Abstract
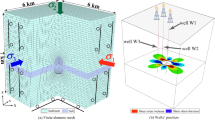
Reducing the drilling preparation time between adjacent wells in deepwater oil and gas blocks can significantly reduce the costs of deepwater oil and gas resource development. Therefore, changing and optimizing the flow of operations between adjacent wells in deepwater drilling is crucial to reduce development costs. This paper proposes a new optimal method for platform navigation between adjacent wells, specifically, a platform of hang-off drilling riser navigation method. The mechanical properties of the suspended riser are analyzed using finite element simulations. Comparing the differences in stress and bending moments using static and dynamic analysis methods, the concept of hang-off drilling riser navigation between adjacent wells is first introduced, and then, a model is developed which takes into account the platform speed and the suspended length, speed, direction, and heading of the riser. The model can be used to design the shortest navigation routes to adjacent wells, significantly reducing the drilling time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
API RP16Q (1993) Recommended practice for design, selection, operation and maintenance of marine drilling riser systems. ANSI/API recommended practice 16Q, 1st edn, November
API RP 16Q (2001) Recommended practice for design selection operation and maintenance of marine drilling riser system
Brekke JN (2001) Key element in ultra-deep water drilling riser management. In: SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Chang YJ, Chen GM, Sun YY, Xu LB (2008) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of deepwater drilling risers subjected to random loads. China Ocean Eng 22(4):683–691
Chang Y, Chen G, Liangbin X et al (2009) Analysis on ultra deepwater drilling riser. Pet Explor Dev 36(4):523–528
Chen W (2011) Status and challenges of chinese deepwater oil and gas development. Pet Sci 8(4):477–484
Chen GM, Liu XQ, Chang YJ et al (2013) Advances in technology of deepwater drilling riser and wellhead. J China Univ Pet Ed Nat Sci 37(5):129–139
DNV OS F201 (2001) Dynamic risers. Det Norske Veritas, Norway
Evangelinos C, Lucor D, Karniadakis GE (2000) DNS-derived force distribution on flexible cylinders subject to vortex-induced vibration. J Fluids Struct 14:429–440
Günen A (2016) Micro-abrasion wear behavior of thermal-spray-coated steel tooth drill bits. Acta Physica Polonica 130(1):217–222. https://doi.org/10.12693/aphyspola.130.217
Hartlen RT, Currie IG (1997) Lift-oscillator model of vortex-induced vibration. J Eng Mech Div 96:577–591
Ju S, Chang Y, Chen G et al (2011) Determination methods for the top tension of ultradeepwater drilling risers. Ocean Eng 29(1):100–104
Liu X, Chen G, Chang Y (2017) Weak point and operation analysis of deepwater drilling riser system in typhoon condition. The 27th international ocean and polar engineering conference, San Francisco, California, USA
Sheng LX, Xu LB, Zhou JL et al (2016) Experience on deepwater drilling riser about hang-off modes in Typhoon condition of South China Sea. In: Offshore Technology Conference Asia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Stahl MJ, Abbassian F (2000) Operating gudielines for emergency disconnect of deepwater drilling risers, OMAE 00-4040
Stansby PK, Slaouti A (1993) Simulation of vortex shedding including blockage by the random-vortex and other methods. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 17:1003–1013
Sun Y, Chen G, Chang Y (2009) Axial direction dynamic analysis on ultradeep-water drilling riser under setting down and recovery operations. China Offshore Oil Gas 8(21):116–119
Williamson R, Sanders W, Jakabosky T et al (2003) Control of contained-annulus fluid pressure buildup. Paper SPE 79875 presented at the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference held in Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 19–21 February
Yang J, Cao S (2008) Current situation and developing trend of petroleum drilling technologies in deep water. Drill Prod Technol 30(2):10–13
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51434009) and National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2016ZX05033004-006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Iskender Akkurt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Yang, J. & Zhou, B. Optimal route design of adjacent wells and mechanical properties of hang-off drilling riser in ocean environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 5073–5078 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2006-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2006-2