Abstract
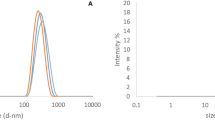
Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Middle-East Asia Minor 1 is a major pest of agricultural production systems. It is controlled by synthetic insecticides. Essential oils are promising eco-friendly alternatives. This study developed and characterized nanoparticles loaded with essential oils of Zanthoxylum riedelianum Engl. (Rutaceae) leaves and evaluated their potential for B. tabaci management. The essential oil exhibited an average yield of 0.02% (w w−1) and showed as major components γ-elemene (24.81%), phytol (18.16%), bicyclogermacrene (16.18%), cis-nerolidol (8.26%), and D-germacrene (6.52%). Characterization of the nanoparticles showed a pH between 4.5 and 6.7, a zeta potential of approximately − 25 mV, particle-size distribution ranging from 450 to 550 nm, and encapsulation efficiency close to 98%. The nanoencapsulation was an efficient process that provided photostability against photodegradation. Bioassays with crude and nanoencapsulated essential oils significantly reduced the number of nymphs and eggs of B. tabaci, with the best results observed at concentrations of 5 and 2% (v v−1). Our results demonstrated that essential oils from Z. riedelianum can be nanoformulated resulting in a stable product while maintaining their biological activity against B. tabaci Middle-East Asia Minor 1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu FOMS, Oliveira EF, Paula HCB, De Paula RCM (2012) Chitosan/cashew gum nanogels for essential oil encapsulation. Carbohydr Polym 89:1277–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.048
Adams RP (2007) Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/quadrupole mass spectroscopy, 4th edn. Allured Publishing Corporation, Carol Stream, p 804
ADAPAR–Agência de Defesa e Agropecuária do Paraná. Agrotóxicos e inseticidas. Disponívelem:<http://www.adapar.pr.gov.br/arquivos/File/defis/DFI/Bulas/Inseticidas/tiger_100_ec.pdf>. Acesso em: 03/08/2020, as 17:30hs
Ahmad KA, Dwivedi HS, Dwivedi P (2015) Pesticide Scenario of India with particular reference to Madhya Pradesh: a review. N Y Sci J 8:69–76
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M (2008) Biological effects of essential oils – a review. Food Chem Toxicol 46:446–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.106
Banerjee S, Chattopadhyay P, Ghosh A, Goyary D, Karmakar S, Veer V (2013) Influence of process variables on essential oil microcapsule properties bycarbohydrate polymer–protein blends. Carbohydr Polym 93:691–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.028
Bilbao-Sáinz AC, Chiou B, Glenn GM, Gregorsky KS, Williams TG, Wood DF, Klamczynski AP, Orts WJ (2013) Solid lipid particles in lipid films to control the diffusive release of 2-heptanone. Pest Manag Sci 69:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3462
Boehme AK, Noletto JA, Haber WA, Setzer WN (2008) Bioactivity and chemical composition of the leaf essential oils of Zanthoxylum rhoifolium and Zanthoxylum setulosum from Monteverde. Nat Prod Res 22:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786410601130224
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods – a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94:223–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022
Calmasur O, Aslan I, Sahin F (2006) Insecticidal and acaricidal effect of three Lamiaceae plant essential oils aginst Tetranychus urticae Koch and Bemisia tabaci Genn. Ind Crop Prod 23:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2005.05.003
Campolo O, Cherif A, Ricupero M, Siscaro G, Grissa-Lebdi K, Russo A (2017) Citrus peel essential oil nanoformulations to control the tomato borer, Tuta absoluta: chemical properties and biological activity. Sci Rep 7(1):13036. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13413-0
Campos EVR, Proença PLF, Oliveira JL, Pereira AES, Ribeiro LNM, Fernandes FO, Goncalves KC, Polanczyk RA, Pasquoto-Stigliani T, Lima R, Melville CC, Della Vechia JF, de Andrade DJ (2018) Fraceto LF (2018) Carvacrol and linalool co-loaded in β-cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan nanoparticles as sustainable biopesticide aiming pest control. Sci Rep 8:7623. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26043-x
Cazo NA, Pereira-Filho ER, Silva MFGF, Fernandes JB, Vieira PC, Puhl AC, Polikarpov I, Forim MR (2012) Poly-ɛ-caprolactone nanoparticles loaded with hydrocortisone: preparation using factorial design and evaluation. Orbital Elec J Chem 4:54–76
