Abstract
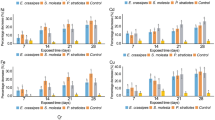
The aim of the study was to evaluate the potential of Gossypium hirsutum L. and Solanum lycopersicum L. plants for sewage sludge stabilization. The plants were cultured for 120 days in two plastic beds of 30 cm × 60 cm × 50 cm (W. L. H) in dimension. The highest removal efficiency of organic carbon, total Kjeldahl nitrogen, total phosphorous, lead and cadmium was obtained 36, 33.6, 23, 74.29 and 91.2%, respectively. The removal rate of above parameters was considerably higher than control (P < 0.05), and in Solanum lycopersicum L., it was higher than Gossypium hirsutum L. (P < 0.05). The pH, electrical conductivity and sodium absorption ratio variation in control with plants were significant (P < 0.05). By increasing electrical conductivity and sodium absorption ratio, the removal efficiency of heavy metals increased. The highest translocation factor (2.44) and bio-concentration factor (1.63) were observed in the Solanum lycopersicum L. for lead. Maximum and minimum cadmium concentrations in the shoot parts of Solanum lycopersicum L. and Gossypium hirsutum L. plants were 1.21 and 0.03 mg/kg, respectively. TF mean for lead and cadmium in Gossypium hirsutum L. was and 0.65 and 1.77; in Solanum lycopersicum L., it was 0.44 and 1.5, respectively. The results showed that the mean of bio-concentration factor in Solanum lycopersicum L. bed for Cd and Pb was 0.39 and 0.63, and for Gossypium hirsutum L., it was 0.3 and 0.58, respectively. The changes in organic carbon, nutrients and heavy metal in sludge were showed that Solanum lycopersicum L and Gossypium hirsutum L. can be used properly to stabilize sewage sludge.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anning AK, Akoto R (2018) Assisted phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil from a mined site with Typha latifolia and Chrysopogon zizanioides. Ecotoxicol environ saf 148:97–104
Alharbi OM, Khattab RA, Ali I (2018) Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J Mol Liq 263:442–453
Ali I, AL-Othman ZA, Alwarthan A (2016) Green synthesis of functionalized iron nano particles and molecular liquid phase adsorption of ametryn from water. J Mol Liq 221:1168–1174
Almasi A, Fazlzadeh M, Khosravi T, Sadeghi E (2012) A new approach to anaerobic-anoxic stabilization pond: treating petroleum refinery wastewater. Arch Des Sci 65:222–234
Almasi A, Sharafi K, Hazrati S, Fazlzadehdavil M (2015) A survey on the ratio of effluent algal BOD concentration in primary and secondary facultative ponds to influent raw BOD concentration. Desalin Water Treat 53:3475–3481
Almasi A, Mohammadi M, Dargahi A, Amirian F, Motlagh ZJ et al (2018) Nitrogenous contamination in iranian vegetables: a review. Pol J Environ Stud 27:2405–2416
Andreolli M, Lampis S, Poli M, Gullner G, Biró B, Vallini G (2013) Endophytic Burkholderia fungorum DBT1 can improve phytoremediation efficiency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 92:688–694
Baruah P, Deka S (2013) Removal of hydrocarbon from crude oil contaminated soil by Cyperus brevifolius Rottb. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 2:123–130
Basheer AA (2018) Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21st century. Chirality 30:402–406
Dargahi A, Azizi A, Karami A, Amirian F, Mohammadi M, Almasi A (2016) Evaluating the chemical and microbial quality of drinking water in harsin city. Int J Pharm Technol 8:16709–16719
De Sanctis M, Del Moro G, Chimienti S, Ritelli P, Levantesi C, Di Iaconi C (2017) Removal of pollutants and pathogens by a simplified treatment scheme for municipal wastewater reuse in agriculture. Sci Total Environ 580:17–25
Dhanwal P, Kumar A, Dudeja S, Chhokar V, Beniwal V (2017) Recent advances in phytoremediation technology. In: Kumar R., Sharma A., Ahluwalia S. (eds) Advances in Environmental Biotechnology. Springer, Singapore, pp 227–241
Elloumi N, Belhaj D, Jerbi B, Zouari M, Kallel M (2017) Effects of sewage sludge on bio-accumulation of heavy metals in tomato seedlings. Span J Agric Res 14:807–820
Enang RK, Yerima BPK, Kome GK, Van Ranst E (2018) Assessing the effectiveness of the Walkley-Black method for soil organic carbon determination in tephra soils of cameroon. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:1–8
Gupta VK, Ali I (2012) Environmental water: advances in treatment, remediation and recycling. Newnes
Hadi P, Xu M, Ning C, Lin CSK, McKay G (2015) A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 260:895–906
Hechmi N, Aissa NB, Abdenaceur H, Jedidi N (2014) Evaluating the phytoremediation potential of Phragmites australis grown in pentachlorophenol and cadmium co-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1304–1313
