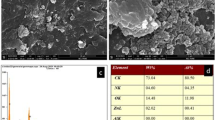
Abstract
One of the main challenges concerning tire industry has always been to increase safety and reduce fuel consumption efficiency of passenger cars tire simultaneously, while other properties such as mechanical and rheological properties do not experience a notable decline. In this study, a special new processing aid agent based on 5,11,17,23-tetrakis (diethylphosphonato)-25,26,27,28-tetrabutoxycalix[4]arene (calix[4]arene phosphonato derivative or CPD), that has a unique dual structure, has been synthesized and its effect on various properties of the tire tread compound has been investigated. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), elemental analysis, and nuclear magnetic resonance (1H MR, 13C NMR, and 31P NMR) were used to confirm the structure of CPD. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to investigate the effect of CPD on filler dispersion within the rubber matrix. The viscoelastic properties of the prepared tire tread compounds were examined by dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA) which showed a great increment in ice and wet grip as well as lower rolling resistance and heat build-up of the selected tire tread compound. The mechanical and rheological properties of the studied tire tread compound were measured by tensile test and moving die rheometer (MDR) test.
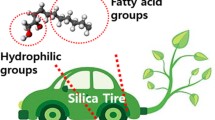
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Essabir H, Raji M, Essassi EM, Rodrigue D, Bouhfid R, Qaiss AEK (2017) Morphological, thermal, mechanical, electrical and magnetic properties of ABS/PA6/SBR blends with Fe3O4 nano-particles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:17120–17130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7639-2
Yang S, Liang P, Peng X, Zhou Y, Hua K, Wu W, Cai Z (2018) Improvement in mechanical properties of SBR/Fly ash composites by in-situ grafting-neutralization reaction. Chem Eng J (Amst Neth) 354:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.112
Liu Z, Zhang Y (2017) Enhanced mechanical and thermal properties of SBR composites by introducing graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with silica particles. Compos A 102:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.08.005
Rezende CA, Bragança FC, Doi TR, Lee LT, Galembeck F, Boué F (2010) Natural rubber-clay nanocomposites: mechanical and structural properties. Polymer 51:3644–3652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.06.026
D’Apuzzo M, Evangelisti A, Nicolosi V (2020) An exploratory step for a general unified approach to labelling of road surface and tyre wet friction. Accid Anal Prev 138:105462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2020.105462
Li Y, Han B, Liu L, Zhang F, Zhang L, Wen S, Lu Y, Yang H, Shen J (2013) Surface modification of silica by two-step method and properties of solution styrene butadiene rubber (SSBR) nanocomposites filled with modified silica. Compos Sci Technol 88:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.08.029
Manna AK, De PP, Tripathy DK, De SK, Peiffer DG (1999) Bonding between precipitated silica and epoxidized natural rubber in the presence of silane coupling agent. J Appl Polym Sci 74:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19991010)74:2%3c389:AID-APP21%3e3.0.CO;2-L
Kim K, Lee JY, Choi BJ, Seo B, Kwag GH, Paik HJ, Kim W (2014) Styrene-butadiene-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer/silica composites: dispersion of silica particles and dynamic mechanical properties. Compos Interfaces 21:685–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/15685543.2014.927720
Sattayanurak S, Noordermeer JW, Sahakaro K, Kaewsakul W, Dierkes WK, Blume A (2019) Silica-reinforced natural rubber: synergistic effects by addition of small amounts of secondary fillers to silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2019:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5891051
Ansarifar MA, Jain A, Nanapoolsin T (2002) Silane-silica reinforcement of some natural rubber vulcanisates. J Rubb Res 5:11–27
Karak N, Gupta BR (2000) Effects of different ingredients and cure parameters on physical properties of a tyre tread compound. Kautsch Gummi Kunstst 53:30–34
Saeed F, Ansarifar A, Ellis RJ, Haile-Meskel Y, Irfan MS (2012) Two advanced styrene-butadiene/polybutadiene rubber blends filled with a silanized silica nanofiller for potential use in passenger car tire tread compound. J Appl Polym Sci 123:1518–1529. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34221
Wang YX, Wu YP, Li WJ, Zhang LQ (2011) Influence of filler type on wet skid resistance of SSBR/BR composites: effects from roughness and micro-hardness of rubber surface. Appl Surf Sci 257:2058–2065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.08.129
Jiao Y, Liu X, Liu K (2018) Experimental study on wet skid resistance at different water-film thicknesses. Ind Lubr Tribol 70:1737–1744. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-11-2017-0362
Pan XD (2005) Impact of reinforcing filler on the dynamic moduli of elastomer compounds under shear deformation in relation to wet sliding friction. Rheol Acta 44:379–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-004-0420-5
Huang R, Pan Q, Chen Z, Feng K (2020) Maleic anhydride modified dicyclopentadiene resin for improving wet skid resistance of silica filled SSBR/BR composites. Appl Sci 10:4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134478
Kim NC, Song SH (2019) Effects of zinc-free processing aids on silica-reinforced tread compounds for green tires. Int J Polym Sci 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9123635