Chamorro ER, Zambón SN, Morales WG, Sequeira AF, Velasco GA (2012) Study of the chemical composition of essential oils by gas chromatography. In: Salih B, editor. Gas chromatography in plant science, wine technology, toxicology and some specific applications. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech 307–324. https://doi.org/10.5772/33201
Christofoli M, Costa ECC, Bicalho KU, Domingues VC, Peixoto MF, Alves CCF, Araújo WL, Cazal CM (2015) Insecticidal effect of nanoencapsulated essential oils from Zanthoxylum rhoifolium (Rutaceae) in Bemisia tabaci populations. Ind Crop Prod 70:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.025
Choi M, Soottitantawat A, Nuchuchua O, Min S, Ruktanonchai U (2009) Physical and light oxidative properties of eugenol encapsulated by molecular inclusion and emulsion–diffusion method. Food Res Intern 42:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2008.09.011
Costa ECC, Christofoli M, Costa GCS, Peixoto MF, Fernandes JB, Forim MR, Pereira KC, Silva FG, Cazal CM (2017) Essential oil repellent action of plants of the genus Zanthoxylum against Bemisia tabaci biotype B (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Sci Hortic 226:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.08.041
Cruz-Estrada A, Gamboa-Angulo M, Borges-Argáez R, Ruiz-Sánchez E (2013) Insecticidal effects of plant extracts on immature whitefly Bemisia tabaci Genn. (Hemiptera: Aleyroideae). Electron J Biotechnol 16:1–6. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol16-issue1-fulltext-6
Diao W, Hu Q, Feng S, Li W, Xu J (2013) Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Green Huajiao (Zanthoxylum schinifolium) against selected food borne pathogens. J Agric Food Chem 61:6044–6049. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4007856
Dou TX, Shid JF, Li Y, Bi FC, Gao HJ, Hu CH, Li CY, Yang QS, Deng GM, Sheng O, He WD, Yi GJ, Dong T (2020) Influence of harvest season on volatile aroma constituents of two banana cultivars by electronic nose and HS-SPME coupled with GC-MS. Sci Hortic 265:109214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109214
El-Zaeddi H, Calín-Sánchez Á, Noguera-Artiaga L, Martínez-Tomé J, Carbonell-Barrachina ÁA (2020) Optimization of harvest date according to the volatile composition of Mediterranean aromatic herbs at different vegetative stages. Sci Hortic 267:109336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109336
Fanela TLM, Baldin ELL, Pannuti LER, Cruz PL, Crotti AEM, Takeara R, Kato MJ (2016) Lethal and inhibitory activities of plant-derived essential oils against Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Biotype B in tomato. Neotrop Entomol 45:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-015-0356-8
Ferreira DF (2019) Sisvar: a computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Braz J Biom 37:529–535. https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450
Fessi H, Puisieux F, Devissaguet JP, Ammoury N, Benita S (1989) Nanocapsule formation by interfacial deposition following solvent displacement. Int J Pharm 55(1):R1–R4. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(89)90281-0
Forim MR, Costa ES, da Silva MFGF, Fernandes JB, Mondego JM, Boiça AL Jr (2013) Development of a new method to prepare nano-/microparticles loaded with extracts of Azadirachta indica, their characterization and use in controlling Plutella xylostella. J Agric Food Chem 61:9131–9139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403187y
Grillo R, Santos NZP, Maruyamac CR, Rosa AH, Lima R, Fraceto LF (2012) Poly(ɛ-caprolactone) nanocapsules as carrier systems for herbicides: Physico-chemical characterization and genotoxicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 15:231–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.019
Guy I, Charles B, Guinaudeau H, Ferreira ME, Arias AR, Fournet A (2001) Essential oils from Zanthoxylum chiloperone and Z. riedelianum growing in Paraguay. Pharm Biol 39:152–154. https://doi.org/10.1076/phbi.39.2.152.6255
Hayles J, Johnson L, Worthley C, Losic D (2017) Nanopesticides: a review of current research and perspectives. (Ed. Grumezescu A.M.) New Pesticides Soil Sens 193–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804299-1.00006-0
Hopkinson J, Pumpa S, Van Brunschot S, Fang C, Frese M, Tay WT, Walsh T (2020) Insecticide resistance status of Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Australian cotton production valleys. Austral Entomol 59(1):202–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/aen.12436