Ibrahim M (2017) Effect of indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi combined with manure on the change in concentration some mineral elements in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). J Plant Nutr 40:2862–2871
Jaafari J, Seyedsalehi M, Safari G, Arjestan ME, Barzanouni H et al (2017) Simultaneous biological organic matter and nutrient removal in an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2O) moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) integrated system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:291–304
Jan S, Parray JA (2016) Biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation of metals in the environment. In: Approaches to heavy metal tolerance in plants, pp 103–107
Kang W, Bao J, Zheng J, Xu F, Wang L (2016) Potential of woody plants from a Tonglushan ancient copper spoil heap for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil1. Int J Phytoremediation 20:111–120
Liu YY, Cui S, Han Q, Zhang QR (2015) Applied mechanics and materials. Trans Tech Publ 768:150–154
Luo K, Ma T, Liu H, Wu L, Ren J et al (2015) Efficiency of repeated phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc from an agricultural soil contaminated with sewage sludge. Int J Phytorem 17:575–582
Maryam G, Majid N, Islam M, Ahmed O, Abdu A (2015) Phytoremediation of copper-contaminated sewage sludge by tropical plants. J Tropical For Sci 27:535–547
Mirza N, Mahmood Q, Pervez A, Ahmad R, Farooq R et al (2010) Phytoremediation potential of Arundo donax in arsenic-contaminated synthetic wastewater. Biores Technol 101:5815–5819
Moreira IT, Oliveira OM, Triguis JA, Queiroz AF, Barbosa RM, et al (2013) Evaluation of the effects of metals on biodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons. Microchem J 110:215–220
Mousavi SA, Almasi A, Kamari Z, Abdali F, Yosefi Z (2015) Application of the central composite design and response surface methodology for the treatment of Kermanshah landfill leachate by a sequencing batch reactor. Desalin Water Treat 56:622–628
Naghipour D, Gharibi H, Taghavi K, Jaafari J (2016a) Influence of EDTA and NTA on heavy metal extraction from sandy-loam contaminated soils. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3512–3518
Naghipour D, Taghavi K, Jaafari J, Mahdavi Y, Ghanbari Ghozikali M et al (2016b) Statistical modeling and optimization of the phosphorus biosorption by modified Lemna minor from aqueous solution using response surface methodology (RSM). Desalin Water Treat 57:19431–19442
Naghipour D, Jaafari J, Ashrafi SD, Mahvi AH (2017) Remediation of heavy metals contaminated silty clay loam soil by column extraction with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and nitrilo triacetic acid. J Environ Eng 143:4017–4026
Perriguey J, Sterckeman T, Morel J-L (2008) Effect of rhizosphere and plant-related factors on the cadmium uptake by maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 63:333–341
Pirsaheb M, Almasi A, Sharafi K, Jabari Y, Haghighi S (2016) A comparative study of heavy metals concentration of surface soils at metropolis squares with high traffic—a case study: Kermanshah, Iran (2015). Acta Med 32:891
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad M, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574
Ren X, Yan R, Wang HC, Kou YY, Chae KJ et al (2015) Citric acid and ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid as effective washing agents to treat sewage sludge for agricultural reuse. Waste Manag 46:440–448
Saleh J, Ghasemi H, Shahriari A, Alizadeh F, Hosseini Y (2017) Phytoremediation potential of tomato for Cd and Cr removal from polluted Soils. World Acad Sci Eng Tech Int JBiol Biomol Agric Food Biotechnol Eng 11:268–271
Scaglia B, Tambone F, Corno L, Orzi V, Lazzarini Y et al (2018) Potential agronomic and environmental properties of thermophilic anaerobically digested municipal sewage sludge measured by an unsupervised and a supervised chemometric approach. Sci Total Environ 637:791–802
Tripathi and Tripathi S (2017) Phytoremediation – Aeration System for Treatment of Urban Wastewater. Austin Chem Eng 4:1047–1054
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ 368:456–464
Zahedi S, Romero-Güiza M, Icaran P, Yuan Z, Pijuan M (2018) Optimization of free nitrous acid pre-treatment on waste activated sludge. Biores Technol 252:216–220
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number 97025) for its financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almasi, A., Mohammadi, M., Mosavi, S.A. et al. Phytoremediation potential of sewage sludge using native plants: Gossypium hirsutum L. and Solanum lycopersicum L.. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6237–6246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2030-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2030-2