Abstract
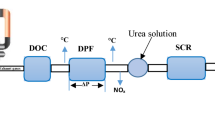
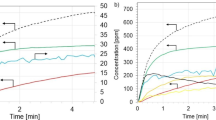
Selective catalytic reduction is an application used to control NOx pollutants in diesel engines. Aqueous urea solution, commercially called AdBlue and obtained by mixing pure water and NH3, is the most commonly used reductant while the V2O5–WO3/TiO2 structure has a widespread use as catalyst in SCR technology. However, the SCR systems included AdBlue and V2O5–WO3/TiO2 structure have low NOx conversion efficiency at low exhaust gas temperatures. The use of hydrocarbons as reductant and catalysts containing silver improves the conversion efficiency of selective catalytic reduction systems at low exhaust temperatures. In this work, selective catalytic reduction of NOx emissions from diesel engines in the presence of hydrocarbons has been studied. While ethanol and biodiesel mixtures were used as hydrocarbons, the Ag–Pt/Al2O3 structure was preferred as the catalyst. Scanning electron microscope and X-ray fluorescence analyses of the catalyst produced by the impregnation method were carried out. In order to determine the NOx conversion efficiency of ethanol–biodiesel mixtures in the selective catalytic reduction system, tests were carried out at different engine loads and different exhaust gas temperatures under actual operating conditions. As a result of the tests carried out, it was concluded that the reductant, which consists of 15% biodiesel and 85% ethanol, has the highest conversion performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arve K, Klingstedt F, Eranen K, Lindfors LE, Murzin DY (2005) Engineering HC-SCR: improved low temperature performance through a cascade concept. Catal Lett 105:133–138
Ayodhya AS, Narayanappa KG (2018) An overview of after-treatment systems for diesel engines. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:35034–35047
Bai S, Han J, Liu M, Qin S, Wang G, Li G (2018) Experimental investigation of exhaust thermal management on NOx emissions of heavy-duty diesel engine under the world Harmonized transient cycle (WHTC). Appl Therm Eng 142:421–432
Boriboonsomsin K, Durbin T, Scora G et al (2018) Real-world exhaust temperature profiles of on-road heavy-duty diesel vehicles equipped with selective catalytic reduction. Sci Total Environ 634:909–921
Chen H, Xie B, Ma J, Chen Y (2018) NOx emission of biodiesel compared to diesel: higher or lower? Appl Therm Eng 137:584–593
Cheng X, Bi XT (2014) A review of recent advances in selective catalytic NOx reduction reactor technologies. Particuology 16:1–18
Cho BK, Lee JH, Crellin CC et al (2012) Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by diesel fuel: plasma-assisted HC/SCR system. Catal Today 191:20–24
Frobert A, Raux S, Rousseau S, Blanchard G (2013) Analysis of the coupling of HC–SCR by ethanol and NH3–SCR on real engine emissions. Top Catal 56:125–129
Guan B, Zhan R, Lin H, Huang Z (2014) Review of state of the art technologies of selective catalytic reduction of NOx from diesel engine exhaust. Appl Therm Eng 66:395–414
Hamidzadeh M, Ghassemzadeh M, Tarlani A, Sahebdelfar S (2018) The effect of hydrothermal impregnation of Ni Co, and Cu on HZSM-5 in the nitrogen oxide removal. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:93–104
Kang W, Choi B, Jung S, Park S (2018) PM and NOx reduction characteristics of LNT/DPF + SCR/DPF hybrid system. Energy 143:439–447
Knothe G, Razon LF (2017) Biodiesel Fuels. Prog Energy Combust Sci 58:36–59
Kylhammar L, Palmqvist A, Skoglundh M (2007) Effects of oxidation and redox-properties on the selectivity of heat-treated Ag/Al2O3 catalysts for HC-SCR of NOx. Top Catal 42–43:119–122
Lee J, Min K (2014) A study of the fouling characteristics of EGR coolers in diesel engines. J Mech Sci Technol 28(8):3395–3401
Lesnik L, Bilus I (2016) The effect of rapeseed oil biodiesel fuel on combustion, performance, and the emission formation process within a heavy-duty DI diesel engine. Energy Convers Manag 109:140–152
Liu F, Shan W, Pan D, Li T, He H (2014) Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 for heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Chin J Catal 35:1438–1445
Liu Y, Liu Z, Mnichowicz B, Harinath AV, Li H, Bahrami B (2016) Chemical deactivation of commercial vanadium SCR catalyst in diesel emission control application. Chem Eng J 287:680–690
Mrad R, Aissat A, Cousin R, Courcot D, Siffert S (2015) Catalysts for NOx selective catalytic reduction by hydrocarbons (HC-SCR). Appl Catal A 504:542–548
Nakomcic-Smaragdakis B, Cepic Z, Cepic M, Stajie T (2014) Data analysis of the flue gas emissions in the thermal-power plant firing fuel oil and natural gas. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:269–280
Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Fino D, Russo N (2015) Catalysis in diesel engine NOx after treatment: a review. Catal Struct React 1(4):155–173
Praveena V, Leenus Jesu Martin M (2018) A review on various after treatment techniques to reduce NOx emissions in a CI engine. J Energy Inst 91:704–720
Ramos A, Munoz J, Andres F, Armas O (2018) NOx emissions from diesel light duty vehicle tested under NEDC and real-world driving conditions. Transp Res D Transp Environ 63:37–48
Resitoglu IA, Altınısık K, Keskin A (2015) The pollutant emissions from diesel engine vehicles and exhaust after treatment systems. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:15–27
Sajjadi B, Raman AA, Arandiyan H (2016) A comprehensive review on properties of edible and non-edible vegetable oil-based biodiesel: composition, specifications and prediction models. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 63:62–92
Sharariar GMH, Lim OT (2018) Investigation of urea aqueous solution injection, droplet breakup and urea decomposition of selective catalytic reduction systems. J Mech Sci Technol 32(7):3473–3481
Sharariar GMH, Wardana MKA, Lim OT (2018) Investigation of urea-water solution spray impingement on the hot surface of automotive SCR system. J Mech Sci Technol 32(6):2935–2946
Sitshebo S, Tsolakis A, Theinnoi K (2009) Promoting hydrocarbon-SCR of NOx in diesel engine exhaust by hydrogen and fuel reforming. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:7842–7850
Wang J, Peng Z, Chen Y, Bao W, Chang L, Feng G (2015) In-situ hydrothermal synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13/cordierite for the catalytic removal of NOx from diesel vehicles by NH3. Chem Eng J 263:9–19
Wang J, Zhao H, Haller G, Li Y (2017) Recent advances in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 on Cu-Chabazite catalysts. Appl Catal B 202:346–354
Xi Y, Ottinger NA, Liu ZG (2017) Influence of hydrocarbon species on its adsorption on a VSCR catalyst under simulated diesel engine operating conditions. Appl Catal B 217:581–590
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Mersin University Scientific Research Projects Unit (Project Code: 2018-2-AP3-2964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: R Saravanan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resitoglu, I.A., Keskin, A., Özarslan, H. et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx emissions by hydrocarbons over Ag–Pt/Al2O3 catalyst in diesel engine. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6959–6966 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02266-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02266-x