Hosseini SF, Zandi M, Rezaei M, Farahmandghavi F (2013) Two-step method for encapsulation of oregano essential oil in chitosan nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and in vitro release study. Carbohyd Polym 95:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.02.031
Ibrahim SS (2019) Essential oil nanoformulations as a novel method for insect pest control in horticulture. Horticultural Crops, IntechOpenhttps://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.80747
Isman MB (2006) Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and increasing regulated world. Annu Rev Entomol 51:45–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151146
Jahani M, Pira M, Aminifard MH (2020) Antifungal effects of essential oils against Aspergillus niger in vitro and in vivo on pomegranate (Punica granatum) fruits. Sci Hortic 264:109188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109188
Khot LR, Sankaran S, Maja JM, Ehsani R, Schuster EW (2012) Applications of nanomaterials in agricultural production and crop protection: a review. Crop Prot 35:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.01.007
Korsmeyer RW, Gumy R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA (1983) Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(83)90064-9
Kumar P, Mishra S, Malik A, Satya S (2014) Preparation and characterization of PEG - Mentha oil nanoparticles for housefly control. Colloids Surf b: Biointerfaces 116:707–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.11.012
Li M, Huang Q, Wu Y (2011) A novel chitosan-poly(lactide) copolymer and its submicron particles as imidacloprid carriers. Pest Manag Sci 67831-836https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2120
Littell RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW, Wolfinger RD (2002) SAS system for mixed models. Cary: Statistical Analysis System Institute, 633.
Liu ZL, Chu SS, Jiang GH (2009) Feeding deterrents from Zanthoxylum schinifolium against two stored-product insects. J Agric Food Chem 57:10130–10133. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9012983
Lopez V, Vos J, Polar P, Krauss U (2008) Discovery learning about sustainable management of whitefly pests and whitefly-borne viruses. Int Cent Trop Agricult (CIAT) 1:12–37
Luo C, Jones CM, Zhang F, Denholm I, Gorman K (2010) Insecticide resistance in Bemisia tabaci biotype Q (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) from China. Crop Prot 29:429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2009.10.001
Magenheim B, Benita S (1991) Nanoparticle characterization: a comprehensive physichemical approach. Pharm Sci 1:221–241
Maji T, Baruah I, Dube S, Hussain MR (2007) Microencapsulation of Zanthoxylum limonella oil (ZLO) in glutaraldehyde crosslinked gelatin for mosquito repellent application. Biores Technol 98:840–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.03.005
Makadia HK, Siegel SJ (2011) Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 3:1377–1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3031377
Marubayashi JM, Yuki VA, Wutke EB (2010) Transmissão do Cowpea mild mottle virus pela mosca branca Bemisia tabaci biótipo B para plantas de feijão e soja. Summa Phytopathol 36:158–160. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-54052010000200009
Mishra PR, Al Shaal L, Müller RH, Keck CM (2009) Production and characterization of Hesperetin nanosuspensions for dermal delivery. Int J Pharm 17:371(1–2):182–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.12.030
Moura NF, Strapazzon J, Loro F, Morel AF, Flach A (2006) Composition of the leaf oils of Rutaceae: Zanthoxylum hyemale A. St. Hill. Z. rhoifolium Lam. and Z. rugosum A. St Hill. Tul J Essent Oil Res 18:4–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2006.9699185
Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NTK (2018) Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10:12871. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr02278j
Nascimento PFC, Nascimento AC, Rodrigues CS, Antoniolli AR, Santos PO, Barbosa Júnior AM, Trindade RC (2007) Atividade antimicrobiana dos óleos essenciais: uma abordagem multifatorial dos métodos. Ver Bras Farmacogn 17:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2007000100020
