Abstract
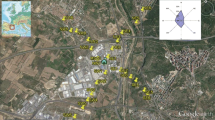
Multi-matrix environmental monitoring was used to evaluate the influence of a municipal solid waste landfill (Ginestreto, Emilia Romagna, Italy) on the level and distribution of heavy elements in the surrounding environment (air, soil and soil biota). Concentrations of As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Sb, Tl and Zn were measured by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in transplanted lichens, topsoils and isopods. The highest accumulation levels found for Cd, Cr, Pb, Sb and Zn in lichens transplanted within the Ginestreto landfill. However, similar concentrations of these heavy elements were also found in lichens exposed in monitoring sites influenced by other man-made sources, such as vehicle traffic and truck movements. The fallout of heavy elements emitted by the landfill had low impact on their levels in topsoil: Cd, Cr, Pb, Sb and Zn showed higher contents in topsoil collected close to the landfill and a slight decrease in concentrations with increasing distance from the landfill. There was no variation in heavy element accumulation in isopods in relation to distance from the landfill. The results of this study indicate that the Ginestreto municipal solid waste landfill had limited impact on the environmental distribution of heavy elements, since accumulation and enrichment in lichens and topsoils were only detected close to the landfill, up to about 100 m from its border.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadi AN, Nwankwoala HO (2013) Evaluation of heavy metal in soils from Enyimba dumpsite in Aba, southeastern Nigeria using contamination factor and geo-accumulation index. Energy Environ Res 3:125–134
Ayrault S, Clochiatti R, Carrot F, Daudin L, Bennett JP (2007) Factors to consider for trace element deposition biomonitoring surveys with lichen transplants. Sci Total Environ 372:717–727
Barbieri M, Sappa M, Vitale S, Parisse B, Battistel M (2014) Soil control of trace metals concentrations in landfills: a case study of the largest landfill in Europe, Malagrotta, Rome. J Geochem Explor 143:146–154
Bargagli R (1998) Trace elements in terrestrial plants: An ecophysiological approach to biomonitoring and biorecovery. Springer, Heidelberg
Bennett JP, Wetmore CM (1999) Changes in element contents of selected lichens over 11-years in northern Minnesota, USA. Environ Exp Bot 41:75–82
Bennett JP, Wetmore CM (2000) 16-Years trends in elements of lichens at Theodore Roosevelt National Park, North Dakota. Sci Total Environ 263:231–241
Bettinelli M, Spezia S, Bizzarri G (1996) Trace element determination in lichens by ICP-MS. At Spectrosc 17:133–141
Bretzel F, Calderisi M (2006) Metal contamination in urban soils of coastal Tuscany (Italy). Environ Monit Assess 118:319–335
Chalvatzaki E, Kopanakis I, Kontaksakis M, Glytos T, Kalogerakis N, Lazaridis M (2010) Measurements of particulate matter concentrations at a landfill site (Crete, Greece). Waste Manag 30:2058–2064
Chuan MC, Shu GY, Liu JC (1995) Solubility of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: effects of redox potential and pH. Water Air Soil Pollut 90(543):556
Conti ME, Cecchetti G (2001) Biological monitoring: lichens as bioindicators of air pollution assessment—a review. Environ Pollut 114:471–492
Conti ME, Tudino M, Stripeikis J, Cecchetti G (2004) Heavy metal accumulation in the lichen Evernia prunastri transplanted at urban, rural and industrial sites in Central Italy. J Atmos Chem 49:83–94
Dallinger R, Prosi F (1988) Heavy metals in terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber Latr. II. Subcellular fractionation of metal accumulating lysosomes from hepatopancreas. Cell Biol Toxicol 4:97–109
Fitz DR, Bumiller K (2000) Evaluation of watering to control dust in high winds. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 50:570–577
Frati L, Brunialti G, Loppi S (2005) Problems related to lichen transplants to monitor trace element deposition in repeated surveys: a case study from Central Italy. J Atmos Chem 52:221–230
Gál J, Markiewicz-Patkowska J, Hursthouse A, Tatner P (2008) Metal uptake by woodlice in urban soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:139–149
