) Stream network pollution by olive oil wastewater risk assessment in Crete. Greece Environ Earth Sci 76(7):278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6592-y
Fakharedine N, El Hajjouji H, Baddi GA, Revel J, Hafidi M (2006) Chemical and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformation during aerobic digestion of olive-mill waste-waters. Process Biochem 41(2):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.06.029
García-Ávila F, Valdiviezo-Gonzales L, Cadme-Galabay M, Gutiérrez-Ortega H, Altamirano-Cárdenas L, Zhindón-Arévalo C, del Pino LF (2020) Considerations on water quality and the use of chlorine in times of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic in the community. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 100049:2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2020.100049
Ghafoor S, Hussain SZ, Waseem S, Arshad SN (2018) Photo-reduction of heavy metal ions and photo-disinfection of pathogenic bacteria under simulated solar light using photosensitized TiO 2 nanofibers. RSC Adv 8(36):20354–20362. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01237G
Grenlie S, Mortenson E (2007) Wastewater treatment and reuse produced from olive oil mills. International project, Birzeit University, Palestine, University of Utah, United States of America,," Unpublished
Hamza A, Fatuase J, Waziri S, Ajayi O (2013) Solar photocatalytic degradation of phenol using nanosized ZnO and-Fe2O3. J Chem Eng Mater Sci 4(7):87–92. https://doi.org/10.5897/JCEMS2013.0162
Hilal HS, Al-Nour GY, Zyoud A, Helal MH, Saadeddin I (2010) Pristine and supported ZnO-based catalysts for phenazopyridine degradation with direct solar light. Solid State Sci 12(4):578–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.01.008
Ibhadon AO, Fitzpatrick P (2013) Heterogeneous photocatalysis: recent advances and applications. Catalysts 3(1):189–218. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010189
Iwissat S (2019) Bioremediation of Olive Mill Wastewater (Zibar) using Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Potential use in Agriculture. Palestine Technical University-Kadoorie, Palestine
Janotti A, Van De Walle GC (2009) Fundamentals of Zinc Oxide as A Semiconductor. Repots Prog Phys 72:126–501. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/72/12/126501
Jeguirim M, Goddard M-L, Tamosiunas A, Berrich-Betouche E, Azzaz AA, Praspaliauskas M, Jellali S (2020) Olive mill wastewater: From a pollutant to green fuels, agricultural water source and bio-fertilizer. Biofuel Produc Renew Energ 149:716–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.079
Lázaro BB (2015) Halloysite and kaolinite: two clay minerals with geological and technological importance. Revista de la Academia de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas, Químicas y Naturales de Zaragoza 70:7–38
Khdair A, Abu-Rumman G (2020) Sustainable environmental management and valorization options for olive mill byproducts in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Region. Processes 8(6):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8060671
Lindner M, Theurich J, Bahnemann D (1997) Photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds: accelerating the process efficiency. Water Sci Technol 35(4):79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00012-7
Liu D-Y, Liu Y-M, Zhang W, Chen X-P, Zou C-Q (2019) Zinc uptake, translocation, and remobilization in winter wheat as affected by soil application of Zn fertilizer. Front Plant Sci 10:426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00426
Ma C, Eggleton RA (1999) Cation exchange capacity of kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner 47(2):174–180. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1999.0470207
Mansour W (2013) Hydrosilyation Reactions Catalyzed by Novel Metalloporphyrin Catalysts Intercalated Inside Clay Nano and Micro Particles. Master Thesis, An-Najah National University, Palestine, 55–65
Mekki A, Dhouib A, Aloui F, Sayadi S (2006) Olive wastewater as an ecological fertiliser, Agronomy for Sustainable Development 26(1). https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2005061
Mohawesh O, Mahmoud M, Janssen M, Lennartz B (2014) Effect of irrigation with olive mill wastewater on soil hydraulic and solute transport properties. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(4):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0285-1
Mousavi SR, Shahsavari M, Rezaei M (2011) A general overview on manganese (Mn) importance for crops production. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5(9):1799–1803
Nassar IM (2019) Continuous flow photodegradation of olive Zebar contaminants with simulated solar light using supported ZnO nanoparticles, MSc Thesis, An-Najah Nationa University, Nablus, Palestine.
