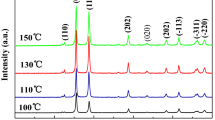
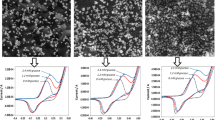
Abstract
Fabrication and attractive performance of CuO nanoparticles coated onto TiO2 substrate (CuO@TiO2) as electrocatalysts for glucose and methanol electrooxidation are detailed in this article. These bi-functional electrocatalysts were prepared by impregnating (5–25 wt%) CuO nanoparticles onto nanosized TiO2 substrate and were characterized for morphology and composition. Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy provided a detailed account of their electrochemical capacity. All samples in CuO@TiO2 series were tested for probable electrocatalysis; however, 5CuO@TiO2 possessed significantly improved electrocatalytic activity for methanol and glucose electrooxidation. This can be attributed to the better conductivity of the electrocatalyst showing that electrocatalytic activity is limited by the amount of CuO loading on CuO@TiO2 electrocatalyst. The involvement of the Cu (II) to Cu (III) reversible redox couple was evident in the electrocatalytic oxidation. The sensitivity of 7.15 μA mM−1 cm−2 and a detection limit of 235.0 μM for glucose at a signal to noise ratio of 3 were obtained using 5CuO@ TiO2-modified glassy carbon electrode.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Popovski, Electrocatalysts in the last 30 years–from precious metals to cheaper but sophisticated complex systems. Bull. Chem. Technol. Maced. 23, 101–112 (2004)
C. Qian, X. Guo, W. Zhang, H. Yang, Y. Qian, F. Xu, S. Qian, S. Lin, T. Fan, Co3O4 nanoparticles on porous bio-carbon substrate as catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 277, 45–51 (2019)
X. Guo, C. Qian, R. Shi, W. Zhang, F. Xu, S. Qian, J. Zhang, H. Yang, A. Yuan, T. Fan, Biomorphic Co-N-C/CoOx composite derived from natural chloroplasts as efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Small 15, 1804855 (2019)
S. Thangavel, N. Raghavan, G. Venugopal, Magnetically Separable Iron Oxide‐Based Nanocomposite Photocatalytic Materials for Environmental Remediation, Photocatalytic Functional Materials for Environmental Remediation (Wiley, 2019), pp. 243–265
R. Raliya, T.S. Chadha, K. Haddad, P. Biswas, Perspective on nanoparticle technology for biomedical use. Curr. Pharm. Des. 22, 2481–2490 (2016)
S.Y. Tee, K.Y. Win, W.S. Teo, L.D. Koh, S. Liu, C.P. Teng, M.Y. Han, Recent progress in energy-driven water splitting. Adv. Sci. 4, 1600337 (2017)
Y. Chen, Y. Wu, C. Liu, L. Guo, J. Nie, Y. Chen, T. Qiu, Low-temperature conversion of ammonia to nitrogen in water with ozone over composite metal oxide catalyst. J. Environ. Sci. 66, 265–273 (2018)
L. Liu, P. Concepción, A. Corma, Modulating the catalytic behavior of non-noble metal nanoparticles by inter-particle interaction for chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes into corresponding azoxy or azo compounds. J. Catal. 369, 312–323 (2019)
Z.D. Mahmoudabadi, E. Eslami, One-step synthesis of CuO/TiO2 nanocomposite by atmospheric microplasma electrochemistry–Its application as photoanode in dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Alloy. Compd. 793, 336–342 (2019)
Q. Yang, M. Long, L. Tan, Y. Zhang, J. Ouyang, P. Liu, A. Tang, Helical TiO2 nanotube arrays modified by Cu–Cu2O with ultrahigh sensitivity for the nonenzymatic electro-oxidation of glucose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 12719–12730 (2015)
A. Mujtaba, N.K. Janjua, Fabrication and electrocatalytic application of CuO@ Al2O3 hybrids. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, H328–H337 (2015)
A. Mujtaba, N.K. Janjua, Electrochemical sensing platform based on CuO@ CeO2 hybrid oxides. J. Electroanal. Chem. 763, 125–133 (2016)
J.-H. Lee, J.-H. Kim, S.S. Kim, CuO–TiO2 p–n core–shell nanowires: sensing mechanism and p/n sensing-type transition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 489–497 (2018)
N.L. Reddy, S. Emin, V.D.S. Kumari, Muthukonda Venkatakrishnan, CuO quantum dots decorated TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst for stable hydrogen generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57, 568–577 (2018)