Garty J, Weissman L, Cohen Y, Karnieli A, Orlovsky L (2001) Transplanted lichens in and around the Mount Carmel National Park and the Haifa Bay industrial region in Israel: physiological and chemical responses. Environ Res Sect 85:159–176
Godinho RM, Wolterbeek H, Verburg T, Freitas MC (2008) Bioaccumulation behaviour of transplants of the lichen Flavoparmelia caperata in relation to total deposition at a polluted location in Portugal. Environ Pollut 151:318–325
Guttova A, Lackovicova A, Pisut I, Pisut P (2011) Decrease in air pollution load in urban environment of Bratislava (Slovakia) inferred from accumulation of metal elements in lichens. Environ Monit Assess 182:361–373
Hames CAC, Hopkin SP (1991) Assimilation and loss of 109Cd and 65Zn by the terrestrial isopods Oniscus asellus and Porcellio scaber. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47:440–447
Han S, Youn JS, Jung YW (2011) Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 source profiles for resuspended road dust collected using mobile sampling methodology. Atmos Environ 45:3343–3351
Harmsen J (2007) Measuring bioavailability: from a scientific approach to standard methods. J Environ Qual 36:1420–1428
Hopkin SP (1990) Species specific differences in the net assimilation of zinc, cadmium, lead, copper and iron by the terrestrial isopods Oniscus asellus and Porcellio scaber. J Appl Ecol 27:460–474
Hopkin SP, Martin MH (1982) The distribution of zinc, cadmium, lead and copper within the woodlouse Oniscus asellus (Crustacea, Isopoda). Oecologia 54:227–232
ILD (2003) Italian Legislative Decree n° 36, January 13, 2003, Implementation of Directive 1999/31/EC on the waste landfill, Official Italian Gazette n° 59, March 12, 2003 (in Italian)
ILD (2006) Italian Legislative Decree n° 152, April 3, 2006 and Subsequent Amendments, Environmental Regulations, Official Italian Gazette n° 88, April 14, 2006 (in Italian)
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:247–256
Jain P, Kim H, Townsend TG (2005) Heavy metal content in soil reclaimed from a municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manag 25:25–35
Kabata-Pendias A (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 413
Koshy L, Jones T, Berube K (2009) Characterization and bioreactivity of respirable airborne particles from a municipal landfill. Biomarkers 14:49–53
Loppi S, Frati L (2006) Lichen diversity and lichen transplants as monitors of air pollution in a rural area of central Italy. Environ Monit Assess 114:361–375
Loppi S, Giovannelli L, Pirintsos SA, Putortì E, Corsini A (1997) Lichens as bioindicators of recent changes in air quality (Montecatini Terme, Italy). Ecol Mediterr 23:53–56
Madrid L, Diaz-Barientos E, Madrid F (2002) Distribution of heavy metal content of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere 49:1301–1308
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieria M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243
Mikhailova I (2002) Transplanted lichens for bioaccumulation studies. In: Nimis PL, Scheidegger C, Wolseley PA (eds) Monitoring with lichens—monitoring lichens. Kluwer Academy Publishers, Berlin, pp 301–304
Mitchell B (2002) Resource and environmental management, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Harlow, p 367
Nannoni F, Santolini R, Protano G (2015a) Heavy element accumulation in Evernia prunastri lichen transplants around a municipal solid waste landfill in central Italy. Waste Manag 43:253–362
Nannoni F, Mazzeo R, Protano G, Santolini R (2015b) Bioaccumulation of heavy elements by Armadillidium vulgare (Crustacea, Isopoda) exposed to fallout of a municipal solid waste landfill. Ecol Ind 49:24–31
Nimis PL, Scheidegger C, Wolseley PA (2002) Monitoring with lichens—monitoring lichens. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Berlin
Odendaal JP, Reinecke AL (2004a) Bioaccumulation of cadmium and zinc, and field validation of a histological biomarker in terrestrial isopods. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72:769–776
Odendaal JP, Reinecke AJ (2004b) Effect of metal mixture (Cd and Zn) on body weight in terrestrial isopods. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:377–384