Oliveira A, Saggioro ME, Moreria CJ, Ferreria V, Pavesi T (2012) Solar Photochemistry for Environmental Remediation, Advanced Oxidation Process for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Molecular Photochemistry - Various Aspects, INTECH, In book. https://doi.org/10.5772/38444
Orolínovaá Z, Mockovčiaková A, Škvarla J (2010) Sorption of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution by magnetic clay composite. Desalin Water Treat 24(1–3):284–292. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2010.1644
Palominos RA, Mondaca MA, Giraldo A, Peñuela G, Pérez-Moya M, Mansilla HD (2009) Photocatalytic oxidation of the antibiotic tetracycline on TiO2and ZnO suspensions. Catal Today 144(1–2):100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2008.12.031
Parida K, Parija S (2006) Photocatalytic degradation of phenol under solar radiation using microwave irradiated zinc oxide. Sol Energy 80(8):1048–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2005.04.025
Prasse C (2021) Reactivity-directed analysis–a novel approach for the identification of toxic organic electrophiles in drinking water. Environ Sci Process Impacts 23:48–65. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00471E
Radich GJ, Kamat VP (2013) Making graphene holey gold nanoparticle mediated hydroxyl radical attack on reduced graphene oxide. Am Chem Soc 7(6):5546–5557. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn401794k
Rinaldi M, Rana G, Introna M (2003) Olive-mill wastewater spreading in southern Italy: effects on a durum wheat crop. Field Crop Res 84(3):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00097-2
Saenko N (2012) The X-ray diffraction study of three-dimensional disordered network of nanographites: experiment and theory. Phys Procedia 23:102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.01.026
Şahin S, Ciğeroğlu Z, Özdemir O, Elhussein E, Gülmez Ö (2020) Investigation of graphene oxide as highly selective adsorbent in recovery of hydroxytyrosol from olive mill wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:4803–4814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02813-x
Saleiro TG, Holanda FNJ (2012) Processing of Red Ceramic Using a Fast Firing Cycle. Cerâmica 58(347):393–399. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132012000300018
Shoemaker DP, Garland CW, Steinfeld J I. (2018) Experiments in physical chemistry. McGraw-Hill, New Yorkhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.01.026
Souza KVd, Peralta-Zamora P (2001) Spectrophotometric determination of phenol in the presence of congeners by multivariated calibration. An Acad Bras Ciênc 73(4):519–524. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0001-37652001000400005
Vidya C, Hiremath S, Chandraprabha M, Antonyraj ML, Gopal IV, Jain A, Bansal K (2013) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Calotropis gigantea. Int J Curr Eng Technol 1:118–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7254-2
Steurer W, Apfolter A, Koch M, Sarlat T, Søndergård E, Ernst W, Holst B (2007) The structure of the α-quartz (0 0 0 1) surface investigated using helium atom scattering and atomic force microscopy. Elsevier 601(18):4407–4411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2007.04.239
Wahyuni E, Aprilita N, Hatimah H, Wulandari A, Mudasir M (2015) Removal of toxic metal ions in water by photocatalytic method. Am Chem Sci J 5(2):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00383-3
Wei C, Zhang F, Hu Y, Feng C, Wu H (2017) Ozonation in water treatment: the generation, basic properties of ozone and its practical application. Rev Chem Eng 33:49–89. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2016-0008
Wiberg E, Holleman FA (2001) Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier 23:1291–1300
Zak AK, Majid WA, Abrishami ME, Yousefi R (2011) X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci 13(1):251–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.11.024
Zyoud A, Dwikat M, AlShakhshir S, Ateeq S, Shteiwi J, Zubi A, Helal MH, Campet G, ParkKwon H, Kim TW, Kharoof M, Shawahna R, Hilal HS (2016) Natural dye-sensitized ZnO nano-particles as photo-catalysts in complete degradation of E. coli bacteria and their organic content. J Photochem Photobio A: Chem 328:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.05.020