A.M. Kumar, A. Khan, R. Suleiman, M. Qamar, S. Saravanan, H. Dafalla, Bifunctional CuO/TiO2 nanocomposite as nanofiller for improved corrosion resistance and antibacterial protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 114, 9–18 (2018)
B. Khodadadi, A.Y. Faal, A. Shahvarughi, Tilia platyphyllos extract assisted green synthesis of CuO/TiO2 nanocomposite: application as a reusable catalyst for the reduction of organic dyes in water. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 13, 51–65 (2019)
S. Zhang, F. Chen, Y. Chi, Z. Dan, F. Qin, Non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on Ti–Cu–O nanotubes prepared from TiCu amorphous alloy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 3825–3831 (2019)
S. Luo, F. Su, C. Liu, J. Li, R. Liu, Y. Xiao, Y. Li, X. Liu, Q. Cai, A new method for fabricating a CuO/TiO2 nanotube arrays electrode and its application as a sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Talanta 86, 157–163 (2011)
J. Chen, L. Xu, R. Xing, J. Song, H. Song, D. Liu, J. Zhou, Electrospun three-dimensional porous CuO/TiO2 hierarchical nanocomposites electrode for nonenzymatic glucose biosensing. Electrochem. Commun. 20, 75–78 (2012)
M. Niu, W. Xu, S. Zhu, Y. Liang, Z. Cui, X. Yang, A. Inoue, Synthesis of nanoporous CuO/TiO2/Pd-NiO composite catalysts by chemical dealloying and their performance for methanol and ethanol electro-oxidation. J. Power Sources 362, 10–19 (2017)
A. Dicks, D.A.J. Rand, Fuel Cell Systems Explained (Wiley, London, 2018)
R.-M. Yuan, H.-J. Li, X.-M. Yin, H.-Q. Wang, J.-H. Lu, L.-L. Zhang, Coral-like Cu-Co-mixed oxide for stable electro-properties of glucose determination. Electrochim. Acta 273, 502–510 (2018)
C. Chen, X.-L. Zhao, Z.-H. Li, Z.-G. Zhu, S.-H. Qian, A.J. Flewitt, Current and emerging technology for continuous glucose monitoring. Sensors 17, 182 (2017)
C. Canales, L. Gidi, G. Ramírez, Electrochemical activity of modified glassy carbon electrodes with covalent bonds towards molecular oxygen reduction. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 1684–1695 (2015)
A. Shalan, M. Rashad, Y. Yu, M. Lira-Cantú, M. Abdel-Mottaleb, A facile low temperature synthesis of TiO2 nanorods for high efficiency dye sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. A 110, 111–122 (2013)
S.M. Solyman, S.A. Hassan, S.A. Sadek, H.S. Abdel-Samad, Redox-initiated bulk polymerization of methyl methacrylate using a CuO/TiO2 catalyst system. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 59, 475–487 (2010)
P.D. File, Joint committee on powder diffraction standards (ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1967), pp. 9–185
D. Reyes-Coronado, G. Rodriguez-Gattorno, M. Espinosa-Pesqueira, C. Cab, R. De Coss, G. Oskam, Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology 19, 145605 (2008)
J. Huang, S. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Wang, S. Wang, S. Wu, S. Zhang, W. Huang, Synthesis and characterization of CuO/TiO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Commun. 7, 1029–1034 (2006)
Z. Liu, C. Zhou, Improved photocatalytic activity of nano CuO-incorporated TiO2 granules prepared by spray drying. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25, 334–341 (2015)
M. Liu, J. Chang, C. Yan, J. Bell, Comparative study of photocatalytic performance of titanium oxide spheres assembled by nanorods, nanoplates and nanosheets. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 3, 72–80 (2012)
S. Agarwala, M. Kevin, A. Wong, C. Peh, V. Thavasi, G. Ho, Mesophase ordering of TiO2 film with high surface area and strong light harvesting for dye-sensitized solar cell. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2, 1844–1850 (2010)
W.Z. Teo, A. Ambrosi, M. Pumera, Direct electrochemistry of copper oxide nanoparticles in alkaline media. Electrochem. Commun. 28, 51–53 (2013)
A. Ambrosi, M. Pumera, Redox-active nickel in carbon nanotubes and its direct determination. Chem. Eur. J. 18, 3338–3344 (2012)
A.J. Bard, L.R. Faulkner, Fundamentals and Applications, Electrochemical Methods, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2001)