Pacheco AMG, Freitas MC, Baptista MS, Vasconcelos MTSD, Cabral JP (2008) Elemental levels in tree-bark and epiphytic-lichen transplants at a mixed environmental in mainland Portugal, and comparisons with an in situ lichen. Environ Pollut 151:326–333
Paoletti MG, Hassall M (1999) Woodlice (Isopoda Oniscidea): their potential for assessing sustainability and use as bioindicators. Agr Ecosyst Environ 74:157–166
Paoli L, Pisani T, Guttová A, Sardella G, Loppi S (2011) Physiological and chemical response of lichens transplanted in and around an industrial area of south Italy: relationship with the lichen diversity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:650–657
Paoli L, Corsini A, Bigagli V, Tannini J, Bruscoli C, Loppi S (2012) Long-term biological monitoring of environmental quality around a solid waste landfill assessed with lichens. Environ Pollut 161:70–75
Paoli L, Grassi A, Vannini A, Maslaňáková I, Bil’ová I, Bačkor M, Corsini A, Loppi S (2015) Epiphytic lichens as indicators of environmental quality around a municipal solid waste landfill (C Italy). Waste Manag 42:67–73
Peijnenburg WJGM (2002) Bioavailability of metals to soil invertebrates. In: Allen HE (ed) Bioavailability of metals in terrestrial ecosystems: importance of partitioning for bioavailability to invertebrates, microbes, and plants. SETAC, Pensacola, USA, pp 89–112
Protano C, Guidotti M, Owczarek M, Fantozzi L, Blasi G, Vitali M (2014) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and metals in transplanted lichen (Pseudovernia furfuracea) at sites adjacent to a solid-waste landfill in central Italy. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:471–481
Prudent P, Domeizel M, Massiani C (1996) Chemical sequential extraction as decision-making tool: application to municipal solid waste and its individual constituents. Sci Total Environ 178:55–61
Reimann C, de Caritat P (1998) Chemical elements in the environment. Springer, Berlin, p 397
Slack RJ, Gronow JR, Voulvoulis N (2004) Hazardous components of household waste. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 34:419–445
Slack RJ, Gronow JR, Voulvoulis N (2005) Household hazardous waste in municipal landfills: contaminants in leachate. Sci Total Environ 337:119–137
Sloof JE (1995) Lichens as quantitative biomonitors for atmospheric trace-element deposition, using transplants. Atmos Environ 29:11–20
Vijver MG, Vink JPM, Jager T, Van Straalen NM, Wolterbeek HT, Van Gestel CAM (2006) Kinetics of Zn and Cd accumulation in the isopod Porcellio scaber exposed to contaminated soil and/or food. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1554–1563
Violante A, Cozzolino V, Perelomov L, Caporale AG, Pigna M (2010) Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:268–292
Wiersma GB (2004) Environmental monitoring. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 792
Witzel B (1998) Uptake, storage and loss of cadmium and lead in the woodlouse Porcellio scaber (Crustacea, Isopoda). Water Air Soil Pollut 108:51–68
Witzel B (2000) The influence of zinc on the uptake and loss of cadmium and lead in the woodlouse Porcellio scaber (Isopoda, Oniscidea). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:43–53
Wolterbeek B (2002) Biomonitoring of trace element air pollution: principles, possibilities and perspectives. Environ Pollut 120:11–21
Zidar P, Drobne D, Strus J, Blejec A (2003) Intake and assimilation of zinc, copper, and cadmium in the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber Latr. (Crustacea, Isopoda). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:1028–1035
Zödl B, Wittmann KJ (2003) Effects of sampling, preparation and defecation on metal concentrations in selected invertebrates at urban sites. Chemosphere 52:1095–1103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: H.N. Hsieh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nannoni, F., Mazzeo, R., Santolini, R. et al. Multi-matrix environmental monitoring to assess heavy element distribution around a municipal solid waste landfill in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 2591–2602 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1342-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1342-y