Zyoud A, Jondi W, AlDaqqah N, Asaad S, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Helal MH, Kwon H, Hilal HS (2017) Self-sensitization of tetracycline degradation with simulated solar light catalyzed by ZnO@ montmorillonite. Solid State Sci 74:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2017.09.009
Zyoud A, Jondi W, Mansour W, Khan MM, Hilal HS (2016) Modes of tetra (4-pyridyl) porphyrinatomanganese (III) ion intercalation inside natural clays. Chem Cent J 10(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-016-0153-4
Zyoud A, Zorba T, Helal M, Zyoud S, Qamhiya N, Hajamohideen A, Zyoud Sh, Hilal HS (2019) Direct sunlight-driven degradation of 2-chlorophenol catalyzed by kaolinite-supported ZnO. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(10):6267–6276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02272-z
Zyoud A, Zu'bi A (2015) A. Photo-degradation of water-organic contaminants and bacteria with safe sensitized TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles: a green sustainable method for water purification. ICAM-E2017 conference, Yildiz Technical University, Turkey
Zyoud AH, Asaad S, Zyoud SH, Zyoud SH, Helal MH, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Hilal HS (2020) Raw clay supported ZnO nanoparticles in photodegradation of 2-chlorophenol under direct solar radiations. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104227
Zyoud AH, Salah H, Zyoud SH, Zyoud SH, Helal MH, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Nassar N, Hilal HS (2021a) ZnO-Based catalyst for aqueous 2-chlorophenol photodegradation under solar simulated light: a continuous flow model. J Metals Mater Miner JOM 73:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04478-w
Zyoud AH, Dwikat M, Anabtawi S, Alkowni R, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Zyoud SH, Helal MH, Zyoud SH, Nassar H, Hilal HS (2021b) ZnO-based catalyst for photodegradation of 2-chlorophenol in aqueous solution under simulated solar light using a continuous flow method. J Metals Mater Miner JOM 73:420–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04478-w
Zyoud AH, Zaatar N, Saadeddin I, Ali C, Park D, Campet G, Hilal HS (2010) CdS-sensitized TiO2 in phenazopyridine photo-degradation: Catalyst efficiency, stability and feasibility assessment. J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.093
Zyoud AH, Zubi A, Hejjawi S, Zyoud SH, Helal MH, Zyoud SH, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Hilal HS (2020) Removal of acetaminophen from water by simulated solar light photodegradation with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles: Catalytic efficiency assessment for future prospects. J Environ Chem Eng 8(4):104038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104038
Zyoud AH, Zubi A, Zyoud SH, Hilal MH, Zyoud S, Qamhieh N, Hajamohideen A, Hilal HS (2019) Kaolin-supported ZnO nanoparticle catalysts in self-sensitized tetracycline photodegradation: Zero-point charge and pH effects. Appl Clay Sci 182:105294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105294
Acknowledgement
The work is part of a project in collaboration between Palestine (M.S, M. R., N. Sh. & S.I., R. Ab., H.S.H. and A.Z.) and Netherland Team (W.V. & K. K.) supported by PADUCO (Project # SRP7, 2018). ANU team members acknowledge support from the University. The XRD and SEM measurements were performed by T.W.K. who acknowledges financial support from “the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2019M1A2A2065618).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Results are mainly based on I.N. Thesis supervised by H.S.H. and A.Z. Sh.Z. measured TOC. M.H.S.H. participated with original ideas about continuous flow rate, glass support and project design. T.W.K. measured XRD and SEM. The work is part of a project in collaboration between Palestine (M.S, M. R., N. Sh. & S.I., R. Ab., H.S.H. and A.Z.) and Netherland Team (E. V. V. & K. K.) supported by PADUCO.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Parveen Fatemeh Rupani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zyoud, A., Nassar, I.M., Salman, M. et al. Nano-ZnO film photocatalysts in bench-scale continuous-flow mineralization of olive mill waste contaminants in water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 4379–4392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03291-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03291-5