Thaptong P, Sae-Oui P, Sirisinha C (2016) Effects of silanization temperature and silica type on properties of silica-filled solution styrene butadiene rubber (SSBR) for passenger car tire tread compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43342. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43342
Song SH (2020) Influence of eco-friendly processing aids on silica-based rubber composites. Appl Sci 10:7244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207244
Harper M, Tardiff J, Haakenson D, Joandrea M, Knych M (2017) Tire tread performance modification utilizing polymeric additives. SAE Int J Veh Dyn Stab NVH 1:179–189. https://doi.org/10.4271/2017-01-1502
Vleugels N, Pille-Wolf W, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JW (2015) Understanding the influence of oligomeric resins on traction and rolling resistance of silica-reinforced tire treads. Rubber Chem Technol 88:65–79. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.14.86947
Veiga VDA, Rossignol TM, Crespo JDS, Carli LN (2017) Tire tread compounds with reduced rolling resistance and improved wet grip. J Appl Polym Sci 134:45334. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45334
Simoes BJ, de Silva D, de Fatima A, Fernandes S (2012) Calix [n] arenes in action: useful host-guest catalysis in organic chemistry. Curr Org Chem 16:949–971. https://doi.org/10.2174/138527212800194746
Sliwa W, Kozlowski C (2009) Calixarenes and resorcinarenes: synthesis, properties and applications. John Wiley, Weinheim. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200903182
Mirmoeini MS, Nikje MMA, Rasouli-Saniabadi M, Taghvaei-Ganjali S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of functionalized calix [4] arene derivatives and preparation of rigid polyurethane foams by the incorporation of calixarene. Macromol Symp 373:1600101. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201600101
Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Rasouli-Saniabadi M, Mirmoeini MS (2015) Application of sulfonamide derivative of calixarene for improvement of mechanical properties and thermal stability of polyurethane composite. J Incl Phenom Macrocyclic Chem 83:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0539-2
Hosseini M, Rahimi M, Sadeghi HB, Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Abkenar SD, Ganjali MR (2009) Determination of Hg (II) ions in water samples by a novel Hg (II) sensor, based on calix [4] arene derivative. Int J Environ Anal Chem 89:407–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310802713195
Nouri M, Mozafari S, Taghvaei-Ganjali S (2011) Synthesis and characterization of nitro derivatives of calix [4] arene as an effective removal agents for Co2 and Pb2 Ions. Iran JOC 3:807–809
Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Zadmard R, Zeyaei M, Rahnama K, Faridbod F, Ganjali MR (2009) Synthesis of a new calix [4] arene and its application in construction of a highly selective silver ion-selective membrane electrode. Res Lett Org Chem 2009:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/601089
Daze KD, Jones CE, Lilgert BJ, Beshara CS, Hof F (2013) Determining the effects of salt, buffer, and temperature on the complexation of methylated ammonium ions and methyllysines by sulfonated calixarenes. Can J Chem 91:1072–1076. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2013-0186
Chenari AB, Saber-Tehrani M, Mamaghani M, Nikpassand M (2019) Covalently anchored chlorosulfonyl-calix [4] arene onto silica gel as an efficient and reusable heterogeneous system for reduction of ketones using NaBH 4. J Incl Phenom Macrocyclic Chem 94:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-019-00894-x
Pang TT, Du LM, Liu HL, Fu YL (2014) Supramolecular p-sulfonated calix [4,6,8] arene for tryptophan detection. Can J Chem 92:1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2014-0150
Pekachaki HM, Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Motiee F, Saber-Tehrani M (2019) Application of calixarene derivatives as tackifier resin in rubber compounds for tire applications. Rubber Chem Technol 92:467–480. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.19.81510
Servati Z, Saber-Tehrani M, Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Zadmard R (2018) Silica bonded calix [4] arene as an efficient, selective and reusable sorbent for rubber chemical additives. J Porous Mater 25:1463–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-018-0559-6
Mohamadi H, Motiee F, Taghvaei-Ganjali S, Saber-Tehrani M (2021) Application of silica supported calix [4] arene derivative as anti-reversion agent in tire tread formulation. Acta Chim Slov 68:128–136. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2020.6225
Mohamadi H, Motiee F, Saber-Tehrani M, Taghvaei-Ganjali S (2019) Preparation and application of chemically bonded silica supported calix [4] arene as reinforced filler in NR/BR blend basedrubber compounds. Russ J Appl Chem 92:809–816. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427219060107
Malekzadeh M, Nouri H, Farahani M (2010) Investigation on the influence of silane coupling agent structure on the properties of nano-silica filled rubber compound. JACR 3:41–45
Li H, Zhong Y, Wu W, Zhang L, Lai X, Zeng X (2017) Phenolic antioxidants based on calixarene: Synthesis, structural characterization, and antioxidative properties in natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 134:45144. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45144