B. Derkus, E. Emregul, C. Yucesan, K.C. Emregul, Myelin basic protein immunosensor for multiple sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 46, 53–60 (2013)
S. Thiagarajan, M. Rajkumar, S.-M. Chen, Nano TiO2-PEDOT film for the simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid and diclofenac. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 2109–2122 (2012)
S. Eloul, C. Batchelor-McAuley, R.G. Compton, Thin film-modified electrodes: a model for the charge transfer resistance in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Solid State Electrochem. 18, 3239–3243 (2014)
S.H. Aboutalebi, A.T. Chidembo, M. Salari, K. Konstantinov, D. Wexler, H.K. Liu, S.X. Dou, Comparison of GO, GO/MWCNTs composite and MWCNTs as potential electrode materials for supercapacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 1855–1865 (2011)
B.A. Boukamp, A linear Kronig-Kramers transform test for immittance data validation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 1885–1894 (1995)
A. Nafady, Electrochemistry with the extremely weak coordinating anions: using of carboranes [H-CB11X6Y5] − (X = H, Cl, Br; Y = H or Me) as supporting electrolyte anions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 755, 1–6 (2015)
E. Biçer, P. Çetinkaya, Electrochemical behaviour of the antibiotic drug novobiocin sodium on a mercury electrode. Croat. Chem. Acta 82, 573–582 (2009)
V. Oncescu, D. Erickson, High volumetric power density, non-enzymatic, glucose fuel cells. Sci. Rep. 3, 1226 (2013)
Z.D. Gao, J. Guo, N.K. Shrestha, R. Hahn, Y.Y. Song, P. Schmuki, Nickel hydroxide nanoparticle activated semi-metallic TiO2 nanotube arrays for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Chem. A Eur. J. 19, 15530–15534 (2013)
R. Ding, J. Liu, J. Jiang, J. Zhu, X. Huang, Mixed Ni–Cu-oxide nanowire array on conductive substrate and its application as enzyme-free glucose sensor. Anal. Methods 4, 4003–4008 (2012)
A. Raziq, M. Tariq, R. Hussain, M.H. Mahmood, I. Ullah, J. Khan, M. Mohammad, Highly sensitive, non-enzymatic and precious metal free electrochemical glucose sensor based on Ni–Cu/TiO2 modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 83, 733–744 (2018)
J. Stanley, R.J. Sree, T. Ramachandran, T. Babu, B.G. Nair, Vertically aligned TiO2 nanotube arrays decorated with CuO mesoclusters for the nonenzymatic sensing of glucose. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17, 2732–2739 (2017)
X. Wang, C.-Y. Ge, K. Chen, Y.X. Zhang, An ultrasensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on controlled petal-like CuO nanostructure. Electrochim. Acta 259, 225–232 (2018)
M.P. Sánchez, M. Barrera, S. González, R. Souto, R. Salvarezza, A. Arvia, Electrochemical behaviour of copper in aqueous moderate alkaline media, containing sodium carbonate and bicarbonate, and sodium perchlorate. Electrochim. Acta 35, 1337–1343 (1990)
M.M. El-Deeb, W.M. El Rouby, A. Abdelwahab, A.A. Farghali, Effect of pore geometry on the electrocatalytic performance of nickel cobaltite/carbon xerogel nanocomposite for methanol oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 259, 77–85 (2018)
A.A. Ensafi, B. Rezaei, Z. Mirahmadi-Zare, H. Karimi-Maleh, Highly selective and sensitive voltammetric sensor for captopril determination based on modified multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 22, 1315–1322 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The research work elucidated in this paper was carried out at laboratory provisions in Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad. Authors greatly acknowledge NUST Islamabad for the SEM and EDX mapping facility. HEC Projects No. 1718 and 4768 are highly acknowledged for Gamry instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mujtaba, A., Janjua, N.K., Yasin, T. et al. Assessing the electrochemical performance of hierarchical nanostructured CuO@TiO2 as an efficient bi-functional electrocatalyst. J IRAN CHEM SOC 17, 649–662 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01797-x