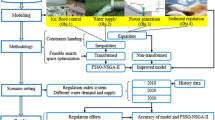
Abstract
The entry of excess nutrients into the reservoir causes problems such as eutrophication, and as a result, we see a decline in the quality of water in the reservoirs and changes in the downstream ecosystem. In this study, a simulation–optimization model has been developed in the framework of selective withdrawal methods to achieve optimal operation policies that can meet the different objectives of the reservoir. A two-dimensional model called CE-QUAL-W2 was used to simulate the reservoir water quality processes. Also, the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) was used as an optimization algorithm in the developed simulation–optimization model. The results show that the dissolved oxygen concentration of the outlet from the lower gate Seimare reservoir for the optimal operation policy is about 30% better than the current operating conditions. In addition, hydropower energy has increased by about 50%. The eutrophication status in the reservoir improved in relation to the existing condition, in most months of the year; the reservoir is in low eutrophication state for optimal operation policy. The results showed the high efficiency of this method and the considerable improvement of the various objectives of the reservoir.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 22(2):361–369
Castelletti A, Yajima H, Giuliani M, Soncini-Sessa R, Weber E (2013) Planning the optimal operation of a multioutlet water reservoir with water quality and quantity targets. J Water Resour Plan Manage 140(4):496–510
Chaves P, Kojiri T (2007) Deriving reservoir operational strategies considering water quantity and quality objectives by stochastic fuzzy neural networks. Adv Water Resour 30(5):1329–1341
Cole TM, Wells SA (2006) CE-QUAL-W2: a two-dimensional, laterally averaged, hydrodynamic and water quality model, version 3.5, Instruction Report EL-06-1, US Army Engineering and Research Development Center, Vicksburg, MS
Cong HB, Huang TL, Chai BB, Zhao JW (2009) A new mixing–oxygenating technology for water quality improvement of urban water source and its implication in a reservoir. Renew Energy 34(9):2054–2060
Deb K, Agrawal S, Pratap A, Meyarivan T (2000) A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. In: International conference on parallel problem solving from nature. Springer, Berlin, 849–858
Dhar A, Datta B (2008) Optimal operation of reservoirs for downstream water quality control using linked simulation optimization. Hydrol Process 22(6):842–853
Gelda RK, Effler SW (2007) Simulation of operations and water quality performance of reservoir multilevel intake configurations. J Water Resour Plan Manage 133(1):78–86
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2006) Optimal reservoir operation considering the water quality issues: a stochastic conflict resolution approach. Water Resour Res 42(12):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004575
Kuo J-T, Lung W-S, Yang C-P, Liu W-C, Yang M-D, Tang T-S (2006) Eutrophication modelling of reservoirs in Taiwan. Environ Model Softw 21(6):829–844
Moridi A (2019) Dealing with reservoir eutrophication in a trans-boundary river. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2951–2960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1775-y
Rani D, Moreira MM (2010) Simulation–optimization modeling: a survey and potential application in reservoir systems operation. Water Resour Manage 24(6):1107–1138
Rossel V, de la Fuente A (2015) Assessing the link between environmental flow, hydropeaking operation and water quality of reservoirs. Ecol Eng 85:26–38
Saadatpour M, Afshar A, Edinger JE (2017) Meta-model assisted 2d hydrodynamic and thermal simulation model (ce-qual-w2) in deriving optimal reservoir operational strategy in selective withdrawal scheme. Water Resour Manage 31(9):2729–2744
Soleimani S, Bozorg-Haddad O, Saadatpour M, Loáiciga HA (2016) Optimal selective withdrawal rules using a coupled data mining model and genetic algorithm. J Water Resour Plan Manage 142(12):04016064
Wang L, Liu L, Zheng B (2013) Eutrophication development and its key regulating factors in a water-supply reservoir in North China. J Environ Sci 25(5):962–970
Yazdi J, Moridi A (2017a) Interactive reservoir-watershed modeling framework for integrated water quality management. Water Resour Manage 31(7):2105–2125
Yazdi J, Moridi A (2017b) Sediment Flushing of reservoirs under environmental considerations. Water Resour Manage 31(6):1899–1914
Yu Y, Wang P, Wang C, Wang X (2018) Optimal reservoir operation using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms for potential estuarine eutrophication control. J Environ Manage 223:758–770
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our greatest appreciation to Department of Environment (DoE of Islamic Republic of Iran) for providing data (Permission letter No 99-440-6497).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Communicated by Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahyaee, A.R., Moridi, A. & Sarang, A. A new optimized model to control eutrophication in multi-purpose reservoirs. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 3357–3370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03042-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03042-y