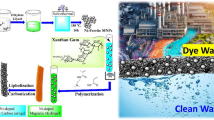
Abstract
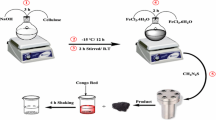
In this study, a novel gelatin-based nanomaterial was produced through mixing a gelatin solution with nanoclay cloisite 30 B, iron salts and basic ammonium in a special setup. Characterization by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy proved that the expected functional groups are present. From the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis, surface area and total pore volume were 48 m2 g−1 and 0.06 cm3 g−1, respectively, showing appropriate textural properties of the sample. Field emission scanning electron microscopy not only showed the morphology of the surface but also visually allowed to estimate the mean diameter of nanoparticles of 14 nm. Further, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy detected some elements, each referred to its source in the preliminary mixture. Among many different applications offered by this material and this technique, batch adsorption of Direct Yellow 12 was chosen and studied as a function of adsorbent mass, solution pH, contact time and initial concentration of the solution. Results demonstrated that acidic condition favors dye removal due to an upraised level of electrostatic attraction between the positively charged surface of nanobioadsorbent and anionic Direct Yellow 12 molecules. Pseudo-second-order model perfectly matched to the kinetics data in all initial concentrations. Adsorption equilibrium data well fitted to the Langmuir equation, giving the maximum capacity of adsorption of 476 mg g−1. Additionally, the nanobioadsorbent was regenerated and reused successfully with showing just a small decrease in capacity. Therefore, gelatin-nanobiocomposite is a promising agent to practically lower the hazardous dyestuff concentration.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alinejad-Mir A, Amooey AA, Ghasemi S (2018) Adsorption of Direct Yellow 12 from aqueous solutions by an iron oxide-gelatin nanoadsorbent; kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J Clean Prod 170:570–580
Aljeboree AM, Alshirifi AN, Alkaim AF (2017) Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab J Chem 10:S3381–S3393
Arami M, Limaee NY, Mahmoodi NM, Tabrizi NS (2005) Removal of dyes from colored textile wastewater by orange peel adsorbent: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 288:371–376
Chen G, Qiao C, Wang Y, Yao J (2014) Synthesis of magnetic gelatin and its adsorption property for Cr (Vi). Ind Eng Chem Res 53:15576–15581
Eren E, Afsin B (2008) Investigation of a basic dye adsorption from aqueous solution onto raw and pre-treated bentonite surfaces. Dyes Pigments 76:220–225
Ghaedi M, Sadeghian B, Pebdani AA, Sahraei R, Daneshfar A, Duran C (2012) Kinetics, thermodynamics and equilibrium evaluation of Direct Yellow 12 removal by adsorption onto silver nanoparticles loaded activated carbon. Chem Eng J 187:133–141
Ghaedi M, Ansari A, Sahraei R (2013a) Zns: Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as novel adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of reactive orange 12 and direct yellow 12 adsorption. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 114:687–694
Ghaedi M, Sadeghian B, Kokhdan SN, Pebdani AA, Sahraei R, Daneshfar A, Mihandoost A (2013b) Study of removal of Direct Yellow 12 by cadmium oxide nanowires loaded on activated carbon. Mater Sci Eng, C 33(4):2258–2265
Giles C, Macewan T, Nakhwa S, Smith D (1960) 786. Studies in adsorption. Part Xi. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc 3973–3993
Gong R, Li M, Yang C, Sun Y, Chen J (2005) Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J Hazard Mater 121:247–250
Hajati S, Ghaedi M, Karimi F, Barazesh B, Sahraei R, Daneshfar A (2014) Competitive adsorption of Direct Yellow 12 and reactive orange 12 on Zns: Mn nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as novel adsorbent. J Ind Eng Chem 20:564–571
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Abdelwahab O (2009a) Treatment of artificial textile dye effluent containing direct yellow 12 by orange peel carbon. Desalination 238:210–232
