Abstract
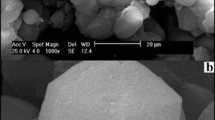
Silica nanoparticles were synthesized and coated with goethite, creating a nanocomposite. The nanocomposite was tested for removal of arsenic, As(V), from aqueous solutions. We used scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, and a Zetasizer to characterize particle size, surface morphology, functional groups, and surface charge of the nanocomposite. SEM results showed that the size of the synthesized silica nanoparticles ranged from 150 to 250 nm. Batch sorption studies were carried out on the adsorption of As(V) as a function of pH, contact time, initial concentration, and ionic strength. Maximum adsorption occurred at pH 3.0. The adsorption capacity did not change significantly with increasing ionic strength. A kinetics study revealed that adsorption of As(V) by the goethite/silica nanocomposite was rapid: Equilibrium was reached within 120 min. Adsorption kinetics followed a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption data were analyzed by both the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. The maximum adsorption capacity of goethite/silica nanocomposite for As(V) from the Langmuir isotherm was 17.64 mg g−1, which is larger than that of several other adsorbents. The nanocomposite adsorbent showed high efficiency in removing arsenic from aqueous solutions, even at low initial concentrations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrandale T (2002) EPA, the arsenic dictator. Governing 15:80
Baskan MB, Pala A (2011) Removal of arsenic from drinking water using modified natural zeolite. Desalination 281:396–403
Basu T, Ghosh UC (2013) Nanao-structured iron(III)-cerium(IV) mixed oxide: synthesis, characterization and arsenic sorption kinetics in the presence of co-existing ions aiming to apply for high arsenic ground water treatment. Appl Surf Sci 283:471–481
Chakravarty S, Dureja V, Bhattacharyya G, Maity S, Bhattacharjee S (2002) Removal of arsenic from groundwater using low cost ferruginous manganese ore. Water Res 36:625–632
Chen R, Zhi C, Yang H, Bando Y, Zhang Z, Sugiur N, Golberg D (2011) Arsenic (V) adsorption on Fe3O4 nanoparticle-coated boron nitride nanotubes. J Colloid Interface Sci 359:261–268
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK (2010) Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J Environ Manage 91:2238–2347
Cooper AM, Hristovski KD, Moller T, Westerhoff P, Sylvester P (2010) The effect of carbon type on arsenic and trichloroethylene removal capabilities of iron (hydr)oxide nanoparticle-impregnated granular activated carbons. J Hazard Mater 183:381–388
Encyclopedia Britannica (2014) Goethite. In: Encyclopedia Britannica Online. Retrieved 23 Nov 2014 from http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/237093/goethite
Feng L, Cao M, Ma X, Zhu Y, Hu C (2012) Super paramagnetic high surface area Fe3O4 nanoparticles as adsorbents for arsenic removal. J Hazard Mater 217–218:436–439
Freundlich H (1906) Uber die adsorption in losungen. Z Phys Chem 57:387–470
Genc-Fuhrman H, Tjell JC, McConchie D (2004) Adsorption of arsenic from water using activated neutralized red mud. Environ Sci Technol 38:2428–2434
Ghosh M, Eddy G, Poinern J, Issa TB, Singh P (2012) Arsenic adsorption on goethite nanoparticles produced through hydrazine sulfate assisted synthesis method. Korean J Chem Eng 29:95–102
Giménez J, Martinez M, de Pablo J, Rovira M, Duro L (2007) Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite, and goethite. J Hazard Mater 141:575–580
Gu Z, Fang J, Deng B (2005) Preparation and evaluation of GAC-based iron-containing adsorbents for arsenic removal. Environ Sci Technol 39:3833–3843
Han C, Li H, Pu H, Yu H, Deng L, Huang S, Luo Y (2013) Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous alumina and their performances for removing arsenic(V). Chem Eng J 217:1–9
Hang C, Li Q, Gao S, Shang JK (2012) As(III) and As(V) adsorption by hydrous zirconium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by a hydrothermal process followed with heat treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:353–361
Hayes KF, Papelis C, Leckie JO (1988) Modeling ionic strength effects on anion adsorption at hydrous oxide/solution interfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 125:717–726
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124
Howard AG, Khdary NH (2005) Nanoscavenger based dispersion preconcentration; sub-micron particulate extractants for analyte collection and enrichment. Analyst 130:1432–1438
Hristovski K, Westerhoff PK, Crittenden JC, Olson LW (2008) Arsenate removal by nanostructured ZrO2 spheres. Environ Sci Technol 42:3786–3790
Hsu JC, Lin CJ, Liao CH, Chen ST (2008) Removal of As(V) and As(III) by reclaimed iron-oxide coated sands. J Hazard Mater 153:817–826
Kocanas-Atakl ZO, Yurum Y (2013) Synthesis and characterization of anatase nanoadsorbent and application in removal of lead, copper and arsenic from water. Chem Eng J 225:625–635
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe, Kungliga Svenksa Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Lakshmipathiraj P, Narasimhan BRV, Prabhakar S, Raju GB (2006) Adsorption of arsenate on synthetic goethite from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 136:281–287
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surface glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1368
