Abstract
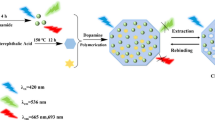
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and quantum dots (QDs) have been widely employed to fabricate highly sensitive and selective sensor. Here, we developed a fluorescence nanosensor based on thioglycolic acid-modified CdTe QDs that is coated with molecularly imprinted polymers for the specific detection of theophylline (THP). Initially, water-soluble thioglycolic acid-modified CdTe QDs were synthesized by refluxing method. Then, MIPs-coated QDs (MIPs-QDs) composite was produced by sol–gel process using THP as a template. Therefore, the selectivity of the molecular imprinting technique and advantages of QDs were combined. The prepared QDs and the MIPs-QDs were characterized using X-ray diffraction technique, transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectrometry. Finally, this sensing system was successfully used to detect THP in human plasma samples with recoveries of 90% to 108%. A very good linear relationship was observed between the decreasing in the fluorescence intensity of MIPs-QDs and increasing the THP concentration within concentration range of 0.14–3.05 µmol L−1, with a correlation coefficient of 0.9992 and detection limit of 0.07 µmol L−1.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.R. Rajabi, M. Shamsipur, A.A. Khosravi, O. Khani, M.H. Yousefi, Selective spectrofluorimetric determination of sulfide ion using manganese doped ZnS quantum dots as luminescent probe. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 107, 256–262 (2013)
M. Shamsipur, H.R. Rajabi, Pure zinc sulfide quantum dot as highly selective luminescent probe for determination of hazardous cyanide ion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 36, 139–145 (2014)
M. Rutkowska, J. Płotka-Wasylka, C. Morrison, P.P. Wieczorek, J. Namieśnik, M. Marć, Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in an analytical chiral separation and analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 102, 91–102 (2018)
L. Chen, J. Li, Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 2922–2942 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00084a
H.R. Rajabi, A. Zarezadeh, Development of a new chemically modified carbon paste electrode based on nano-sized molecular imprinted polymer for selective and sensitive determination of naproxen. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 10911–10920 (2016)
L.M. Madikizela, N.T. Tavengwa, H. Tutu, L. Chimuka, Green aspects in molecular imprinting technology: from design to environmental applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 17, 14–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2018.01.001
A.M. Piloto, D.S.M. Ribeiro, S.S.M. Rodrigues, C. Santos, J.L.M. Santos, M.G.F. Sales, Plastic antibodies tailored on quantum dots for an optical detection of myoglobin down to the femtomolar range. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23271-z
J. Mayahi, H.R. Rajabi, Comparison study on separation of morin: ultrasound assisted molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles-solid phase extraction versus solidification of floating organic-drop assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. New J. Chem. 41, 14236–14245 (2017)
E.E. Ferapontova, E.M. Olsen, K.V. Gothelf, Communication an RNA aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of theophylline in serum an RNA aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of theophylline in serum. Communication (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja711326b
S.R. El-Shabouri, S.A. Hussein, S.E. Emara, Colorimetric determination of theophylline and aminophylline with diazotized p-nitroaniline. Talanta 36, 1288–1290 (1989)
G.F. Johnson, W.A. Dechtiaruk, H.M. Solomon, Gas-chromatographic determination of theophylline in human serum and saliva. Clin. Chem. 21, 144–147 (1975)
E.P. Gil, H.T. Tang, H.B. Halsall, W.R. Heineman, A.S. Misiego, Competitive heterogeneous enzyme immunoassay for theophylline by flow-injection analysis with electrochemical detection of p-aminophenol. Clin. Chem. 36, 662–665 (1990)
M.C. Gutiérrez, A. Gómez-Hens, D. Pérez-Bendito, Stopped-flow fluorimetric determination of theophylline in pharmaceutical preparations. Analyst. 113, 559–562 (1988)
M. Sánchez-Cabezudo, J.M. Fernández-Romero, M.D. Luquede Castro, Fluorimetric-flow injection determination of theophylline based on its inhibitory effect on immobilized alkaline phosphatase. Anal. Chim. Acta 308, 159–163 (1995)
H. Jiang, K. Ling, X. Tao, Q. Zhang, Theophylline detection in serum using a self-assembling RNA aptamer-based gold nanoparticle sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 70, 299–303 (2015)
J. Wang, W. Cheng, F. Meng, M. Yang, Y. Pan, P. Miao, Hand-in-hand RNA nanowire-based aptasensor for the detection of theophylline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 101, 153–158 (2018)
A.A. Ensafi, N. Kazemifard, B. Rezaei, Development of a nano plastic antibody for determination of propranolol using CdTe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 252, 846–853 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.078
A.A. Ensafi, N. Kazemifard, B. Rezaei, Development of a selective prilocaine optical sensor based on molecularly imprinted shell on CdTe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 242, 835–841 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.175
M. Bagher, M. Shamsipur, S. Dehdashtian, H. Reza, Development of a selective and sensitive voltammetric sensor for propylparaben based on a nanosized molecularly imprinted polymer—carbon paste electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 36, 102–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.11.021
J. Yang, M.-H. Wu, Z.-Z. Lin, Z.-Y. Huang, Detection of trace leucomalachite green with a nanoprobe of CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted silica: via synchronous fluorescence quenching. New J. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj04517d
W. Zhang, X.W. He, Y. Chen, W.Y. Li, Y.K. Zhang, Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 2553–2558 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.004
D.P. Malliaros, S.S. Wong, A.H.B. Wu, J. Campbell, H. Leonard, S. Houser, M. Berg, T. Gornet, C. Brown, Y.J. Feng, Quantitative determination of theophylline by an automated chemiluminescent immunoassay in serum and plasma: comparison to other methods of analysis. Ther. Drug Monit. 19, 224–229 (1997)
M. Li, Y. Sato, S. Nishizawa, T. Seino, K. Nakamura, N. Teramae, 2-aminopurine-modified abasic-site-containing duplex DNA for highly selective detection of theophylline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 2448–2449 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8095625
K. Ling, H. Jiang, Y. Li, X. Tao, C. Qiu, F.-R. Li, A self-assembling RNA aptamer-based graphene oxide sensor for the turn-on detection of theophylline in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 86, 8–13 (2016)
K.S. Park, S.S. Oh, H.T. Soh, H.G. Park, Target-controlled formation of silver nanoclusters in abasic site-incorporated duplex DNA for label-free fluorescence detection of theophylline. Nanoscale 6, 9977–9982 (2014)
Y. Sato, Y. Zhang, S. Nishizawa, T. Seino, K. Nakamura, M. Li, N. Teramae, Competitive assay for theophylline based on an abasic site-containing DNA duplex aptamer and a fluorescent ligand. Chem. Eur. J. 18, 12719–12724 (2012)
C. Frauendorf, A. Jäschke, Detection of small organic analytes by fluorescing molecular switches. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 9, 2521–2524 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(01)00027-X
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakery, M., Ensafi, A.A. & Rezaei, B. Detection of theophylline using molecularly imprinted polymers based on thioglycolic acid-modified CdTe quantum dots. J IRAN CHEM SOC 17, 601–608 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01798-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01798-w