Abstract
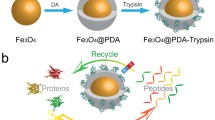
In present work, green tea is used for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. During synthesis of MNPs, no additional reducing agents required because green tea extract itself contains polyphenols reducing agent, comparatively other reported methods. Surface of the green tea-synthesized nanoparticles is functionalized with tetraethyl orthosilicate and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Functionalized MNPs are applied for the microwave digestion of protein molecules. Functionalized MNPs contain negative charge, and thus adsorb peptide fragments after microwave digestion of protein molecules. The functionalized MNPs can assist, accelerate and effectively enhance the digestion efficiency, sequence coverage and detection sensitivity of peptides for the microwave-assisted tryptic digestion of proteins in matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). The reason is attributed to the fact that proteins or partially digested proteins are easily attracted or concentrated onto the surface of functionalized MNPs, resulting in higher efficiency of digestion reactions in the microwave experiments. Besides, the functionalized MNPs could act as a microwave absorber to accelerate and enrich the protein fragments in a short period of time (30–50 s). Various experimental conditions such as enzyme-to-protein ratio 1:30, MNPs concentration 600 µg, heating time 40 s and incubation time 15 min were investigated in the MALDI-TOF-MS. Thus, the current technique proves the suitability, cheapness and ecofriendly nature of MNPs and its utility for various biotechnological and proteome research in near future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Karas, F. Hillenkamp, Anal. Chem. 60, 2299 (1988)
E. Nordhoff, F. Kirpekar, P. Roepstorff, Mass Spectrom. Rev. 15, 67 (1998)
I.G. Gut, Hum. Mutat. 23, 437 (2003)
C.H. Teng, K.C. Ho, Y.S. Lin, Y.C. Chen, Anal. Chem. 76, 4337 (2004)
P.R. Sudhir, H.F. Wu, Z.C. Zhou, Anal. Chem. 77, 7380 (2005)
Q.L. Zhang, L.C. Du, Y.X. Weng, L. Wang, H.Y. Chen, J.Q. Li, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 15077 (2004)
K. Tanaka, H. Waki, Y. Ido, S. Akita, Y. Yoshida, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2, 151 (1988)
C.T. Chen, Y.C. Chen, Anal. Chem. 77, 5912 (2005)
W.Y. Chen, Y.C. Chen, Anal. Chem. 79, 2394 (2007)
Y.F. Huang, H.T. Chang, Anal. Chem. 78, 1485 (2006)
J.A. McLean, K.A. Stumpo, D.H. Russell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 5304 (2005)
J. Wei, J.M. Buriak, G. Siuzdak, Nature 399, 243 (1999)
S.F. Ren, L. Zhang, Z.H. Cheng, Y.L. Guo, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 333 (2005)
H. Kawasaki, T. Yonezawa, T. Watanabe, R. Arakawa, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 16278 (2007)
K. Shrivas, K. Agrawal, H.F. Wu, Analyst 136, 2852 (2011)
L. Hua, J. Chen, L. Ge, S.N. Ta, J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 1133 (2007)
K. Shrivas, H.F. Wu, Anal. Chim. Acta 628, 198 (2008)
K. Agrawal, H.F. Wu, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 22, 283 (2008)
N. Hasan, H.F. Wu, Y.H. Li, M. Nawaz, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 396, 2909 (2010)
S.K. Kailasa, H.F. Wu, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 396, 1115 (2010)
L.A. Shastri, S.K. Kailasa, H.F. Wu, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 23, 2247 (2009)
K. Shrivas, S.K. Kailasa, H.F. Wu, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 23, 3603 (2009)
M. Che, C.O. Bennett, Adv. Catal. 36, 55 (1989)
W. Stober, A. Fink, E. Bohn, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62 (1968)
J.O. Park, K.Y. Rhee, S.J. Park, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 6945 (2010)
S.Y. Chang, N.-Y. Zheng, C.-S. Chen, C.-D. Chen, Y.-Y. Chen, C.R.C. Wang, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 910 (2007)
P.-C. Lin, M.-C. Tseng, A.-K. Su, Y.-J. Chen, C.-C. Lin, Anal. Chem. 79, 3401 (2007)
A. Sethuraman, M. Han, R.S. Kane, G. Belfort, Langmuir 20, 7770 (2004)
N.B. Pramanik, U.A. Mirza, Y.H. Ing, Y.H. Liu, P.L. Bartner, P.C. Weber, A.K. Bose, Protein Sci. 11, 2676 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Institute of Technology, Raipur, and IIT Kharagpur, for providing all necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Tapadia, K. Green tea-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles accelerate the microwave digestion of proteins analyzed by MALDI-TOF-MS. J IRAN CHEM SOC 13, 1723–1732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0889-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0889-8