Li Q, Xu XT, Cui H, Pang J, Wei ZB, Sun Z, Zhai J (2012) Comparison of two adsorbents for the removal of pentavalent arsenic from aqueous solutions. J Environ Manag 98:98–106
Li C, Xu W, Jia D, Liu X (2013) Removal of arsenic from drinking water by using the Zr-loaded resin. J Chem Eng Data 58:427–435
Liu X, Ao H, Xiong X, Xiao J, Liu J (2012) Arsenic removal from water by iron-modified bamboo charcoal. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1033–1034
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Hurel C, Marmier N, Roméo M (2009) Arsenic adsorption onto hematite and goethite. C R Chim 12:876–881
Martinson CA, Reddy KJ (2009) Adsorption of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 336:406–411
Mohan D, Pittaman CU (2007) Arsenic removal from water and wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53
Nickson R, McArthur J, Burgess W, Ahmed KM, Ravenscroft P, Rahman M (1998) Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh ground water. Nature 395:338
Pehlivan E, Tran TH, Ouedraogo WKI, Schmidt C, Zachmann D, Bahadir M (2013) Removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions by iron coated rice husk. Fuel Process Technol 106:511–517
Pontinus FW, Brown KG, Chen CJ (1994) Health implications of arsenic in drinking water. J Am Water Works Assoc 86:52–63
Prucek R, Tucek J, Kolarik J, Filip J, Marusak Z, Sharma VK, Zboril R (2013) Ferrate(VI)-induced arsenite and arsenate removal by in situ structural incorporation into magnetic iron(III) oxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 47:3283–3292
Ravenscroft P, Brammer H, Richards K (2009) Arsenic pollution: a global synthesis. Wiley, London
Reddy KJ, McDonald KJ, King H (2013) A novel arsenic removal process for water using cupric oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 397:96–102
Saikia J, Saha B, Das G (2011) Efficient removal of chromate and arsenate from individual and mixed system by malachite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 186:575–582
Severn Trent Services (2014) Arsenic Removal Media—Bayoxide®. Severn Trent Services. Retrieved 23 Nov 2014 from https://www.severntrentservices.com/Drinking_Water_Treatment_Inorganic_Removal_Systems/Arsenic_Removal_Media_Bayoxide_prod_589.aspx
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertz-Picciotto I, Duggan HM, Wood R, Kosnett MJ, Smith MT (1992) Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 97:259–267
Stanic T, Dakovic A, Zivanovic A, Tomasevic-Xanovic M, Dondur V, Milicevic S (2009) Adsorption of arsenic (V) by iron (III)-modified natural zeolite tuff. Environ Chem Lett 7:161–166
Tang W, Li Q, Gao S, Shang JK (2011) Arsenic (III, V) removal from aqueous solution by ultra α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized from solvent thermal method. J Hazard Mater 192:131–138
Thirunavukkarasu OS, Viraraghavan T, Subramanian KS (2001) Removal of arsenic in drinking water by iron oxide-coated sand and ferrihydrite-batch studies. Water Qual Res J Can 36:55–70
Trujillo-Reyes J, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Supported and unsupported nanomaterials for water and soil remediation: are they a useful solution for worldwide pollution? J Hazard Mater 280:487–503
Tuutijarvi T, Lu J, Sillanpaa M, Chen G (2009) As(V) adsorption on maghemite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 166:1415–1420
USEPA (2002) Federal Register, vol 67, pp 78203–78209
Valencia-Trejo E, Valencia-Mendez M, Alfardo-Cueas-Villanueva R, Garnica-Romo MG, Cortes-Martinez R (2010) Effect of temperature on the removal of arsenate from aqueous solutions by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Appl Sci Environ Sanit 5:171–184
Van Halem D, Heijman SGJ, Amy GL, van Dijk JC (2009) Subsurface arsenic removal for small-scale application in developing countries. Desalination 248:241–248
Wainipee W, Cuadros J, Sephton MA, Unsworth C, Gill MG, Strekopytov S, Weiss DJ (2013) The effects of oil on As(V) adsorption on illite, kaolinite, montmorillonite and chlorite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 121:487–502
Xu Y, Axe L (2005) Synthesis and characterization of iron-oxide coated silica and its effect on metal adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 282:11–19
Xu W, Wang J, Wang L, Sheng G, Liu J, Yu H, Huang XJ (2013) Enhanced arsenic removal from water by hierarchically porous CeO2–ZrO2 nanospheres: role of surface- and structure-dependent properties. J Hazard Mater 260:498–507
Zhang T, Sun DD (2013) Removal of arsenic from water using multifunctional micro-/nano-structured MnO2 spheres and microfiltration. Chem Eng J 225:271–279
Zhang G, Ren Z, Zhang X, Chen J (2013) Nanostructured iron(III)–copper(II) binary oxide: a novel adsorbent for enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Water Res 47:4022–4031
Zhu H, Jia Y, Wu X, Wang H (2009) Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 172:1591–1596
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Kevin Olsen, Department of Chemistry, Montclair State University, Montclair, NJ, for recording the FT-IR spectra of adsorbents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attinti, R., Sarkar, D., Barrett, K.R. et al. Adsorption of arsenic(V) from aqueous solutions by goethite/silica nanocomposite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3905–3914 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0902-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0902-2