Gutsche CD, Iqbal M (2003) p-tert-Butylcalix[4]arene. Org Synth 68:234–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471264180.os068.29
Mohindra Chawla H, Srinivas K (1993) Synthesis of 25, 26, 27-tris (ethoxycarbonyl-methoxy)-28-(4-methyl-7-coumarinyloxy-carbonylmethoxy) calix-4-arene. Indian J Chem B32:1162–1164
Asfari Z, Reinhoudt DN, Verboom W, Durie A, Egberink RJ (1992) Ipso nitration of p-tert-butylcalix [4] arenes. J Org Chem 57:1313–1313. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00030a050
Conner M, Janout V, Regen SL (1992) Synthesis and alkali metal binding properties of “upper rim” functionalized calix [4] arenes. J Org Chem 57:3744–3746. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00039a048
Zadmard R, Junkers M, Schrader T, Grawe T, Kraft A (2003) Capsule-like assemblies in polar solvents. J Org Chem 68:6511–6521. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo034592q
Siriwong C, Khansawai P, Boonchiangma S, Sirisinha C, Sae-Oui P (2021) The influence of modified soybean oil as processing aids in tire application. Polym Bull 78:3589–3606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03296-z
Thepsuwan U, Sae-oui P, Sirisinha C, Thaptong P (2019) Influence of halloysite nanotube on properties of tire tread compounds filled with silica and carbon black hybrid filler. J Appl Polym Sci 136:46987. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46987
Ghoreishy MHR, Taghvaei S, Mehrabian RZ (2011) The effect of silica/carbon black filler systems on the fatigue properties of the tread compound in passenger tires. Polym Sci Technol 24:329–337
Roshanaei H, Khodkar F, Alimardani M (2020) Contribution of filler-filler interaction and filler aspect ratio in rubber reinforcement by silica and mica. Iran Polym J 29:901–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-020-00850-4
Ahmadi Shooli S, Tavakoli M (2016) Styrene butadiene rubber/epoxidized natural rubber (SBR/ENR50) nanocomposites containing nanoclay and carbon black as fillers for application in tire-tread compounds. J Macromol Sci B 55:969–983. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2016.1230464
Ahmadi-Shooli S, Tavakoli M (2019) A comparative study of the dynamic-mechanical properties of styrene butadiene rubber/epoxidized natural rubber dual filler nanocomposites cured by sulfur or electron beam irradiation. J Macromol Sci B 58:619–633. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2019.1574428
Gabriel CFS, Gabino ADAP, de Sousa AMF, Furtado CRG, Nunes RCR (2019) Tire tread rubber compounds with ternary system filler based on carbon black, silica, and metakaolin: contribution of silica/metakaolin content on the final properties. J Elastomers Plast 51:712–726. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244318819196
Ezzoddin S, Abbasian A, Aman-Alikhani M, Taghvaei-Ganjali S (2013) The influence of non-carcinogenic petroleum-based process oils on tire compounds’ performance. Iran Polym J 22:697–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-013-0168-9
Mondal T, Bhowmick AK, Ghosal R, Mukhopadhyay R (2018) Expanded graphite as an agent towards controlling the dispersion of carbon black in poly (styrene-co-butadiene) matrix: an effective strategy towards the development of high-performance multifunctional composite. Polymer 146:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMER.2018.05.031
Sae-oui P, Suchiva K, Thepsuwan U, Intiya W, Yodjun P, Sirisinha C (2016) Effects of blend ratio and SBR type on properties of silica-filled SBR/NR tire tread compounds. Rubber Chem Technol 89:240–250. https://doi.org/10.5254/RCT.15.84859
Dinkel J (1995) Where the silica meets the road. Discover 16:32–33
Zaeimoedin Z (2019) Development of ENR-based compounds for green tire tread applications with improved performance, processing characteristics and sustainability. Loughborough University, Loughborough. https://doi.org/10.26174/thesis.lboro.9948320.v1
Sae-Oui P, Suchiva K, Sirisinha C, Intiya W, Yodjun P, Thepsuwan U (2017) Effects of blend ratio and SBR type on properties of carbon black-filled and silica-filled SBR/BR tire tread compounds. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2476101
Robak B, Rogoża J, Łapkowski M (2019) Low-molecular-weight styrene-butadiene copolymers (L-SSBR) as processing aids used for silica-filled rubber: Synthesis, functionalization and application. J Elastomers Plast 51:244–261. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244318784611
Takino H, Nakayama R, Yamada Y, Kohjiya S, Matsuo T (1997) Viscoelastic properties of elastomers and tire wet skid resistance. Rubber Chem Technol 70:584–594. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3538445
Surya I, Ismail H (2016) The effect of the addition of alkanolamide on properties of carbon black-filled natural rubber (SMR-L) compounds cured using various curing systems. Polym Test 50:276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2016.01.014
Surya I, Ismail H, Azura AR (2014) The comparison of alkanolamide and silane coupling agent on the properties of silica-filled natural rubber (SMR-L) compounds. PolymTest 40:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.08.007
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamrahjou, N., Sadat-Mansouri, S.N., Taghvaei-Ganjali, S. et al. Calix[4]arene phosphonato derivative as a novel and capable processing aid agent for improving dynamic, mechanical, and thermal behavior of tire tread rubber compounds. Iran Polym J 31, 729–740 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-022-01026-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-022-01026-y