Naveen NC, Chaubey R, Kumar D, Rebijith KB, Rajagopal R, Subrahmanyam B, Subramanian S (2017) Insecticide resistance status in the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci genetic groups Asia-I, Asia-II-1 and Asia-II-7 on the Indian subcontinent. Sci Rep 7:40634. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40634
Nerio LS, Olivero-Verbel J, Stashenko E (2010) Repellent activity of essential oils: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.048
Nguyen HM, Hwang I, Parkc J, Park H (2012) Photoprotection for deltamethrin using chitosan-coated beeswax solid lipid nanoparticles. Pest Manag Sci 68:1062–1068. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3268
Oliveira EF, Paula HCB, Paula RCM (2014) Alginate/cashew gun nanoparticles for essential oil encapsulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 113:146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.038
Pascual-Villalobos MJ, López MD, Castañé C, Soler A, Riudavets J (2015) Encapsulated essential oils as an alternative to insecticides in funnel traps. J Econ Entomol 108(4):2117–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tov127
Pares RB, Alves DS, Alves LFA, Godinho CC, Gobbo Neto L, Ferreira TT, Nascimento MM, Ascari J, Oliveira DF (2021) Acaricidal activity of Annonaceae plants for Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae) and metabolomic profile by HPLC-MS/MS. Neotrop Entomol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00885-z
Paula HCB, Sombra FM, Cavalcante RF, Abreu FOMS, De Paula RCM (2011) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/cashew gum beads oaded with Lippia sidoides essential oil. Mater Sci Eng C 31:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.08.013
Pereira KC, Quintela ED, Silva DJ, Nascimento VA, Rocha DVM, Silva JFA, Forim MR, Silva FG, Cazal CM (2018) Characterization of nanospheres containing Zanthoxylum riedelianum fruit essential oil and their insecticidal and deterrent activities against Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Molecules 23:2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082052
Pereira SS, Lopes LS, Marques RB, Figueiredo KA, Costa DA, Chaves MH, Almeida FRC (2010) Antinociceptive effect of Zanthoxylum rhoifolium Lam. (Rutaceae) in models of acute pain in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol 129:227–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.03.009
Peres MC, Costa GCS, Reis LEL, Silva LD, Peixoto MF, Alves CCF, Forim MR, Quintela ED, Araújo WL, Cazal CM (2020) In natura and nanoencapsulated essential oils from Xylopia aromatic reduce oviposition of Bemisia tabaci in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Pest Sci 93:807–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-019-01186-6
Prieto JA, Patiño O, Delgado WA, Moreno JP, Cuca LE (2011) Chemical composition, insecticidal, and antifungal activities of fruit essential oils of three Colombian Zanthoxylum species. Chil J Agricult Res 71:73–82. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392011000100009
Puškárová A, Bučková M, Kraková L, Pangallo D, Kozics K (2017) The antibacterial and antifungal activity of six essential oils and their cyto/genotoxicity to human HEL 12469 cells. Sci Rep 7:8211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08673-9
Quintela ED, Abreu AG, Lima JFS, Mascarin GM, Santos JB, Brown JK (2016) Reproduction of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) B biotype in maize fields (Zea mays L.) in Brazil. Pest Management Science 72: 2181–2187. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4259
R Development Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Viena: R Foundation for Statistical Computing 2018 Disponível em: www.R-project.org. Acesso em: 28/07/2018, as 20:30hs.
Rguez S, Slimene IB, Abid G, Hammemi M, Kefi A, Elkahoui S, Ksouri R, Sellamia IH, Djébali N (2020) Tetraclinis articulata essential oil reduces Botrytis cinerea infections on tomato. Sci Hortic 266:109291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109291
Rodrigues CS, Nakasu EYT, Ortiz GV, Pereira JL, Lucena-Leandro VS, Rêgo-Machado CM, Souza TA, Martins TP, Nagata AKI (2021) Evidence of spread of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) mediated by internal transportation of ornamental plants in Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 50(5):850–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00881-3
Sahayaraj K, Madasamy M, Anbu Radhika S (2016) Insecticidal actvity of bio-silver and gold nanoparticles against Pericallia ricini Fab. (Lepidoptera: Archidae). J Biopest 9(1):63–72.
