Abstract
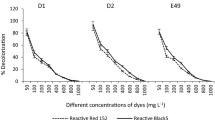
In a biological treatment of an industrial effluent, the indigenous bacteria have already been used. In this study, the three bacteria strains which are potent in the decolorization of azo dyes were isolated from dairy effluent and used for decolorization of Reactive Black5 and Reactive Red120 azo dyes and decolorization test of each dye was conducted at five concentration levels (10, 50, 100, 150, and 200 mg/l). The pH of which was adjusted to 7 and incubated at 37 °C for 3 days. The strains were identified as Staphylococcus sp. and Micrococcus luteus strains by 16S rRNA gene sequences analysis. The strains were deposited in GenBank with accession numbers of KX180131, KX180132, and KX180133 and submitted to laboratory identifier named Staphylococcus sp. MEH038S, Micrococcus luteus strain SEH038S, and Micrococcus luteus strain FEH038S. Three days into incubation, the lowest efficiency was at a concentration level of 200 mg/l for each dye. Decolorization efficiencies for Staphylococcus sp. MEH038S, Micrococcus luteus strain SEH038S, and Micrococcus luteus strain FEH038S at the concentration level of 200 mg/l for Reactive Red120 were 89.7, 87.1, and 89.3%, and for Reactive Black5 were 90.8, 90.0, and 89.9%, respectively. Based upon this study, dairy effluents can be used as a suitable alternative to the decolorization of textile wastewater. This study demonstrates a report on grounds of elucidation for the use of non-indigenous bacteria in the treatment of industrial wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z, Dönmez G (2003) A comparative study on the biosorption characteristics of some yeasts for Remazol Blue reactive dye. Chemosphere 50:1075–1083
Ali N, Hameed A, Ahmed S (2009) Physicochemical characterization and bioremediation perspective of textile effluent, dyes and metals by indigenous bacteria. J Hazard Mater 164:322–328
Anwar F et al (2014) Characterization of reactive red-120 decolorizing bacterial strain Acinetobacter junii FA10 capable of simultaneous removal of azo dyes and hexavalent chromium Water. Air, & Soil Pollution 225:2017
Buchaman R, Gibbons N (1974) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology Williams and Wilkins. Baltimore 197:654–701
Buthelezi SP, Olaniran AO, Pillay B (2012) Textile dye removal from wastewater effluents using bioflocculants produced by indigenous bacterial isolates. Molecules 17:14260–14274
Chaieb K, Hagar M, Radwan NR (2016) Biodegradation and decolorization of azo dyes by adherent Staphylococcus lentus strain. Appl Biol Chem 59:405–413
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Biores Technol 97:1061–1085
Daâssi D, Mechichi T, Nasri M, Rodriguez-Couto S (2013) Decolorization of the metal textile dye Lanaset Grey G by immobilized white-rot fungi. J Environ Manag 129:324–332
Das A, Mishra S (2016) Decolorization of different textile azo dyes using an isolated bacterium Enterococcus durans GM13. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 5:676–686
Forss J, Lindh MV, Pinhassi J, Welander U (2017) Microbial biotreatment of actual textile wastewater in a continuous sequential rice husk biofilter and the microbial community involved. PLoS ONE 12:e0170562
Govindwar SP, Kurade MB, Tamboli DP, Kabra AN, Kim PJ, Waghmode TR (2014) Decolorization and degradation of xenobiotic azo dye Reactive Yellow-84A and textile effluent by Galactomyces geotrichum. Chemosphere 109:234–238
Gupta V (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—a review. J Environ Manag 90:2313–2342
Hadibarata T, Yusoff ARM, Aris A, Hidayat T, Kristanti RA (2012) Decolorization of azo, triphenylmethane and anthraquinone dyes by laccase of a newly isolated Armillaria sp. F022. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1045–1054
Hassan M, Alam M, Anwar M (2013) Biodegradation of textile azo dyes by bacteria isolated from dyeing industry effluent. Int Res J Biol Sci 2:27–31
He M, Tan L, Ning S, Song L, Shi S (2017) Performance of the biological aerated filter bioaugmented by a yeast Magnusiomyces ingens LH-F1 for treatment of Acid Red B and microbial community dynamics. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:39
Hema N, Suresha S (2014) Bioremediation of textile dye effluent by Shewanella putrefaciens. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 4:109–116
Hu T-L (2001) Kinetics of azoreductase and assessment of toxicity of metabolic products from azo dyes by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Sci Technol 43:261–269
Hussain S, Maqbool Z, Ali S, Yasmeen T, Imran M, Mahmood F, Abbas F (2013) Biodecolorization of reactive black-5 by a metal and salt tolerant bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. RA20 isolated from Paharang drain effluents in Pakistan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:331–338
Imran M, Arshad M, Asghar HN, Asghar M, Crowley DE (2014) Potential of Shewanella sp. strain IFN4 to decolorize azo dyes under optimal conditions. Int J Agric Biol 16
Imran M, Shaharoona B, Crowley DE, Khalid A, Hussain S, Arshad M (2015) The stability of textile azo dyes in soil and their impact on microbial phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:163–168
Jadhav SU, Jadhav MU, Kagalkar AN, Govindwar SP (2008) Decolorization of Brilliant Blue G dye mediated by degradation of the microbial consortium of Galactomyces geotrichum and Bacillus sp. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 39:563–570