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Abdelwahab O (2009b) Treatment of artificial textile dye effluent containing direct yellow 12 by orange peel carbon. Desalination 238:210–232
Li S, Gong Y, Yang Y, He C, Hu L, Zhu L, Sun L, Shu D (2015) Recyclable CNTs/FE3O4 magnetic nanocomposites as adsorbents to remove bisphenol a from water and their regeneration. Chem Eng J 260:231–239
Liu F, Wang J, Li L, Shao Y, Xu Z, Zheng S (2009) Adsorption of Direct Yellow 12 onto ordered mesoporous carbon and activated carbon. J Chem Eng Data 54:3043–3050
Marzbali MH, Esmaieli M, Abolghasemi H, Marzbali MH (2016) Tetracycline adsorption By H3PO4-activated carbon produced from apricot nut shells: a batch study. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:700–709
Marzbali MH, Mir AA, Pazoki M, Pourjamshidian R, Tabeshnia M (2017) Removal of Direct Yellow 12 from aqueous solution by adsorption onto spirulina algae as a high-efficiency adsorbent. J Environ Chem 5:1946–1956
Mirsoleimani-Azizi SM, Setoodeh P, Samimi F, Shadmehr J, Hamedi N, Rahimpour MR (2018) Diazinon removal from aqueous media by mesoporous Mil-101 (Cr) in a continuous fixed-bed system. J Environ Chem 6:4653–4664
Moghaddam SS, Moghaddam MA, Arami M (2010) Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: optimization through response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 175:651–657
Namasivayam C, Sumithra S (2005) Removal of direct red 12b and methylene blue from water by adsorption onto Fe (iii)/Cr (iii) hydroxide, an industrial solid waste. J Environ Manag 74:207–215
Nandi BK, Goswami A, Purkait MK (2009) Adsorption characteristics of brilliant green dye on kaolin. J Hazard Mater 161:387–395
Nazari G, Abolghasemi H, Esmaieli M, Pouya ES (2016) Aqueous phase adsorption of cephalexin by walnut shell-based activated carbon: a fixed-bed column study. Appl Surf Sci 375:144–153
Parikh N, Parekh K (2015) Technique to optimize magnetic response of gelatin coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26:202
Pezoti O Jr, Cazetta AL, Souza IP, Bedin KC, Martins AC, Silva TL, Almeida VC (2014) Adsorption Studies Of Methylene Blue Onto Zncl2-Activated Carbon Produced From Buriti Shells (Mauritia Flexuosa L). J Ind Eng Chem 20:4401–4407
Pouretedal H, Sadegh N (2014) Effective removal of amoxicillin, cephalexin, tetracycline and penicillin g from aqueous solutions using activated carbon nanoparticles prepared from vine wood. J Water Process Eng 1:64–73
Shadmehr J, Mirsoleimani-Azizi S, Zeinali S, Setoodeh P (2018) Electrocoagulation process for propiconazole elimination from wastewater: experimental design for correlative modeling and optimization. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1–12
Song W, Gao B, Xu X, Xing L, Han S, Duan P, Song W, Jia R (2016) Adsorption–desorption behavior of magnetic amine/Fe3O4 functionalized biopolymer resin towards anionic dyes from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 210:123–130
Wawrzkiewicz M (2013) Removal of Ci basic blue 3 dye by sorption onto cation exchange resin, functionalized and non-functionalized polymeric sorbents from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Chem Eng J 217:414–425
Zhang D, Yin J, Zhao J, Zhu H, Wang C (2015) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline from water by petroleum coke-derived highly porous activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1504–1512
Zheng Y, Yao G, Cheng Q, Yu S, Liu M, Gao C (2013) Positively charged thin-film composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of cationic dyes through submerged filtration. Desalination 328:42–50
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the continuous support from University of Mazandaran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Gobinath Ravindran.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amooey, A.A., Alinejad-Mir, A., Ghasemi, S. et al. The removal of Direct Yellow 12 from synthetic aqueous solution by a novel magnetic nanobioadsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 8343–8354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02298-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02298-3