Sahayaraj K (2017) Nano and bio-nanoparticles for insect control. Res J Nanosci Nanotechnol CC:CC-CC. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjnn.2017
Schaffazick SR, Guterres SS, Freitas LL, Pohlmann AR (2003) Caracterização e estabilidade físico-química de sistemas poliméricos nanoparticulados para administração de fármacos. Quim Nova 26:726–737. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422003000500017
Sanches MM, Gelelete TB, Santos ALR, Sosa-Gómez DR, Sihler W, Souza ML (2021) Optimization of large-scale production of Chrysodeixis includens nucleopolyhedrovirus for its use as a biopesticide. Neotrop Entomol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00887-x
Sertkaya E, Kaya K, Sylu S (2010) Acaricidal activities of the essential oils from several medicinal plants against the carmine spider mite (Tetranychus cinnabarinus Boisd.) (Acarina: Tetranychidae). Ind Crop Prod 31:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2009.09.009
Simões CMO, Schenkel EP, Gosmann G, Mello JCP, Mentz LA, Petrovick PR (2004) Farmacognosia: da planta ao medicamento, 5ª ed., Ed. da UFSC: Porto Alegre
Souza PS, Lobo FA, Rosa AH, Fraceto LF (2012) Desenvolvimento de nanocapsulas de poli-ɛ-(caprolactona) contendo o herbicida atrazina. Quím Nova 35:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422012000100024
Stokes JB, Redfern RE (2008) Effect of sunlight on Azadirachtin: antifeeding potency. J Environ Sci Health A 17:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934528209375019
Tavallali V, Rowshan V, Gholami H, Hojati S (2020) Iron-urea nano-complex improves bioactive compounds in essential oils of Ocimum basilicum L. Sci Hortic 265:109222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109222
Torres LC, Souza B, Lourenção AL, Costa MB, Amaral BB, Carbonell SAM, Chiorato AF, Tanque RL (2012) Resistência de genótipos de feijoeiro a Bemisia tabaci biótipo B. Bragantia 71:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0006-87052012005000031
Van Den Dool H, Kratz PD (1963) A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas-liquid partition chromatography. J Chromatogr A 11:463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)80947-X
Wu Y, Luo Y, Wang Q (2012) Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of essential oils encapsulated in zein nanoparticles prepared by liquid-liquid dispersion method. LWT - Food Sci Technol 48:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.03.027
Xie W, Liu Y, Wang S, Wu Q, Pan H, Yang X, Guo L, Zhang Y (2014) Sensitivity of Bemisia Tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) to several new insecticides in China: effects of insecticide type and whitefly species, strain, and stage. J Insect Sci 14(261):10–1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieu123
Yang FL, Li XG, Zhu F, Lei CL (2009) Structural characterization of nanoparticles loaded with garlic essential oil and their insecticidal activity against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Agric Food Chem 57:10156–10162. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9023118
Yang NW, Li AL, Wan FH, Liu WX, Johnson D (2010) Effects of plant essential oils on immature and adult sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci biotype B. Crop Prot 29:1200–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2010.05.006
Funding
This work was financially supported by funding from the Foundation for Research Assistance of the Goiás State (FAPEG), Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology Goiano (IF Goiano) and Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology Southeast of Minas Gerais (IF Sudeste MG). We also thank the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq, – process number 403302/2013–7). Scholarships granted by CNPq and/or FAPEG to M.C and E.C.C.C are also gratefully acknowledged. Research fellowships awarded by CNPq to WLA are also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Edited by Leandro P Ribeiro
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christofoli, M., Costa, E.C.C., Peixoto, M.F. et al. Nanoparticles Loaded with Essential Oil from Zanthoxylum riedelianum Engl. Leaves: Characterization and Effects on Bemisia tabaci Middle-East Asia Minor 1. Neotrop Entomol 51, 761–776 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-022-00980-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-022-00980-9