Jain K, Shah V, Chapla D, Madamwar D (2012) Decolorization and degradation of azo dye–Reactive Violet 5R by an acclimatized indigenous bacterial mixed cultures-SB4 isolated from anthropogenic dye contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 213:378–386
Jirasripongpun K, Nasanit R, Niruntasook J, Chotikasatian B (2007) Decolorization and degradation of CI Reactive Red 195 by Enterobacter sp. Int J Sci Technol 12:6–11
Kale R, Sabale M, Thorat P (2010) Decolorization and degradation of textile azo dye golden yellow HE 2 R by adapted bacteria nature. Environ Pollut Technol 9:351–354
Kumari S, Naraian R (2016) Decolorization of synthetic brilliant green carpet industry dye through fungal co-culture technology. J Environ Manag 180:172–179
Kurade MB, Waghmode TR, Kagalkar AN, Govindwar SP (2012) Decolorization of textile industry effluent containing disperse dye Scarlet RR by a newly developed bacterial-yeast consortium BL-GG. Chem Eng J 184:33–41
Lade H, Kadam A, Paul D, Govindwar S (2015) Biodegradation and detoxification of textile azo dyes by bacterial consortium under sequential microaerophilic/aerobic processes. EXCLI J 14:158
Liao C-S, Hung C-H, Chao S-L (2013) Decolorization of azo dye reactive black B by Bacillus cereus strain HJ-1. Chemosphere 90:2109–2114
Maqbool Z et al (2016) Use of RSM modeling for optimizing decolorization of simulated textile wastewater by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain ZM130 capable of simultaneous removal of reactive dyes and hexavalent chromium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11224–11239
Miao Y (2005) Biological remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a review on current treatment technologies. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227
Nouren S et al (2017) By-product identification and phytotoxicity of biodegraded Direct Yellow 4 dye. Chemosphere 169:474–484
Ogugbue CJ, Morad N, Sawidis T, Oranusi NA (2012) Decolorization and partial mineralization of a polyazo dye by Bacillus firmus immobilized within tubular polymeric gel 3. Biotechnology 2:67–78
Oturkar CC, Nemade HN, Mulik PM, Patole MS, Hawaldar RR, Gawai KR (2011) Mechanistic investigation of decolorization and degradation of Reactive Red 120 by Bacillus lentus BI377. Biores Technol 102:758–764
Pandey A, Singh P, Iyengar L (2007) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 59:73–84
Pathak H, Soni D, Chauhan K (2014) Evaluation of in vitro efficacy for decolorization and degradation of commercial azo dye RB-B by Morganella sp. HK-1 isolated from dye contaminated industrial landfill. Chemosphere 105:126–132
Rana S, Sharma R (2013) Microbial degradation of synthetic textile dyes: a cost effective and eco-friendly approach. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:2983–2989
Saharan BS, Ranga P (2011) Optimisation of cultural conditions for decolourization of textiles Azo dyes by Bacillus subtilis SPR42 under submerged fermentation. Int J Adv Biotech Res 2:148–153
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang J-S, Govindwar S (2011) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 42:138–157
Saroj S, Kumar K, Pareek N, Prasad R, Singh R (2014) Biodegradation of azo dyes Acid Red 183, Direct Blue 15 and Direct Red 75 by the isolate Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3. Chemosphere 107:240–248
Singh RP, Singh PK, Singh RL (2014) Bacterial decolorization of textile azo dye acid orange by Staphylococcus hominis RMLRT03. Toxicol Int 21:160
Singh S, Chatterji S, Nandini P, Prasad A, Rao K (2015) Biodegradation of azo dye Direct Orange 16 by Micrococcus luteus strain SSN2. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:2161–2168
Tripathi A, Srivastava S (2011) Ecofriendly treatment of azo dyes: biodecolorization using bacterial strains. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinform 1:37
Uhnáková B et al (2011) Biodegradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by oxidases in basidiomycetous fungi and estrogenic activity of the biotransformation products. Biores Technol 102:9409–9415
Vijayanand S, Hemapriya J (2013) Bacterial bioremediation of textile azo dyes: a review. Ind J Appl Res 3:480–482
Yan B, Du C, Xu M, Liao W (2012) Decolorization of azo dyes by a salt-tolerant Staphylococcus cohnii strain isolated from textile wastewater. Front Environ Sci Eng 6:806–814
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of honorable experts at Water and Wastewater Microbiology Laboratory in the Faculty of Health, honorable experts in Cellular and Molecular Research Center of the Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences and Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology. This study was financially supported by the Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, IR. Iran [Grant Number 122431].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Tanmoy Karak.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, M., Forouzandeh, S., Nourmoradi, H. et al. /+//Biodecolorization of Reactive Black5 and Reactive Red120 azo dyes using bacterial strains isolated from dairy effluents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 3615–3624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1750-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1750-7